Genetic diversity within and among 50 populations of confectionery sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) collected from different geographical areas of Iran was evaluated by using microsatellite and retrotransposon markers. The number of... more
Red rice genotypes are characterized by their huge nutritional values. Apart from this property, they also possess valuable sources of resistance to many biotic and abiotic stresses. In the present investigation, a total of 215 red rice... more
Analysis of Structural Variation Between O. sativa and the 3 AA Genome OMAP Accessions.
Germin and Germin-like proteins (GLPs) are a class of plant proteins that are part of the Cupins superfamily, found in several plant organs including roots, seeds, leaves, and nectar glands. They play a crucial role in plant defense... more
Salinity stress affects global food producing areas by limiting both crop growth and yield. Attempts to develop salinity-tolerant rice varieties have had limited success due to the complexity of the salinity tolerance trait, high... more
As the world's population expands from 7.6 billion to 10 billion over the next 30 years, scientists and farmers across the globe must explore every angle necessary to provide a safe, stable and sustainable food supply for generations to... more
High resource availability can reduce anti-herbivore resistance (a plant's ability to defend against herbivores and reduce damage) in rice, Oryza sativa L, but may also increase tolerance (a plant's ability to withstand damage by, for... more
After the completion of its genomic sequencing, rice (Oryza sativa L.) has become firmly established as the premiere model plant among monocot crops. Various genetic resources have been developed for rice to accelerate the identification... more
Brown planthopper (BPH, Nilaparvata lugens Stal.) is the most damaging rice pest affecting stable rice yields worldwide. Currently, methods for controlling BPH include breeding a BPH-resistant cultivar and using synthetic pesticides.... more
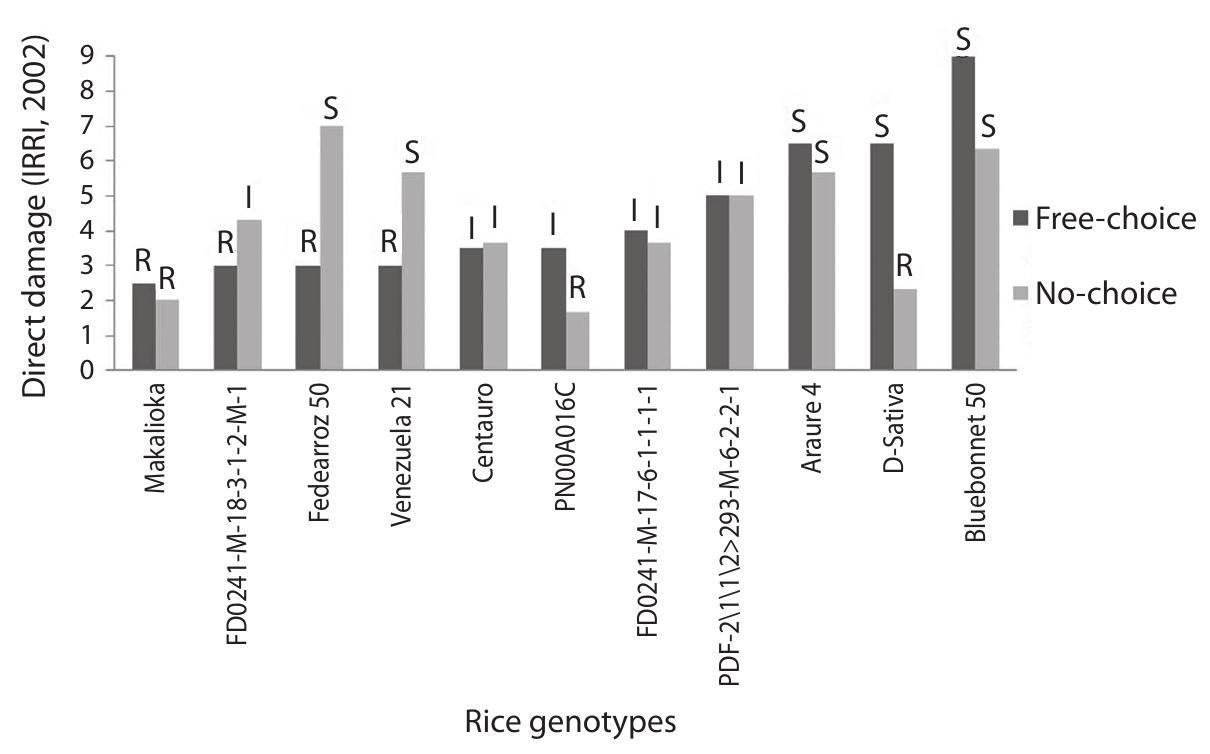
Tagosodes orizicolus is one of the main plagues of rice in tropical America causing two types of damages, the direct one, feeding and oviposition effect, and an indirect one, by the transmission of the "Rice hoja blanca virus". During... more
Resistance evaluation of modern rice varieties to brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens STÅL. The research was performed to understand the resistance of modern rice varieties to the field population of brown planthopper (BPH). The research... more
Background Bph3, a major brown planthopper (BPH) resistance locus derived from the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati (RH), has been used as a stable donor of traits that improve highly susceptible aromatic rice varieties in Thailand. Map-based... more
Background: Brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens Stål, is one of the most destructive insect pests of rice. The molecular responses of plants to sucking insects resemble responses to pathogen infection. However, the molecular... more
Three wild rice species and six cultivated rice varieties were evaluated to determine their mechanisms of resistance to Nilaparvata lugens (Stal.). Wild rice species, Oryza officinalis, O. punctata, and O. latifolia and cultivated rices... more
Brown planthopper (BPH) is a phloem sap-sucking insect pest of rice which causes severe yield loss. We cloned the BPH18 gene from the BPH-resistant introgression line derived from the wild rice species Oryza australiensis. Map-based... more
Terpenoid compounds in resistant rice varieties that acted as allelochemicals affecting feeding behavior of the brown planthoppers (BPHs) were extracted by solid phase microextraction (SPME) and analyzed by using gas chromatography-mass... more
Terpenoid compounds in resistant rice varieties that acted as allelochemicals affecting feeding behavior of the brown planthoppers (BPHs) were extracted by solid phase microextraction (SPME) and analyzed by using gas chromatography-mass... more
Background Rice is staple food for over two billion people. Planthoppers like BPH and WBPH occur together in most of rice growing regions across Asia and cause extensive yield loss by feeding and transmission of disease-causing viruses.... more
Rice is the most significant global food security. Several biotic factors limit rice production, breeding biotic-resistant rice has, therefore, become an increasingly important goal. Two elite rice lines, IR71033-121-15 (IR71033) and... more
Some germplasm collections have a high number of accessions, which makes it difficult to explore the genetic variability present in the germplasm bank due to the redundancy and the difficulty of detailed analysis of all conserved... more
The rice sesquiterpene synthase II gene (OsSTPS2, LOC_Os04g27430), which is involved in the antixenosis defense mechanism of rice against brown planthopper (BPH) infestation, was identified in the BPH-resistant rice variety Rathu Heenati... more
Background: The development of rice varieties with broad-spectrum resistance to insect pests is the most promising approach for controlling a fast evolving insect pest such as the brown planthopper (BPH). To cope with rapid evolution,... more
Background: Bph3, a major brown planthopper (BPH) resistance locus derived from the rice cultivar Rathu Heenati (RH), has been used as a stable donor of traits that improve highly susceptible aromatic rice varieties in Thailand. Map-based... more
Background: Rice contains the lowest grain Fe content among cereals. One biological limiting factor is the tolerance of rice to Fe toxicity. Reverse and forward genetic screenings were used to identify tolerance to Fe toxicity in 4,500 M... more
ABSTRACT: The brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens Stål, is one of the most serious insect pests in rice production worldwide. The BPH resistance genes in an indica cultivar 'Abhaya' were studied using 400 BC4F2 and F3... more
Rice is the most significant global food security. Several biotic factors limit rice production, breeding biotic-resistant rice has, therefore, become an increasingly important goal. Two elite rice lines, IR71033-121-15 (IR71033) and... more
Abstract: The genetic diversity in 106 glutinous rice landraces of Assam, India, was analyzed using SSR markers. The apparent amylose content (AAC) in Chokuwa (12.24%) was higher than Bora (0.145%) genotypes. The SSR markers showed high... more
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) markers were used in characterization of 113 cowpea accessions comprising of 108 from Ghana and 5 from abroad. Leaf tissues from plants cultivated at the University of Ghana were genotyped at... more
Terpenoid compounds in resistant rice varieties that acted as allelochemicals affecting feeding behavior of the brown planthoppers (BPHs) were extracted by solid phase microextraction (SPME) and analyzed by using gas chromatography-mass... more
Terpenes comprise the most diverse collection of secondary metabolites and are the compounds that give wonderful aromas, tastes and pharmaceuticals. Terpene hydrocarbon scaffolds are generated by the action of mechanistically... more
Abstract: The genetic diversity in 106 glutinous rice landraces of Assam, India, was analyzed using SSR markers. The apparent amylose content (AAC) in Chokuwa (12.24%) was higher than Bora (0.145%) genotypes. The SSR markers showed high... more
To organize data resulting from the phenotypic characterization of a library of 30 000 T-DNA enhancer trap (ET) insertion lines of rice (Oryza sativa L cv. Nipponbare), we developed the Oryza Tag Line (OTL) database... more
Data from five protein-coding loci related to dairy production were used to study the genetic diversity and population structure of Argentine and Bolivian Creole cattle breeds. Genomic DNA was extracted from blood samples of six Creole... more
Brown planthopper (BPH; Nilaparvata lugens) is a phloem feeding insect which is one of the most serious threats to rice crops in many countries throughout Asia. 1H NMR spectroscopy, combined with chemometrics, was used to analyze the... more
Terpenoid compounds in resistant rice varieties that acted as allelochemicals affecting feeding behavior of the brown planthoppers (BPHs) were extracted by solid phase microextraction (SPME) and analyzed by using gas chromatography-mass... more
Data from five protein-coding loci related to dairy production were used to study the genetic diversity and population structure of Argentine and Bolivian Creole cattle breeds. Genomic DNA was extracted from blood samples of six Creole... more
Data from five protein-coding loci related to dairy production were used to study the genetic diversity and population structure of Argentine and Bolivian Creole cattle breeds. Genomic DNA was extracted from blood samples of six Creole... more
The North-Eastern region (NER) of India, comprising of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura, is a hot spot for genetic diversity and the most probable origin of rice. North-east rice collections are... more