Key research themes
1. How can the original landscape and environmental context of bog sites deepen our understanding of bog bodies deposition?
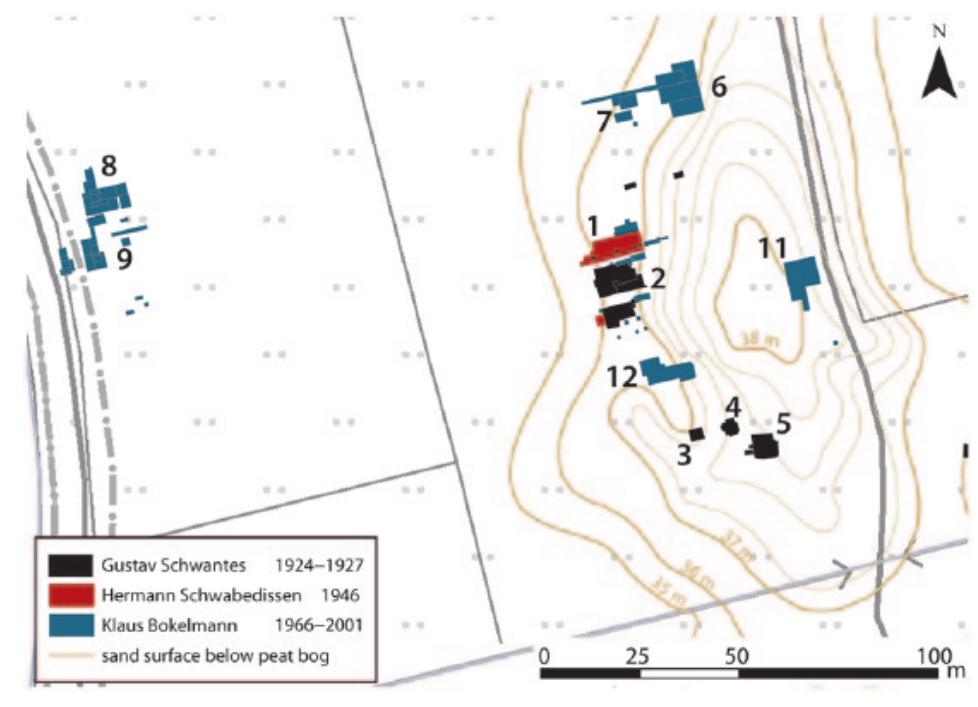
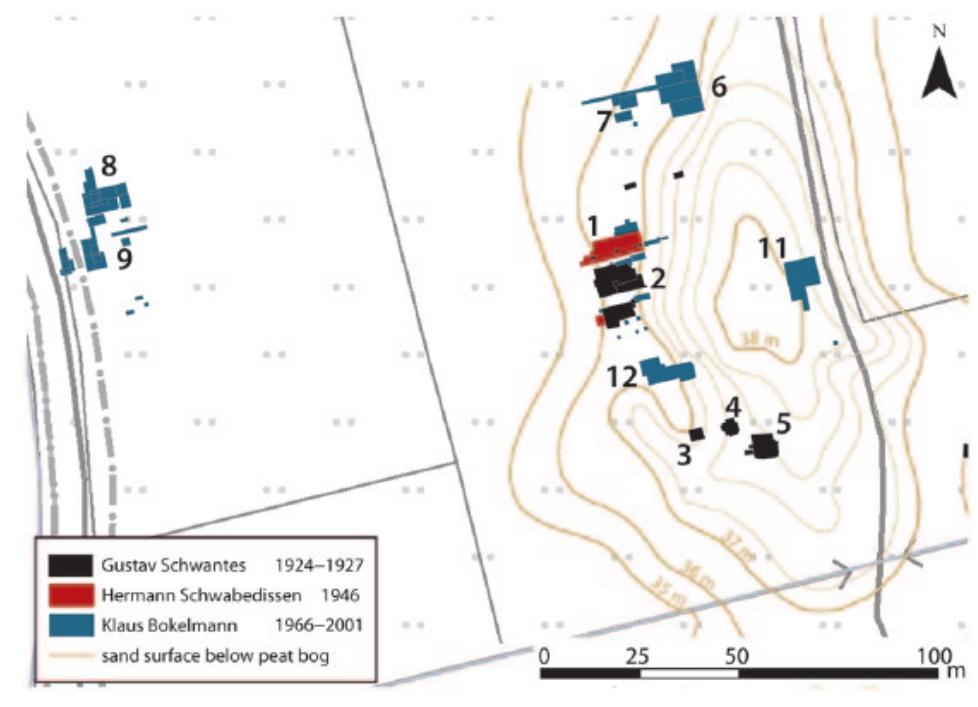
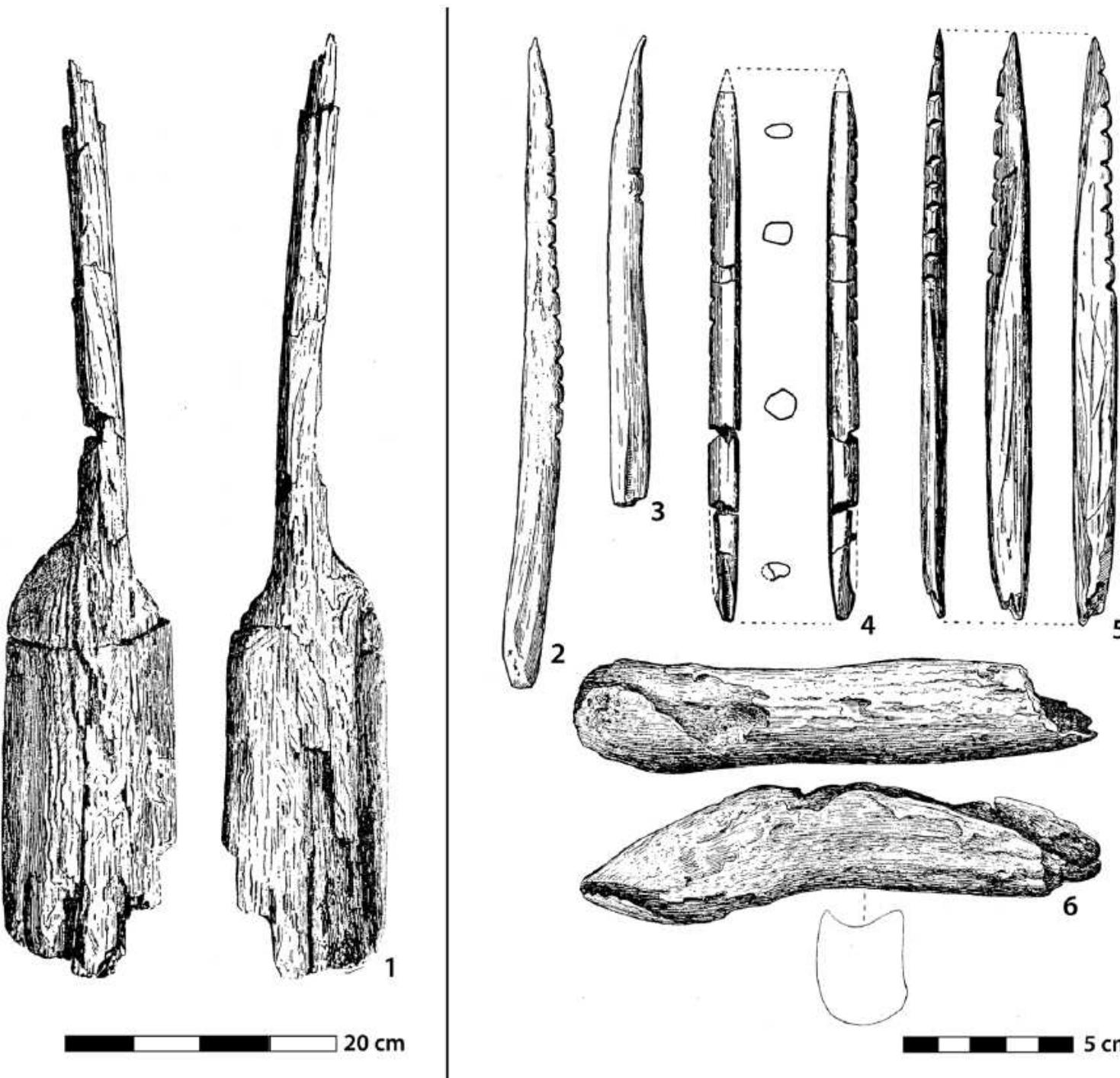
This research area focuses on reconstructing the physical and cultural landscape settings of bog body deposition to provide new insights into the contextual meaning and archaeological interpretation of bog bodies. By integrating data from physical geography, geomorphology, palynology, and archaeology, researchers aim to overcome the historic focus on single-site material culture in favor of broader spatial and temporal contextualization, enabling better understanding of deposition motives, ritual significance, and site formation processes.
2. What are the challenges and emerging strategies in the conservation and preservation of bog bodies post-excavation?
Given the unique and composite material nature of bog bodies—often involving skin, muscle, bone, and other tissues—this theme examines conservation complexities, including chemical and physical characterization, stabilization, and long-term care strategies. Research highlights the integration of conservation science, storage methodologies, and ethical considerations necessary to preserve these rare archaeological human remains.
3. How do hydrological dynamics and peat properties influence bog development and restoration, and what implications do these have for bog sites preservation?
Research under this theme investigates the biophysical processes controlling raised bog ecosystems, focusing on peat volumetric oscillations (bog surface breathing) and hydrological self-regulation. Understanding these dynamics provides essential insight for bog restoration, ecosystem resilience, and the protection of archaeological deposits, as hydrological conditions critically affect peat preservation and indirectly the conservation conditions for artifacts and bog bodies.