Key research themes
1. How can depth-resolved morphodynamic models improve understanding of sediment transport processes in the swash zone at wave time scales?
This research theme focuses on the development, validation, and application of high-resolution, depth-resolved numerical models that simulate coupled hydrodynamics and sediment transport in the swash zone at the scale of individual waves or solitary wave events. Understanding sediment transport at these fine temporal and spatial scales is crucial for accurately predicting beach morphodynamics, given the swash zone's highly dynamic and rapidly changing nature. Such models aim to capture complex processes including turbulent flow structures, sediment suspension profiles, infiltration/exfiltration effects, and bed-level changes, which are difficult to observe experimentally due to scale and measurement constraints. These models contribute to enhanced prediction capabilities for beach erosion, accretion, and response to wave forcing, informing coastal management and hazard mitigation.
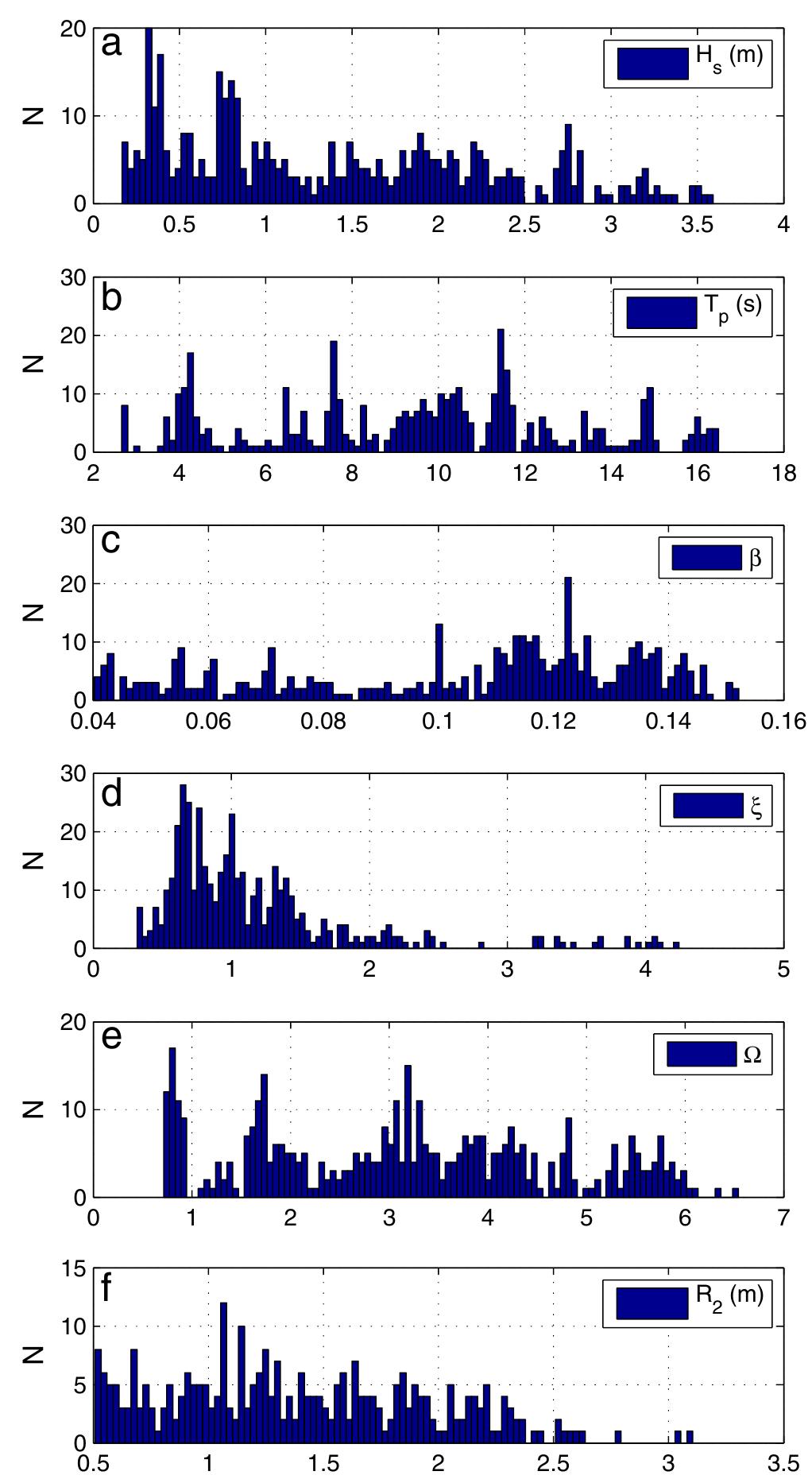
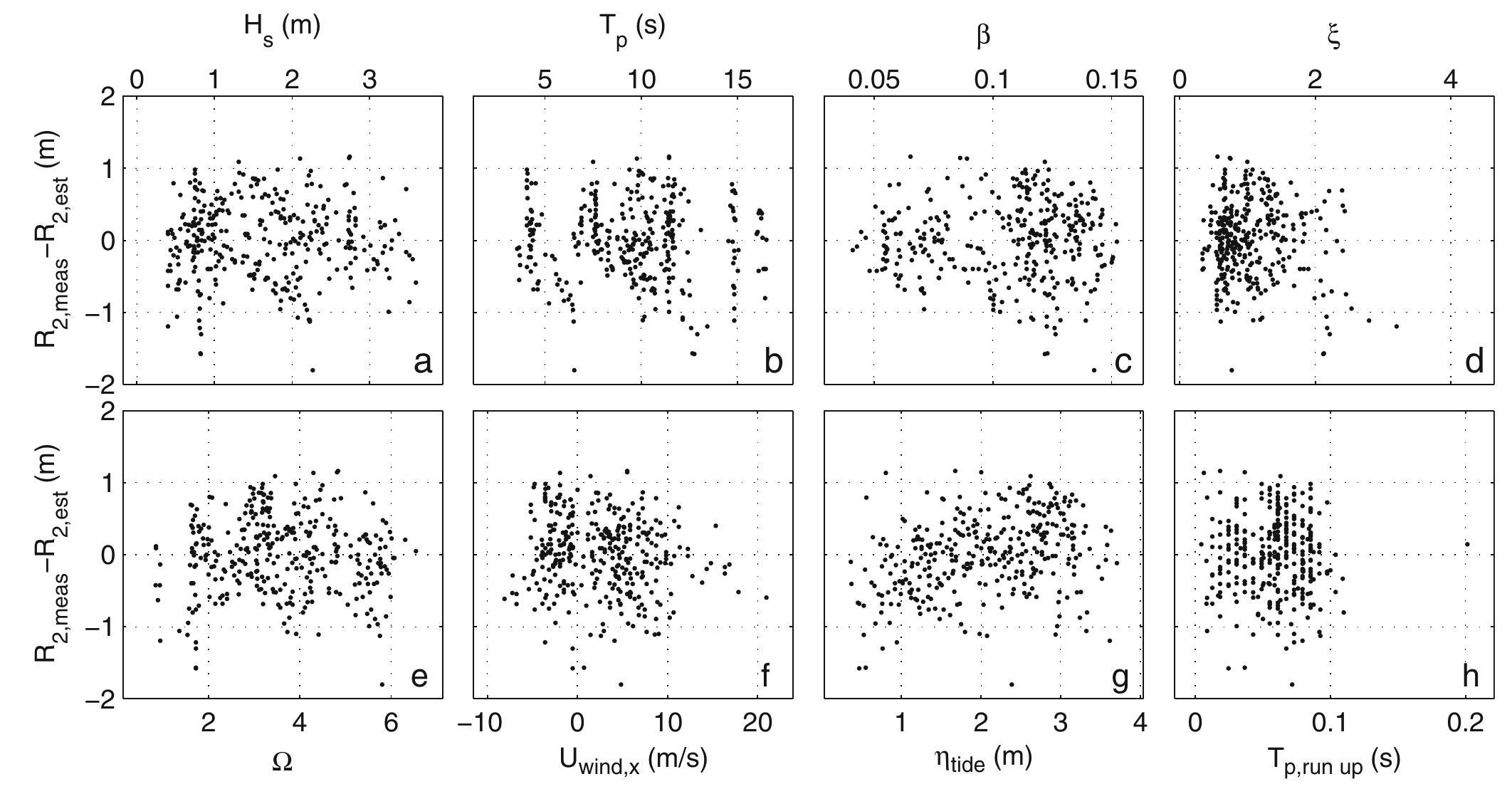
2. What are the spatiotemporal patterns and controlling factors of swash zone dynamics observed through high-frequency optical monitoring at microtidal, dissipative beaches?
This area investigates the use of high-frequency coastal video and optical monitoring systems to observe and quantify swash zone dynamics including shoreline position, wave run-up/run-down, and wave breaking locations, with a focus on microtidal, low-energy dissipative sandy beaches. It explores how wave energy, seabed morphology such as submerged sandbars, and hydrodynamic conditions influence alongshore and cross-shore variability, wave energy dissipation, and shoreline morphological responses. This research contributes to coastal management by providing accurate, high-resolution morphological and hydrodynamic datasets critical for understanding sediment transport processes and legal boundary delineations for coastal zone planning.
3. How do sediment characteristics and physical processes affect sediment transport dynamics and morphodynamics in the swash zone, especially regarding particle shape, size, and groundwater influences?
This theme examines how sediment properties such as grain size, shape, and permeability, together with hydrodynamic conditions and groundwater table variations, influence sediment transport pathways, erosion-accretion patterns, and boundary layer dynamics in the swash zone. It includes field experiments tracking pebble displacement and studies on infiltration/exfiltration effects on sediment mobility. Understanding these relationships is essential for predicting beach surface texture evolution, informing replenishment strategies, and improving models of sediment transport under varying environmental and climatic conditions.