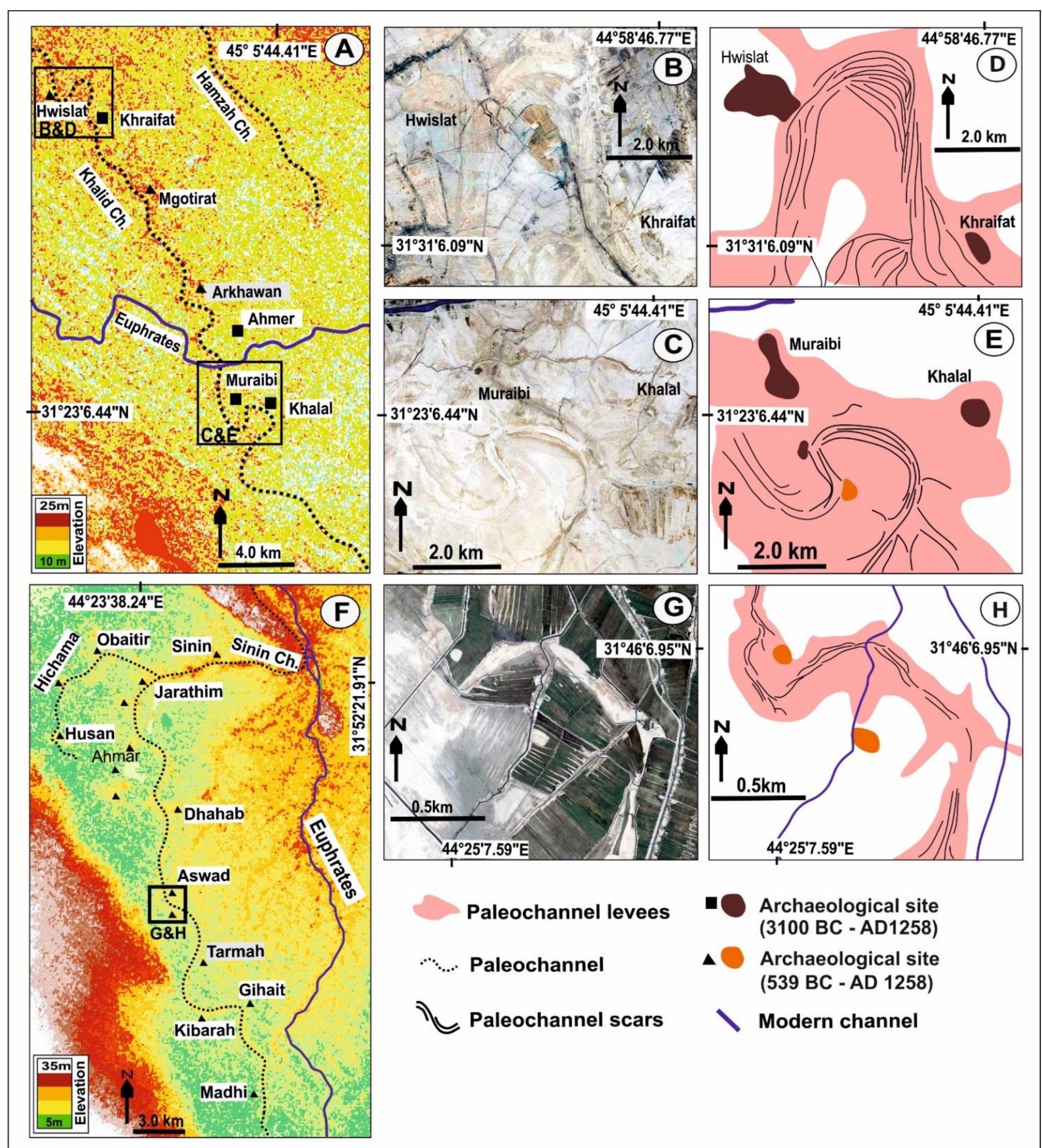
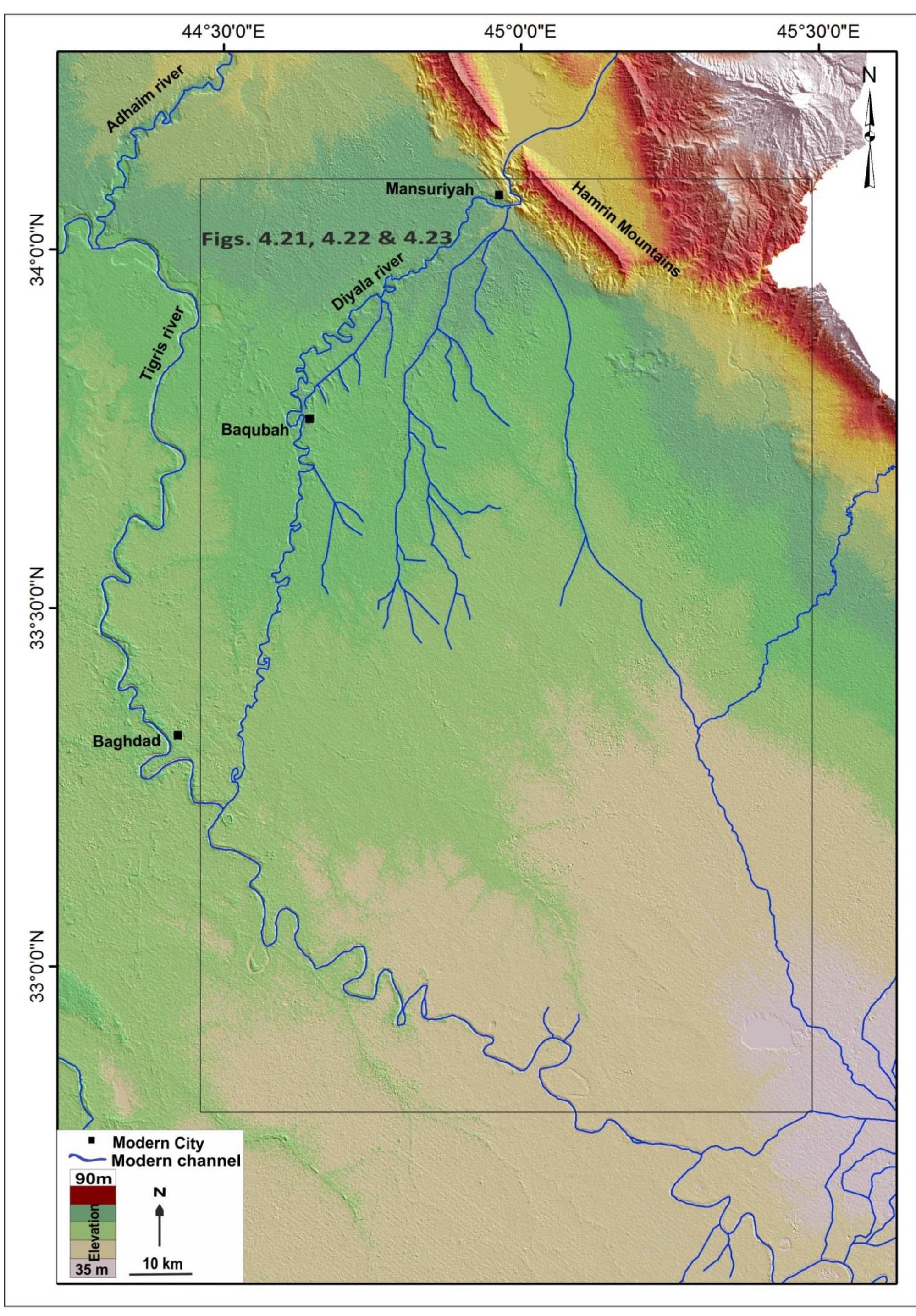
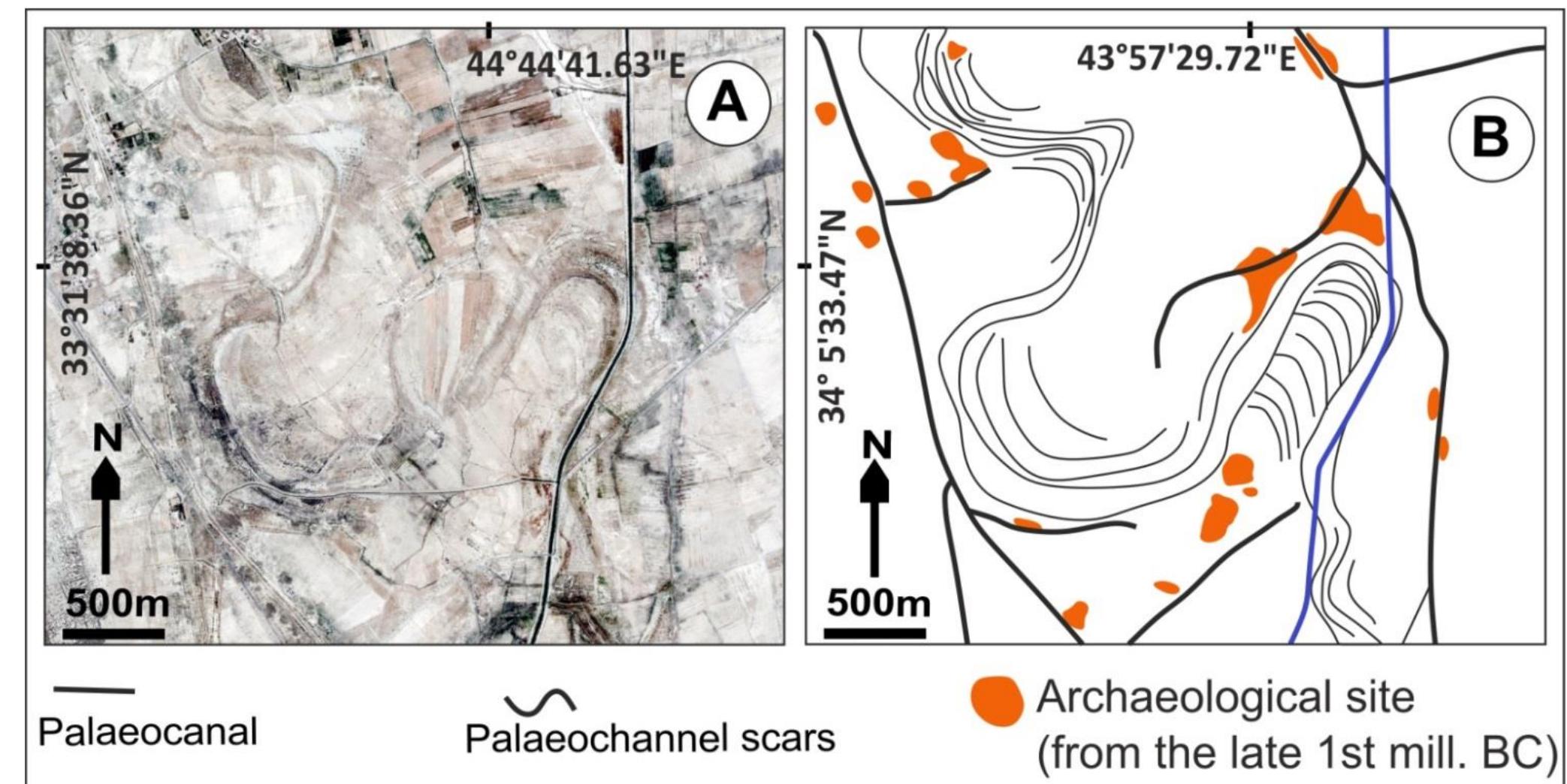
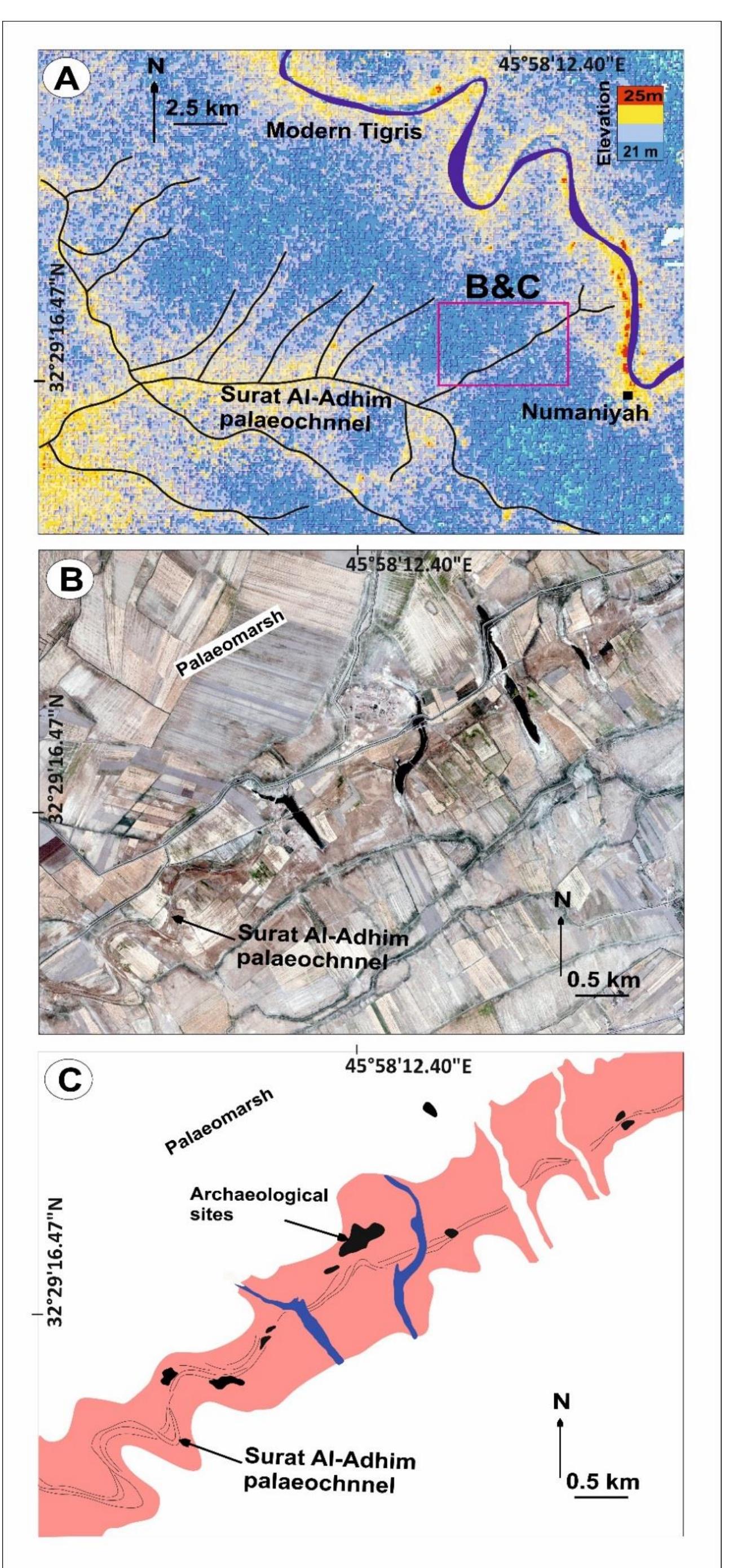
Wide estuaries are natural magnets for urban development. Several of the World’s major cities developed around estuaries, but at the same time encroached upon some of the most complex and vital ecosystems. Sea-level rise threatens to...
moreWide estuaries are natural magnets for urban development. Several of the World’s major cities developed around estuaries, but at the same time encroached upon some of the most complex and vital ecosystems. Sea-level rise threatens to submerge both rare wetland habitat and essential urban areas and infrastructure. This prospect discloses the urgency of balancing urban development and environmental protection in Metropolitan Estuaries. The hard task of dealing with this threat may provide the opportunity to promote an integrated approach to regional planning, where the necessary adaptation of cities to sea-level rise could equally promote the preservation, or even the enhancement, of wetland habitat. The two case study metropolitan estuaries, San Francisco Bay (California, USA) and the Tagus Estuary (Lisbon, Portugal), share striking similarities in terms of morphology. They both host large metropolitan areas and important wetland ecosystems. Nevertheless, a finer analysis of development patterns reveals crucial differences in the extent of shoreline alteration and types of land use that now encroach upon natural estuarine habitat. The comparative study of both estuaries provides mutually beneficial insights on the shortcomings of each system, and helps identify opportunities to enhance coastal zone management, adaptive governance and environmental planning efforts. The evolution of both estuaries throughout the Holocene is reconstructed, with special emphasis on the process of anthropogenic alteration. While this impact has been significant and continuous in the Tagus Estuary for over two millennia, large scale disturbance of the San Francisco Bay was concentrated in the last two centuries. The legal frameworks that have guided, with varying degrees of effectiveness, the process of wetland reclamation and landfilling share a common ancestry in the Roman Law. These have evolved continuously in Lisbon and the State has upheld with relative success the provision to keep estuarine lowlands in public control, even as they were steadily transformed to farmland. In San Francisco, a period of deep disturbances over the Sacramento River’s hydrology was coupled with extremely fast and under regulated development of lowlands. During a short period, the property of these lands, which would theoretically fall within the Public Trust, was transferred to local governments and private landowners, which led to their steady transformation onto salt ponds, industrial zones and even residential neighborhoods. As a consequence, the Bay Area now has extensive developed areas at very low elevations, vulnerable to low levels of sea-level rise, and remaining wetlands are now heavily encroached upon by urban development. Around the Tagus Estuary, while most original wetlands have long been drained for farmland, the remaining patches are adjacent to non-urban land uses, which could facilitate future efforts of restoration or allow wetland migration with rising seas. A comparative modelling of sea-level rise flooding over existing land uses reveals that, while around the Tagus Estuary most reclaimed lowlands are reserved for farmland and urban development over landfill is limited, the extent of developed urban areas at very low elevations is much greater around the SF Bay, which renders the region more vulnerable to early stages of SLR. Nonetheless, both cities have begun to incorporate climate adaptation onto their main environmental planning blueprints, for which they can be seen as early adopters of local sea-level rise adaptation strategies. Through interviews with stakeholders and document analysis, the planning and decision-making exercises that led to the recent elaboration of the first Tagus Estuary Management Plan, and the Bay Plan Climate Change Amendment, are analyzed and discussed. Lisbon benefits from a very simple, top-down, planning structure, with a handful of public entities directly communicating and articulating stakes and approaches along the planning process. A lack of transparency as to some specific interventions and a still somewhat incipient tradition of public participation have contributed to protract the Plan’s final approval. The Bay Area institutional framework is well-used to collaborative planning efforts, which are usually successful in articulating conflicting interests, but are prone to limitations derived from narrow, and often difficult to expand, mandates for environmental planning agencies, within an extremely complex, multi-level, governance structure involving three levels of government and very active interest groups. While broad mitigation/adaptation strategies are decided at the National or State levels, the actual implementation of SLR adaptation measures often require a great deal of involvement of local actors. Given that it is at this juncture that adaptation takes a concrete spatial expression, this is also the moment when land-use conflicts arise. Local governments are left with much of the burden of mediating competing interests, between urban development, environmental protection, and other social demands. In some instances, the prospect of shoreline development may be very attractive for both property owners/developers and local governments, given the potential land value and economic benefits, but these have to be weighed against the medium-/long-term costs of defending these assets from rising sea-levels. In San Francisco Bay, there is an increasing awareness of the challenges posed by SLR, but the institutional arrangements are complex, and communication between the different public agencies/departments is not always as streamlined as it could be. Some agencies and departments need to adapt their procedures in order to remove institutional barriers to adaptation, but path dependence is an obstacle. The several projects where different federal and state agencies are partnered with local governments highlight the benefits of a more frank and regular communication between public actors. It also emphasizes the benefits of a coordination of efforts and strategies, something that was eroded in the transition from government-led policies to a new paradigm of local-based adaptive governance. Whereas the articulation of public actors is often easy to address by increasing communication and coordination, conflicts involving private landowners and developers may be much complicated by the threat of litigation. The lack of a strong legal backing to public environmental protection mandates is a major obstacle to shoreline planning around the Bay and elsewhere, and this is highlighted by the extreme caution of some public agencies in upholding their jurisdictions over private property. Environmental NGOs have, in the case of California, a big role to play, as they are able to resort to the same legal and lobbying instruments as the developers, and may help even-out the field between public stakeholders with limited legal and economic resources, and powerful private developers with nothing to lose. There is seemingly a sense of urgency in pushing for the development of shoreline properties, as public opposition to development on locations exposed to SLR is most likely to increase in the coming decades. At the same time, NGOs and public agencies are aware of the stress wetlands will be under as the rates of SLR increase towards the end of the century. “Green”, or ecosystem-based, adaptation is already on the way around the Bay. Large scale wetland restoration projects have already been concluded, and further action now often requires articulation with the reinforcement of flood defense structures, given the level of urban encroachment. While levee setback, or removal, would provide greater environmental benefit, the need to protect urban areas and infrastructure has led to the trial of ingenious solutions for promoting wetland resilience while upgrading the level of protection granted by levees.