Key research themes
1. What are the strategies and barriers to the beneficial reuse of dredged and remobilized sediments in environmental and construction applications?
This research theme focuses on identifying practical and sustainable ways to repurpose dredged sediments from aquatic environments, addressing both technical and regulatory challenges. It emphasizes the circular economy potential of sediment reuse in agriculture, coastal resilience, and civil engineering, investigating treatments needed to mitigate contamination and improve sediment properties for reuse. The importance lies in transforming sediment management from waste disposal to resource utilization, reducing environmental impacts and promoting sustainability.
2. How do sediment resuspension processes impact contaminant mobility and ecological risk in aquatic environments?
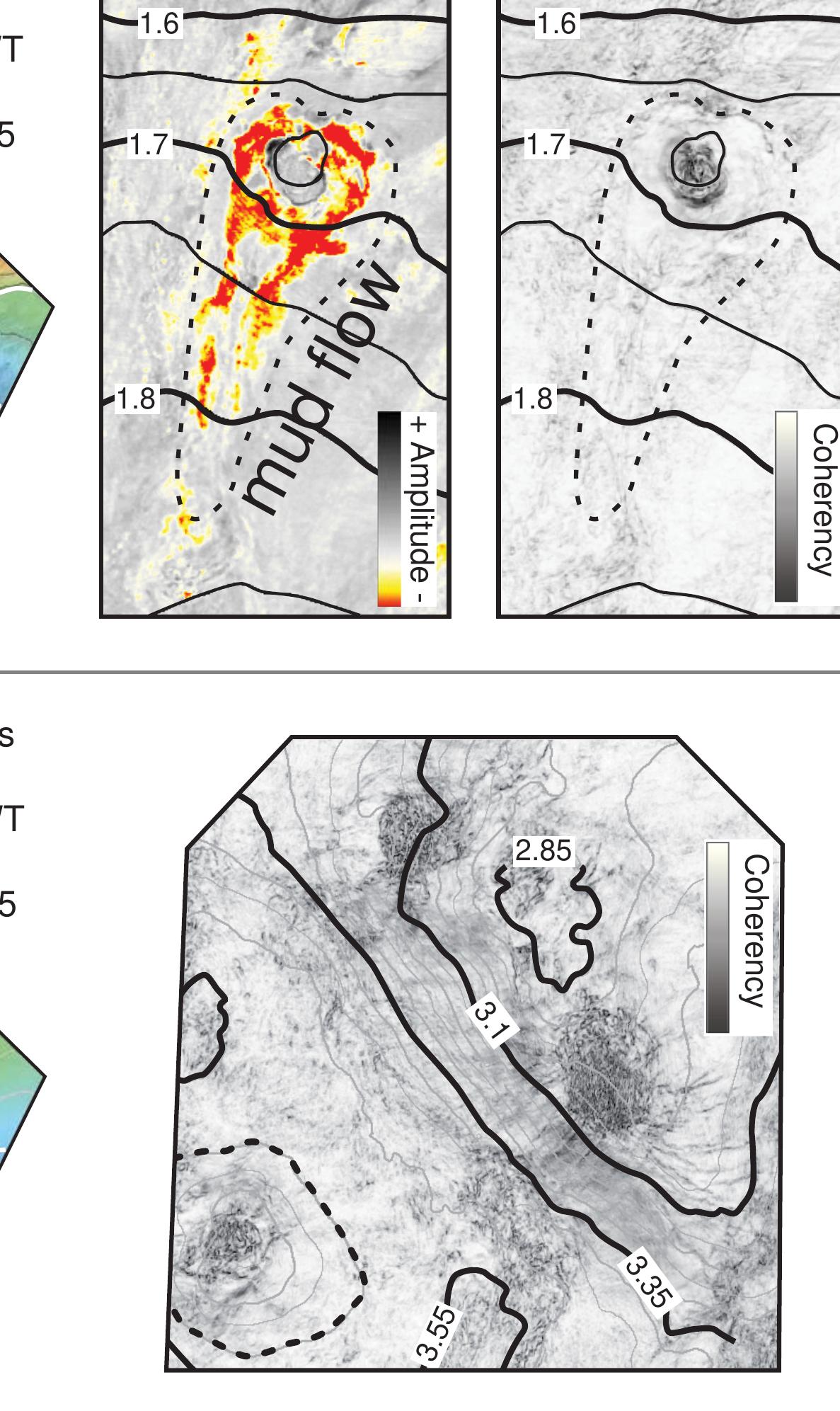
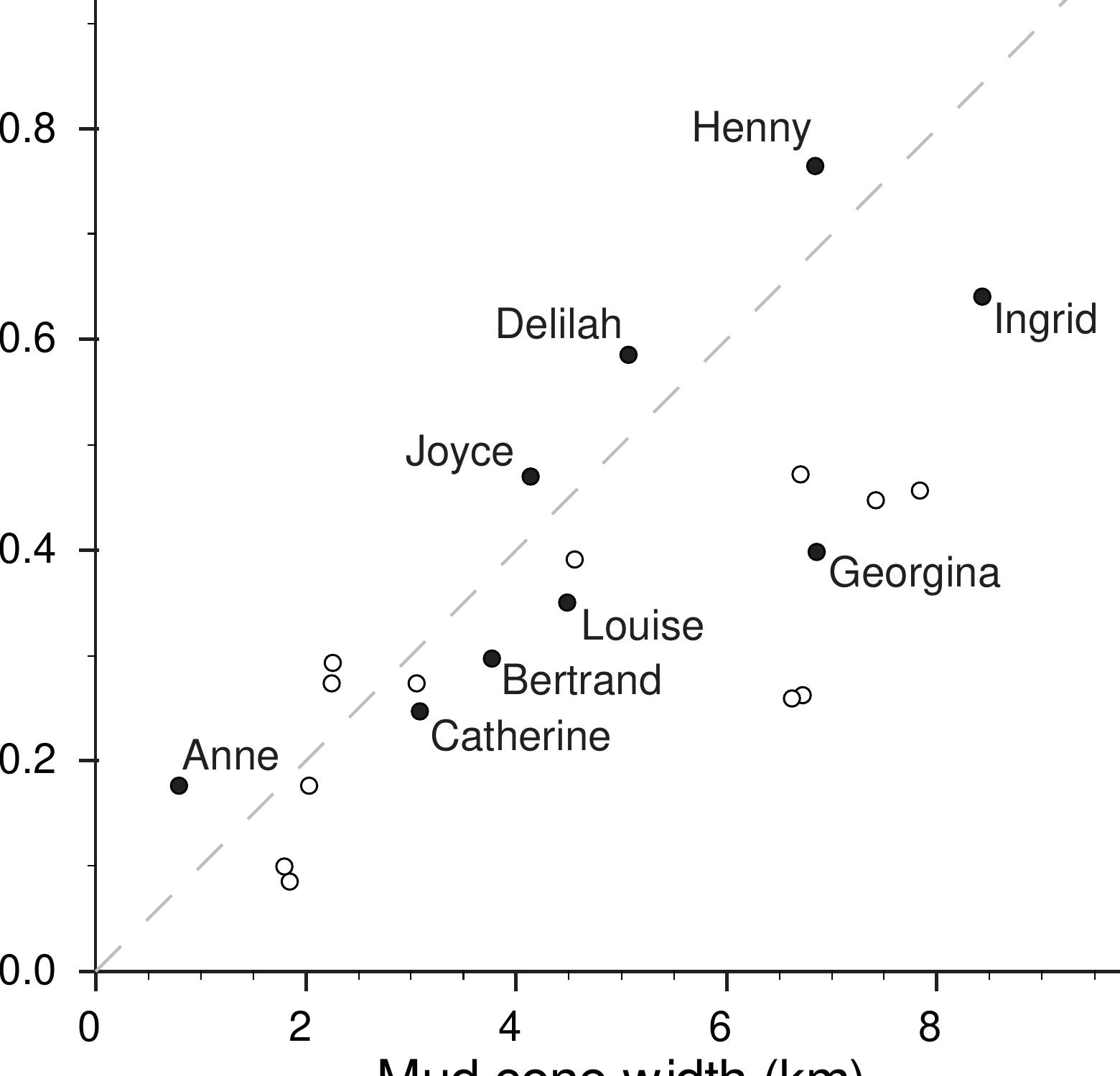
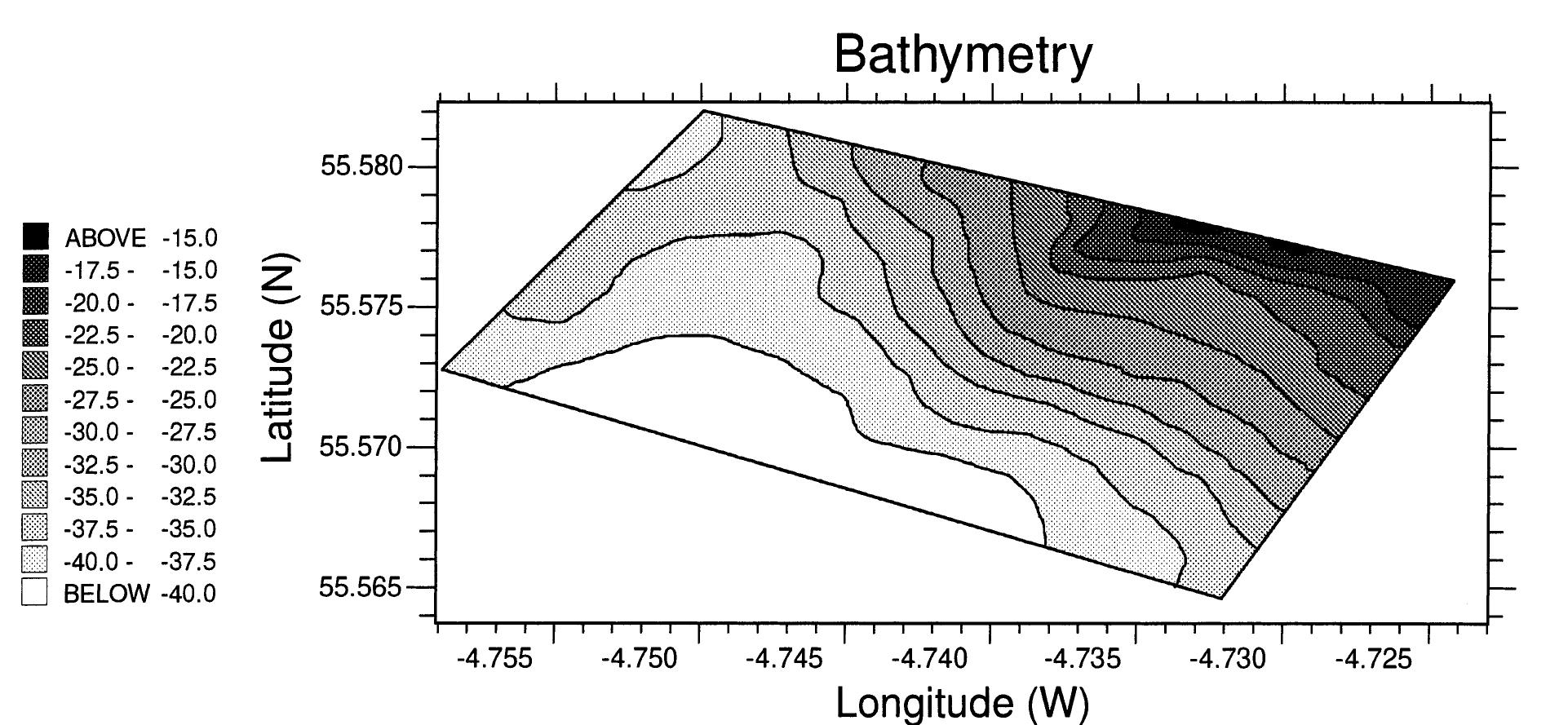
Research under this theme investigates physical and biological mechanisms driving sediment resuspension and its consequences for contaminant redistribution, bioavailability, and ecological exposure. It considers natural and anthropogenic drivers, including hydrodynamic forces and vessel-induced disturbance, focusing on contaminant remobilization from legacy polluted sediments and the implications for sediment stability and risk management. Understanding these processes is critical for predicting contaminant fate and guiding remediation strategies.
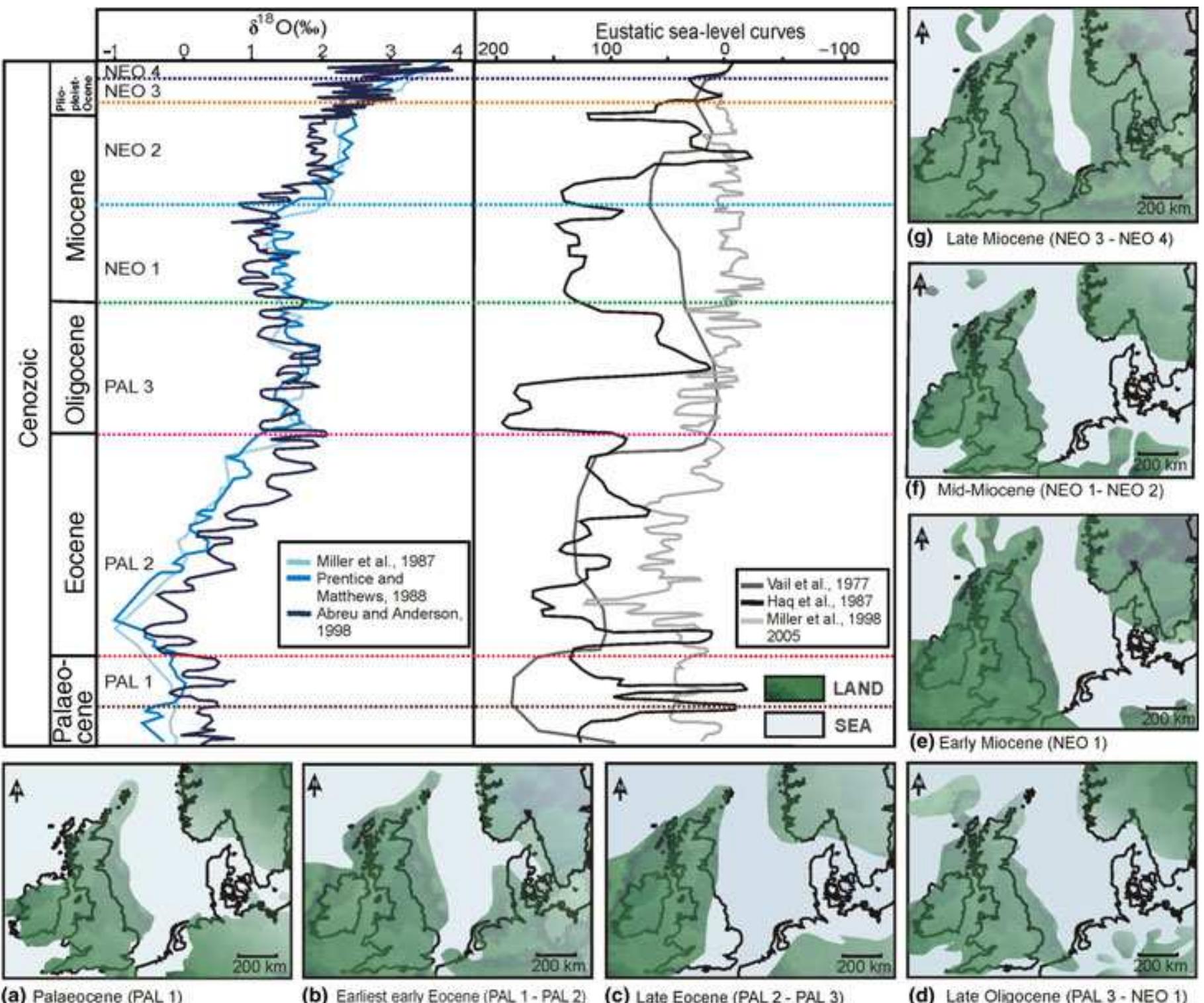
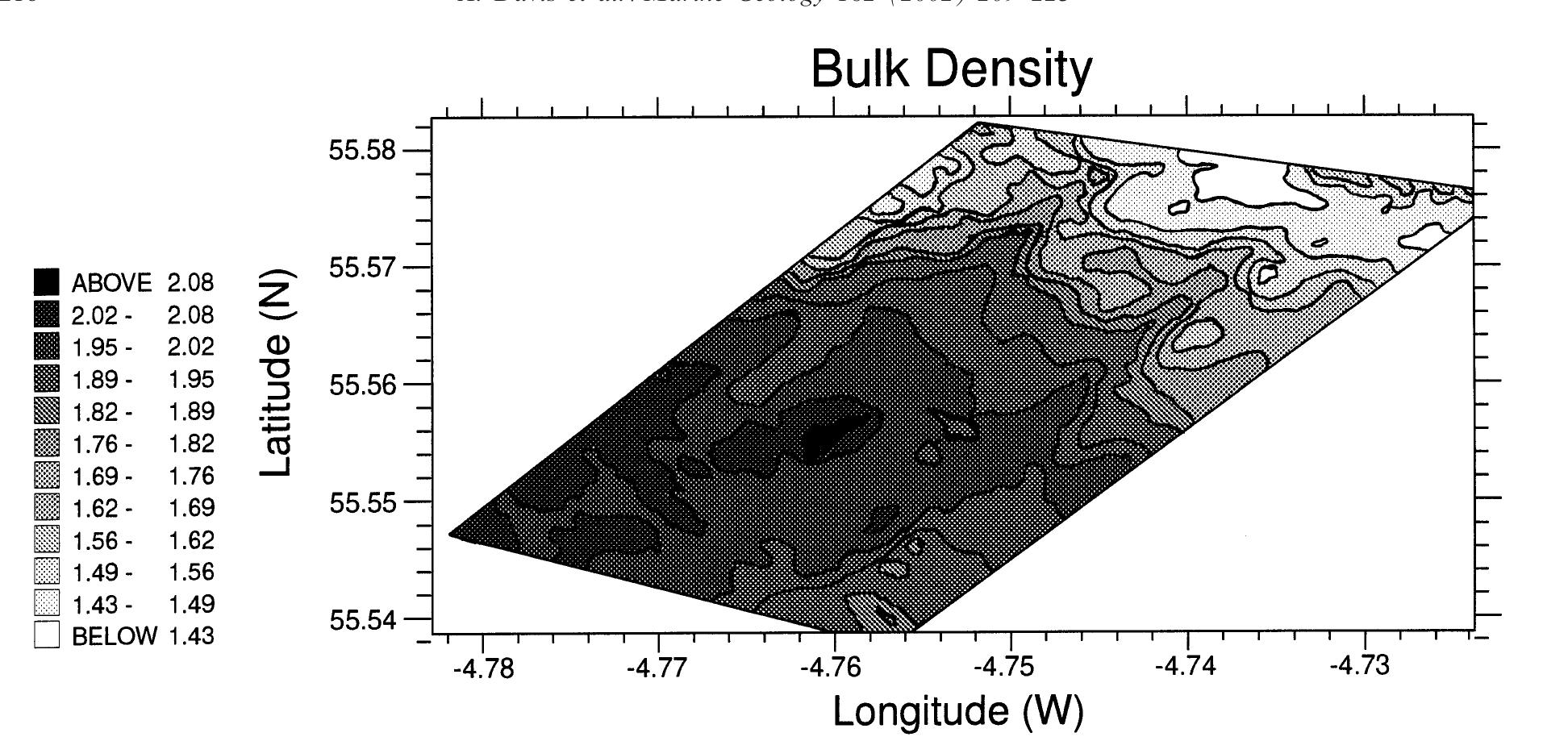
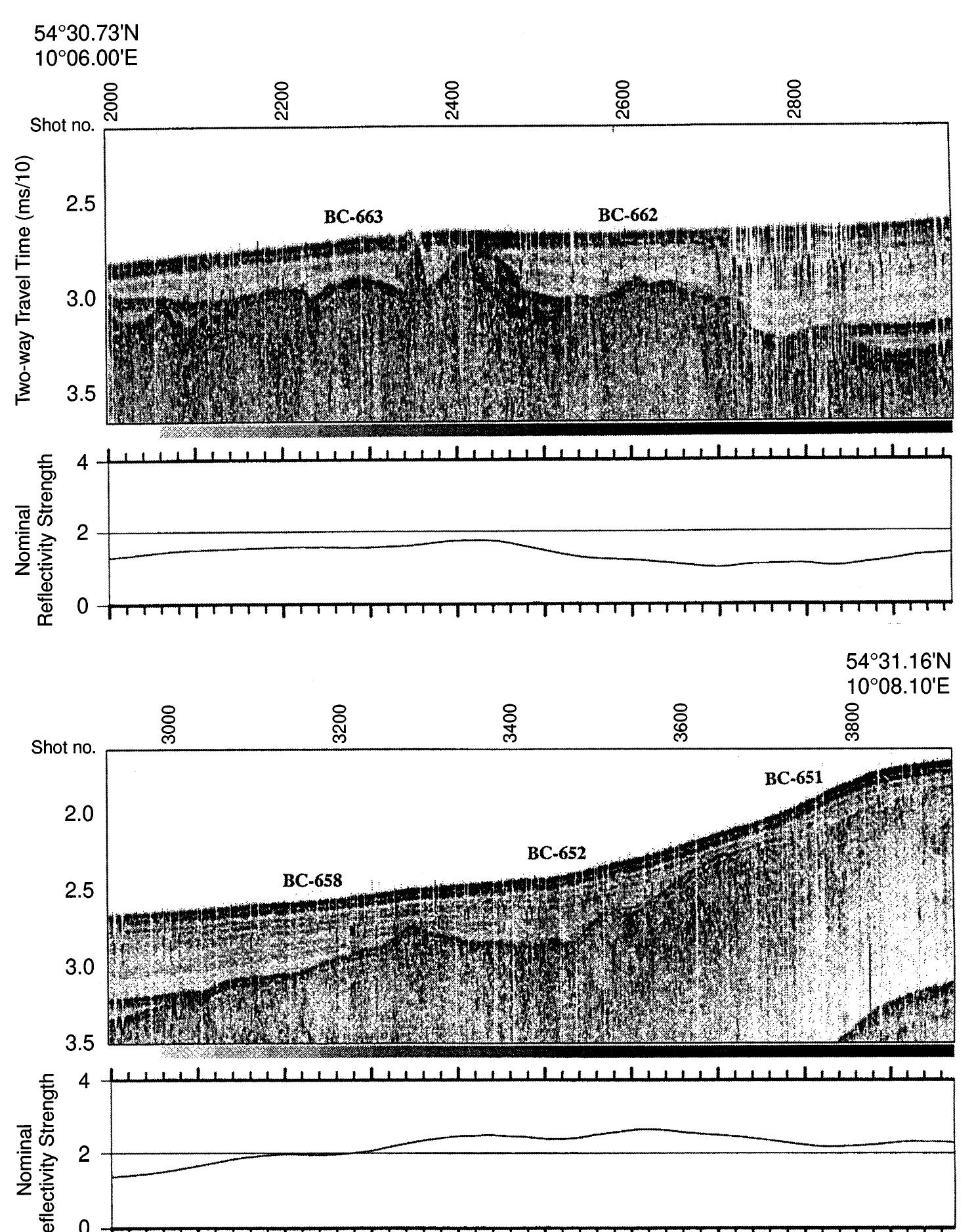
3. How can sediment records and core analyses be used to reconstruct contamination history and support environmental forensic investigations?
This topical area focuses on the use of sediment stratigraphy, geochemical profiling, and sedimentological analyses to provide historical records of contaminant input, sedimentation rates, and environmental changes. The research advances methodologies for sediment sampling, dating, and chemical characterization to identify pollutant sources, timing, and depositional environments, thereby supporting regulatory and legal frameworks for environmental responsibility and remediation.