Detection of hydrologic trends and variability
2002, Journal of Hydrology
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00514-5…
16 pages
1 file
Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
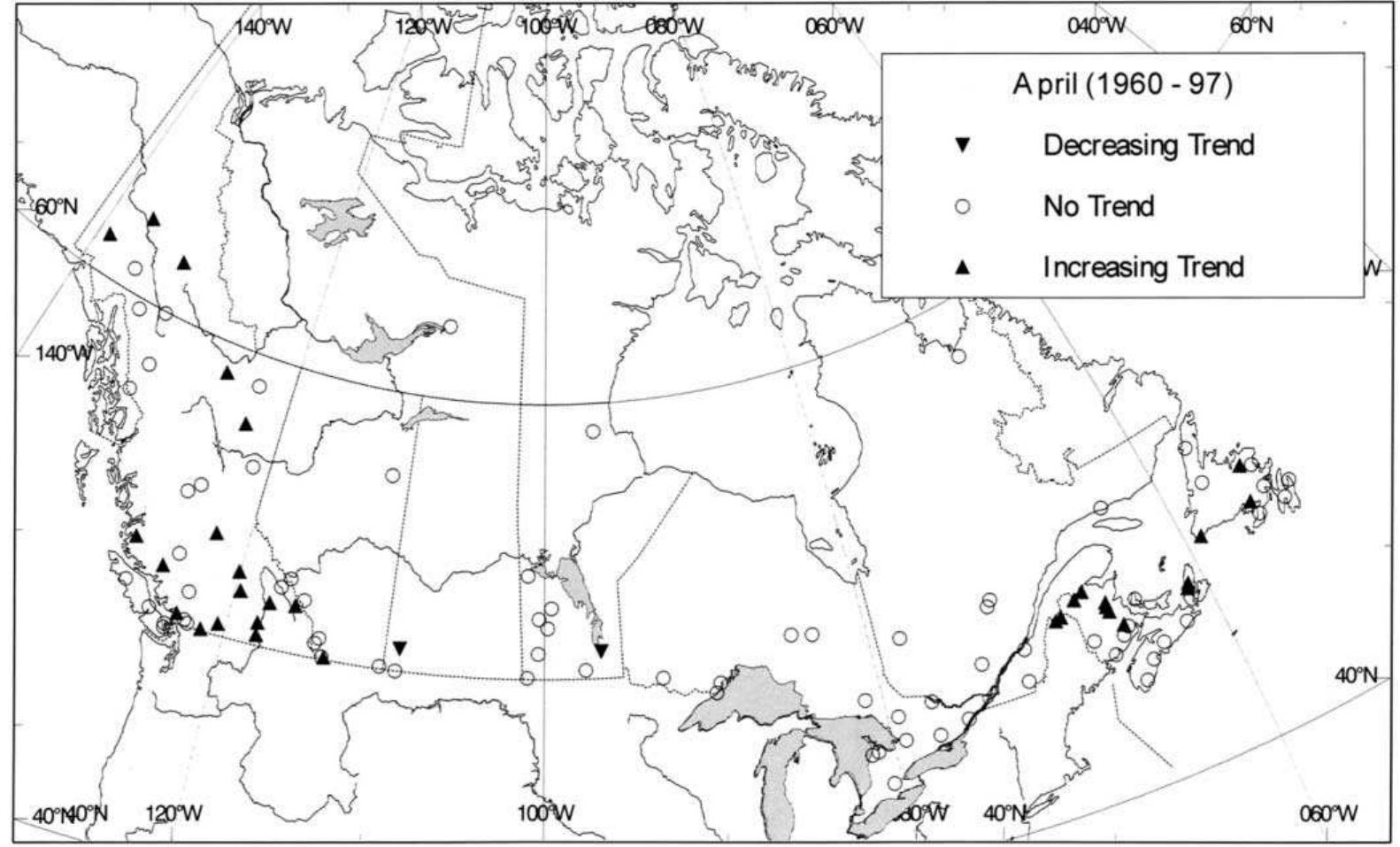
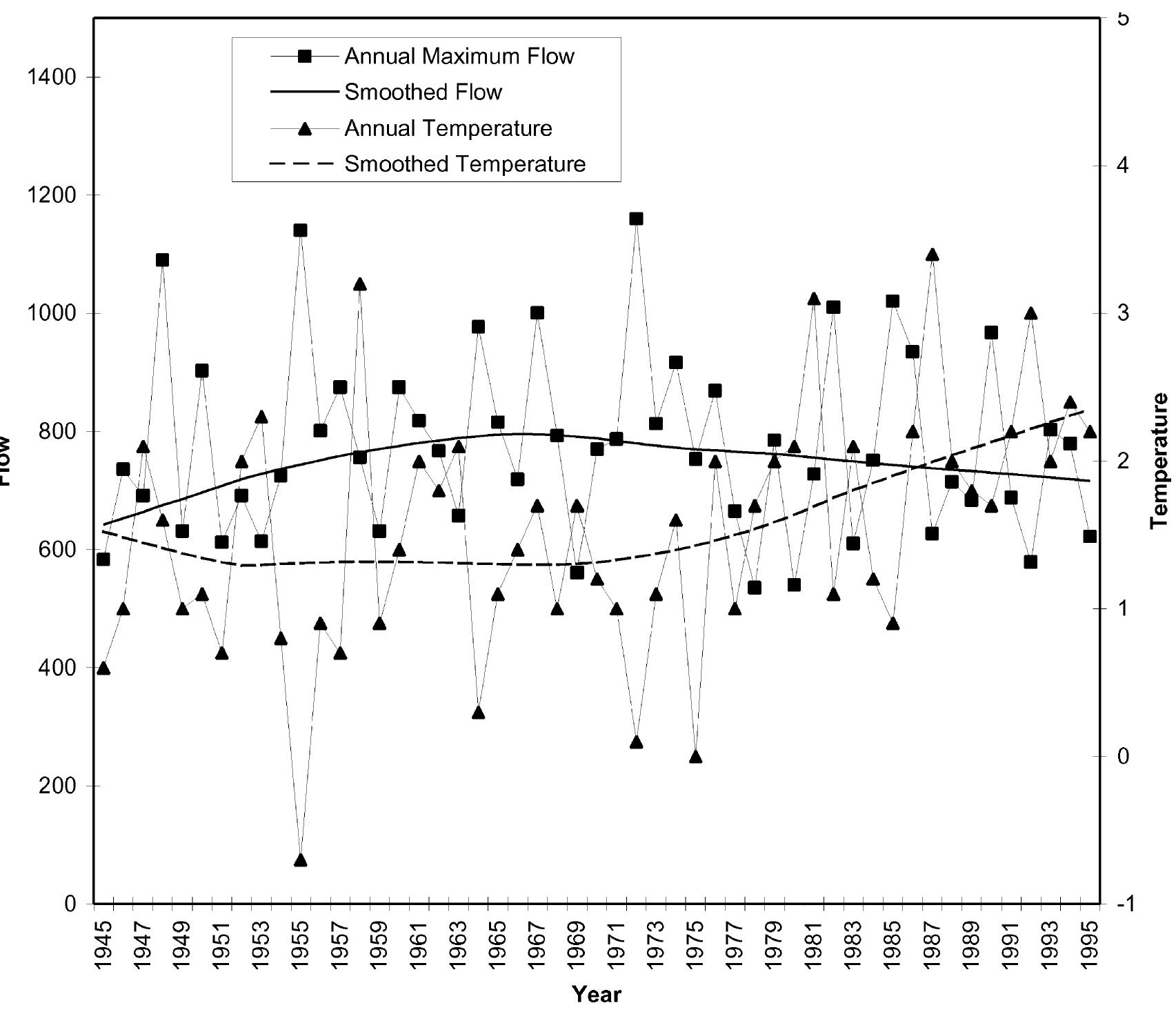
This paper describes the development and application of a procedure that identi®es trends in hydrologic variables. The procedure utilizes the Mann±Kendall non-parametric test to detect trends, a permutation approach to estimate the test distribution, and accounts for the correlation structure in the data in determining the signi®cance level of the test results. The research investigates 18 hydrologic variables that re¯ect different parts of the hydrologic cycle. The hydrologic variables are analyzed for a network of 248 Canadian catchments that are considered to re¯ect natural conditions. A selection of catchments identi®ed to have trends in hydrologic variables is studied further to investigate the presence of trends in meteorological variables and the relationship between the hydrologic and the meteorological response to climatic change. It is concluded that a greater number of trends are observed than are expected to occur by chance. There are differences in the geographic location of signi®cant trends in the hydrologic variables investigated implying that impacts are not spatially uniform. q









Related papers
Canadian Water Resources Journal, 2004
A study of trends and variability of hydrological variables was conducted for natural streamflow gauging stations within two watersheds that are important sources of flow within the Mackenzie River Basin. A comparison was made between trend results for the Liard River Basin and for the Athabasca River Basin. These basins represent a north-south transect of high elevation headwater basins within the Mackenzie River system and are significant since they produce 34% of the annual flow, while occupying only 24% of the total drainage area. Trend analysis was conducted using the Mann-Kendall test with an approach that corrects for serial correlation. The global (or field) significance of the results for each watershed was evaluated using a bootstrap resampling approach. The relationships between trends in hydrological variables and trends in meteorological variables were investigated using partial correlation analysis. The results reveal more trends in some hydrological variables than are expected to occur by chance. In general, both basins exhibit an increase in winter flows and some increase in spring runoff. These increased flows are somewhat offset by decreases (not field significant) in summertime flow. Almost 50% of the stations used in the analysis show an increasing trend in annual minimum flows. Other differences in trend responses are noted for the two watersheds and possible explanations for the differences are hypothesized.
Hydrological Processes, 2010
The potential impacts of climate change can alter the risk to critical infrastructure resulting from changes to the frequency and magnitude of extreme events. As well, the natural environment is affected by the hydrologic regime, and changes in high flows or low flows can have negative impacts on ecosystems. This article examines the detection of trends in extreme hydrological events, both high and low flow events, for streamflow gauging stations in Canada. The trend analysis involves the application of the Mann-Kendall non-parametric test. A bootstrap resampling process has been used to determine the field significance of the trend results. A total of 68 gauging stations having a nominal record length of at least 50 years are analysed for two analysis periods of 50 and 40 years. The database of Canadian rivers investigated represents a diversity of hydrological conditions encompassing different extreme flow generating processes and reflects a national scale analysis of trends. The results reveal more trends than would be expected to occur by chance for most of the measures of extreme flow characteristics. Annual and spring maximum flows show decreasing trends in flow magnitude and decreasing trends in event timing (earlier events). Low flow magnitudes exhibit both decreasing and increasing trends.
Bodenkultur, 2011
The research discusses the analysis of trends of essential hydrometeorological elements using selected statistical methods. The main aim of our research project was to compare the time series of flows with an adequate series of rainfall values; air temperatures and snow cover depths, and thereby try to determine what kind of changes occur in low mountains areas (study areas: Bohemian Forest, Ore Mountains, Jeseniky Mt.). We verified the absolute and relative homogeneity of the data series, as well as the presence of a trend in the data series. The following statistical tests, in particular, were used for this purpose: Pettitt test; Standard Normal Homogeneity test; two Wilcoxon tests; and a Mann-Kendall test. Simple-mass and double-mass curves of monthly and annual values were also applied in the case of flow and rainfall values; furthermore, quarter-year as well as cold and warm half-year periods were studied. Trends in flow development do not highly correspond to rainfall tendencies. Since the end of the 70s and especially in the 80s (Bohemian Forest and Jeseniky Mt. and later in 90s Ore Mt.), a substantial increase in runoff occurred during the winter months. Starting in 1980, average annual temperatures have been rising, which corresponds very well to a reduction in snow cover.
Water Resources Research, 2001
This study presents trends computed for the past 30-50 years for 11 hydroclimatic variables obtained from the recently created Canadian Reference Hydrometric Basin Network database. It was found that annual mean streamflow has generally decreased during the periods, with significant decreases detected in the southern part of the country. Monthly mean streamflow for most months also decreased, with the greatest decreases occurring in August and September. The exceptions are March and April, when significant increases in streamflow were observed. Significant increases were identified in lower percentiles of the daily streamflow frequency distribution over northern British Columbia and the Yukon Territory. In southern Canada, significant decreases were observed in all percentiles of the daily streamflow distribution. Breakup of river ice and the ensuing spring freshet occur significantly earlier, especially in British Columbia. There is also evidence to suggest earlier freeze-up of rivers, particularly in eastern Canada. The trends observed in hydroclimatic variables are entirely consistent with those identified in climatic variables in other Canadian studies. precipitation and temperature are likely to have impacted the hydrology of Canadian rivers, such as volume and timing of streamflow and river ice conditions. The hydrologic regime of a stream under specific geomorphic conditions represents the integrated basin response to various climatic inputs, with precipitation and temperature being very important ones. The evolution of basin geomorphology is very slow compared with possible climatic changes caused by anthropogenic increases of greenhouse gases. Therefore the changes in the hydrologic regimes of pristine or stable, unregulated basins generally reflect changes in climatic conditions and thus can be used as indicators for the purpose of climate change detection. It is thus important to analyze trends in various hydrologic variables of river basins which are not subjected to human regulation. In addition to providing an understanding of the impacts of climatic change on society and ecosystems, such analyses may provide independent corroborative evidence to confirm and/or to verify the results of trend detection for climate variables.
Journal of Hydrology, 1997
This paper evaluates the possible effects of climate change on four hydrologic variables pertaining to the magnitude and timing of hydrologic events within the Churchill-Nelson River Basin in westcentral Canada. By using the Mann-Kendall trend test, and a regionalization procedure, the severity of climatic effects within the river basin may be quantified and used to increase awareness of future consequences for water resource systems planning and management strategies. It was found that the magnitude of hydrologic events decreased over time while snowmelt runoff events occurred earlier.
Journal of Hydrology, 2009
It is generally accepted that the seasonal cycle of precipitation and temperature in cordillera of the western US exhibits a north-south pattern for annual, interannual and decadal time scales related to largescale climate patterns. In this paper we explore these relationships, with special attention to the role of local and regional physiographic, hydrogeologic and anthropogenic conditions on low-frequency climate and terrestrial response modes. The goal is to try to understand the spatio-temporal structure in historical precipitation, temperature and streamflow records (P-T-Q) in terms of climate, physiography, hydrogeology, and human impacts. Spatial coherence in time series is examined by classification of factor loadings from principal component analysis. Classification pattern of P-T-Q stations indicate that local physiography, the hydrogeology, and anthropogenic factors transform atmospheric forcing and terrestrial response into unique clusters. To study the temporal structure, dominant low-frequency oscillatory modes are identified for a region from historical P-T-Q records using singular spectrum analysis. Noise-free time trajectories are reconstructed from the extracted low-frequency modes (seasonal-decadal) for each contributing watershed area corresponding to streamflow observation stations, and the phase-plane plots are obtained. Together, the spatial classification and phase plane provides a means of detecting how large-scale hydroclimatic patterns relate to major landforms and anthropogenic impacts across the CRB. The main result of this paper is that resolving the relative impact of basin-wide patterns of climate, physiography and anthropogenic factors (irrigation, dams, etc.) on runoff response can be a useful tool for detection and attribution for each source of variability.
Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2021
East of the Continental Divide in the cold interior of Western Canada, the Mackenzie and Nelson River basins have some of the world's most extreme and variable climates, and the warming climate is changing the landscape, vegetation, cryosphere, and hydrology. Available data consist of streamflow records from a large number (395) of natural (unmanaged) gauged basins, where flow may be perennial or temporary, collected either year-round or during only the warm season, for a different series of years between 1910 and 2012. An annual warm-season time window where observations were available across all stations was used to classify (1) streamflow regime and (2) seasonal trend patterns. Streamflow trends were compared to changes in satellite Normalized Difference Indices. Clustering using dynamic time warping, which overcomes differences in streamflow timing due to latitude or elevation, identified 12 regime types. Streamflow regime types exhibit a strong connection to location; there is a strong distinction between mountains and plains and associated with ecozones. Clustering of seasonal trends resulted in six trend patterns that also follow a distinct spatial organization. The trend patterns include one with decreasing streamflow, four with different patterns of increasing streamflow, and one without structure. The spatial patterns of trends in mean, minimum, and maximum of Normalized Difference Indices of water and snow (NDWI and NDSI) were similar to each other but different from Normalized Difference Index of vegetation (NDVI) trends. Regime types, trend patterns, and satellite indices trends each showed spatially coherent patterns separating the Canadian Rockies and other mountain ranges in the west from the poorly defined drainage basins in the east and north. Three specific areas of change were identified: (i) in the mountains and cold taiga-covered subarctic, streamflow and greenness were increasing while wetness and snowcover were decreasing, (ii) in the forested Boreal Plains, particularly in the mountainous west, streamflows and greenness were decreasing but wetness and snowcover were not changing, and (iii) in the semi-arid to sub-humid agricultural Prairies, three patterns of increasing streamflow and an increase in the wetness index were observed. The largest changes in streamflow occurred in the eastern Canadian Prairies.
Journal of Hydrology, 2011
SummaryWithin the past few decades, Minnesota's land use change has responded rapidly to prevailing economic growth conditions, resulting in hydrologic characteristic alterations of the landscape and shifting the hydrologic balance of its watersheds. Regionalization using mean annual and mean monthly streamflow values was used to delineate hydrologic regimes with distinct temporal flow variations. By identifying hydrologic relationships between watersheds through an initial regionalization of mean annual streamflow time-series data, hydrologic regimes, each composed of watersheds with common hydrologic controlling variables, were identified. This paper summarizes how by applying factor analysis techniques to complete a statewide regionalization for Minnesota, hydrologic regimes were identified, each with a specific hydrologic signature; varying between three and four runoff periods of different durations. A geographic information system database was established to display the results of the regionalization and to identify hydrologic regime changes between the 1936-2008, 1936-1980, and 1950-2008 analysis intervals. Results delineated five hydrologic regimes for each of the three analysis periods. By focusing on each specific regime, further analyses were completed to identify significant increasing and decreasing trend characteristics. Review of the temporal variation for each regime using Kendall Tau trend analyses suggests that although variation in annual precipitation has an important influence on hydrologic variability, land cover and management proved to be a more direct controlling agent. Understanding the consequences of anthropogenic land use change on hydrologic processes within each defined regime should be the focus of future analyses.
Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions, 2013
This study uses a 133 yr data set from the 1055 km 2 Skjern River catchment in a western Danish catchment to evaluate: long-term past climate changes in the area; the capability of a conceptual hydrological model NAM to simulate climate change impacts on river discharge; and the occurrences of droughts and floods in a changing climate. The degree of change in the climatic variables is examined using the non-parametric Mann-Kendall test. During the last 133 yr the area has experienced a significant change in precipitation of 46 % and a temperature change of 1.3 • C leading to (simulated) increases in discharge of 103 % and groundwater recharge of 172 %. Only a small part of the past climatic changes was found to be correlated to the climatic drivers: NAO, SCA and AMO. The NAM model was calibrated on the period 1961-1970 and showed generally an excellent match between simulated and observed discharge. The capability of the hydrological model to predict climate change impact was investigated by looking at performances outside the calibration period. The results showed a reduced model fit, especially for the modern time periods (after the 1970s), and not all hydrological changes could be explained. This might indicate that hydrological models cannot be expected to predict climate change impacts on discharge as accurately in the future, as they perform under present conditions, where they can be calibrated. The (simulated) stream discharge was subsequently analyzed using flood and drought indices based on the threshold method. The extreme signal was found to depend highly on the period chosen as reference to normal. The analysis, however, indicated enhanced amplitude of the hydrograph towards the drier extremes superimposed on the overall discharge increase leading to more relative drought periods.
2004
Changes in global climate will have significant impact on local and regional hydrological regimes, which will in turn affect ecological, social and economical systems. However, climate-change impact studies on hydrologic regime have been relatively rare until recently, mainly because Global Circulation Models, which are widely used to simulate future climate scenarios, do not provide hourly or daily rainfall reliable enough for hydrological modeling. Nevertheless, more reliable rainfall series corresponding to future climate scenarios can be derived from GCM outputs using the so called 'downscaling techniques'. This study applies two types of statistical (a stochastic and a regression based) downscaling techniques to generate the possible future values of local meteorological variables such as precipitation and temperature in the Chute-du-Diable sub-basin of the Saguenay watershed in northern Québec, Canada. The downscaled data is used as input to two different hydrologic models to simulate the corresponding future flow regime in the catchment. In addition to assessing the relative potential of the downscaling methods, the paper also provides comparative study results of the possible impact of climate change on river flow and total reservoir inflow in the Chute-du-Diable basin. Although the two downscaling techniques do not provide identical results, the time series generated by both methods indicates a general increasing trend in the mean daily temperature values. While the regression based downscaling technique resulted in an increasing trend in the mean and variability of daily precipitation values, such a trend is not obvious in the case of precipitation time series downscaled with the stochastic weather generator. Moreover, the hydrologic impact analysis made with the downscaled precipitation and temperature time series as input to the two hydrological models suggest an overall increasing trend in mean annual river flow and reservoir inflow as well as earlier spring peak flows in the basin.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
References (5)
- von Storch, H., Navarra, A. (Eds.), 1995. Analysis of Climate Varia- bility Springer, New York.
- Westmacott, J.R., Burn, D.H., 1997. Climate change effects on the hydrologic regime within the Churchill-Nelson River Basin. Journal of Hydrology 202, 263±279.
- Whit®eld, P.H., Cannon, A.J., 2000. Recent variations in climate and hydrology in Canada. Canadian Water Resources Journal 25 (1), 19±65.
- Yulianti, J.S., Burn, D.H., 1998. The impact of climate change on low stream¯ow in the prairies region of Canada. Canadian Water Resources Journal 23 (1), 45±60.
- Zhang, X., Harvey, K.D., Hogg, W.D., Yuzyk, T.R., 2001. Trends in Canadian stream¯ow. Water Resources Research 37 (4), 987± 998.
 Don Burn
Don Burn