Key research themes
1. How does bed sediment entrainment and transport depend on hydrodynamic forces and sediment characteristics in stream and river environments?
This research area focuses on understanding the initiation of sediment motion (entrainment) and the subsequent bedload transport fluxes driven by flow hydrodynamics over erodible beds. Insights on entrainment thresholds, force balances on sediment grains, and the influence of turbulent flows are essential to predict sediment dynamics and morphological changes in rivers. This theme matters because sediment entrainment controls fluvial processes such as erosion, deposition, channel morphology evolution, and sedimentary sequences, which have critical implications in river engineering, ecology, and geomorphology.
2. What are the effects of vegetation and bed surface arrangement on bedload transport and bed morphology in fluvial systems?
This theme addresses how vegetation presence and different bed surface configurations (loose, armored, water-worked) influence sediment entrainment, bedload transport rates, and channel morphology. Vegetation alters flow resistance, turbulence, and shear stresses, affecting the threshold of sediment motion and transport capacity. Likewise, natural reorganization of bed material changes spatial sediment distribution and bedform development. These factors are critical for river management, habitat conservation, and sediment budget assessments.
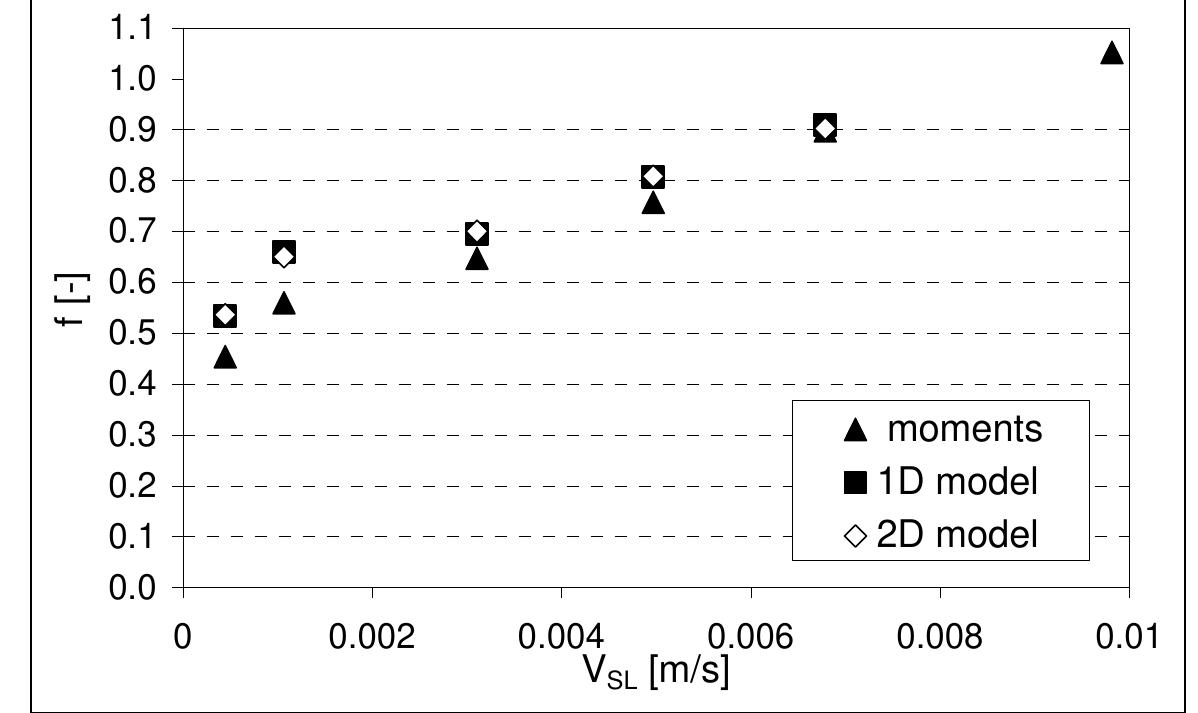
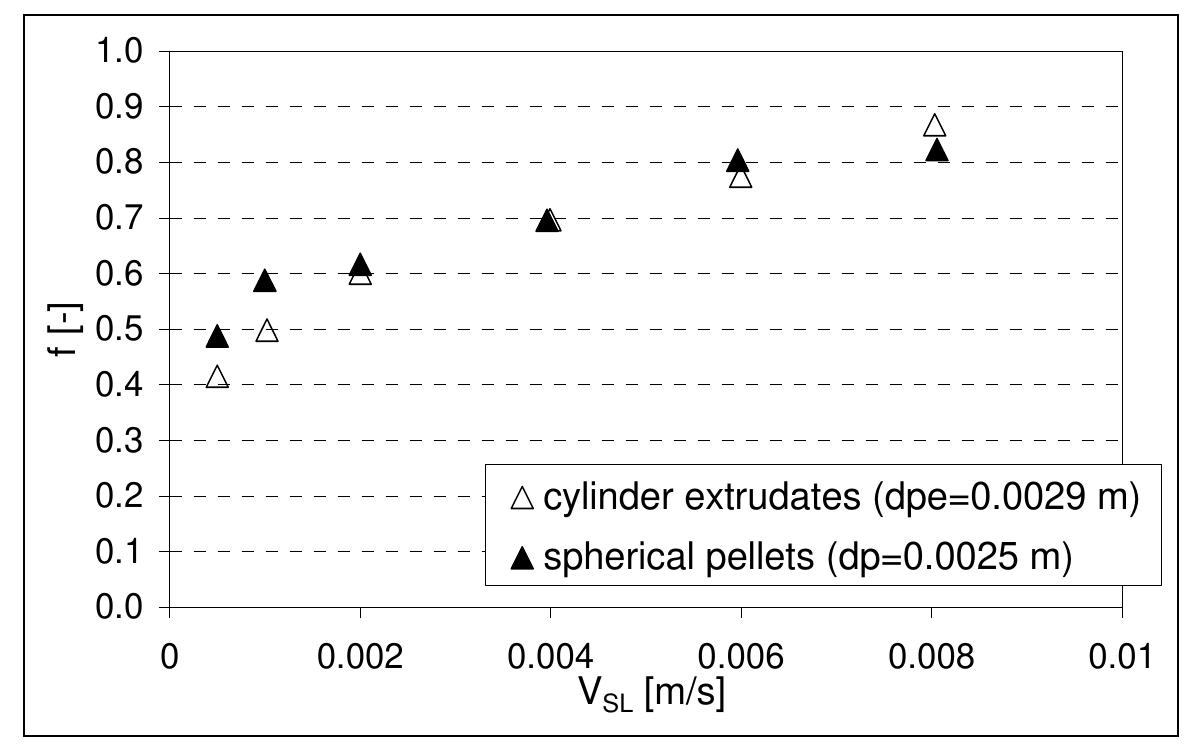
3. How do flow regimes and bed roughness characteristics affect hydraulic jumps, fluidized bed regimes, and heat/mass transfer in trickle and fluidized beds?
This multifaceted research area investigates hydrodynamic phenomena such as hydraulic jumps occurring over smooth and rough beds, fluidization regimes in circulating fluidized beds, and the associated heat and mass transfer processes in trickle and fluidized beds involving gas-liquid-solid interactions. Understanding these processes enables optimized design of hydraulic structures, catalytic reactors, and sediment management systems, while addressing challenges in turbulent multiphase flows with complex particle-fluid interactions.