This paper describes our participation in the Robust WSD Task within the CLEF 2008. The aim of this pilot task is exploring methods which can take profit of WSD information in order to improve the IR systems. In our approach we have used... more
Word sense disambiguation (WSD) is a problem to determine a word according to the context in which it occurs. There are plenty amount of works done in WSD for some languages such as English, but research work on Assamese WSD remains... more
In natural language processing (NLP), word sense disambiguation (WSD) is defined as the task of assigning the appropriate meaning (sense) to a given word in a text or discourse. Natural language is ambiguous, so that many words can be... more
Distributional semantic methods to approximate word meaning with context vectors have been very successful empirically, and the last years have seen a surge of interest in their compositional extension to phrases and sentences. We present... more
The intelligent tutoring sytems (ITS) are generations of computer based educational sysems that supports the teaching and learning processes with the aim of helpping students to achieve maximum learning goals. A major advanage of these... more
Search engines are based on models to index documents, match queries and documents and rank documents. Research in Information Retrieval (IR) aims at defining these models and their parameters in order to optimize the results. Using... more
Word sense disambiguation (WSD) is a problem to determine a word according to the context in which it occurs. There are plenty amount of works done in WSD for some languages such as English, but research work on Assamese WSD remains... more
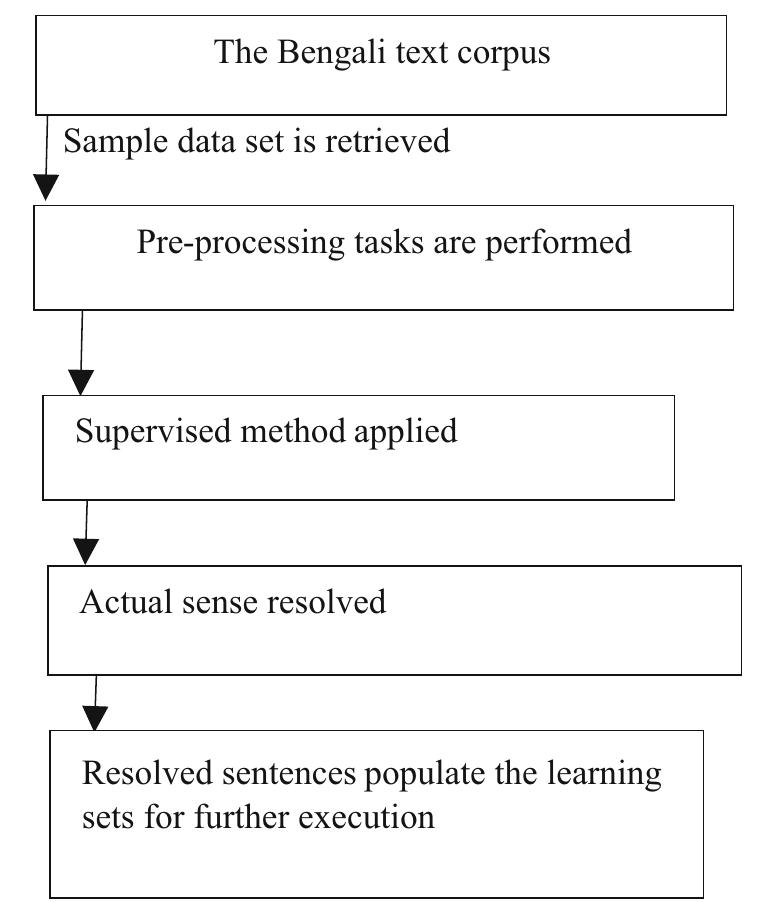
An attempt is made in this paper to report how a supervised methodology has been adopted for the task of Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) in Bengali with necessary modifications. At the initial stage, four commonly used supervised methods,... more
An attempt is made in this paper to report how a supervised methodology has been adopted for the task of Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) in Bengali with necessary modifications. At the initial stage, four commonly used supervised methods,... more
Vector space representations of words capture many aspects of word similarity, but such methods tend to make vector spaces in which antonyms (as well as synonyms) are close to each other. We present a new signed spectral normalized graph... more
Much as the social landscape in which languages are spoken shifts, language too evolves to suit the needs of its users. Lexical semantic change analysis is a burgeoning field of semantic analysis which aims to trace changes in the... more
Despite the incremental nature of Dynamic Syntax (DS), the semantic grounding of it remains that of predicate logic, itself grounded in set theory, so is poorly suited to expressing the rampantly context-relative nature of word meaning,... more
The intelligent tutoring sytems (ITS) are generations of computer based educational sysems that supports the teaching and learning processes with the aim of helpping students to achieve maximum learning goals. A major advanage of these... more
Language is dynamic and constantly evolving: both the usage context and the meaning of words change over time. Identifying words that acquired new meanings and the point in time at which new word senses emerged is elementary for word... more
We present a state-of-the-art algorithm for measuring the semantic similarity of word pairs using novel combinations of word embeddings, WordNet, and the concept dictionary 4lang. We evaluate our system on the SimLex-999 benchmark data.... more
Despite the incremental nature of Dynamic Syntax (DS), the semantic grounding of it remains that of predicate logic, itself grounded in set theory, so is poorly suited to expressing the rampantly context-relative nature of word meaning,... more
The lexicon of any natural language encodes a huge number of distinct word meanings. Just to understand this article, you will need to know what thousands of words mean. The space of possible sentential meanings is infinite: In this... more
This article proposes a system based on the interpretation on the Quranic text that has been translated into English language using word sense disambiguation. This system is based on a combination of three traditional semantic similarity... more
ABSTARCT-The intelligent tutoring systems (ITS) is the most recent alternative advancement to human tutors in the teaching and learning processes in today's educational environments that started over the past three decades. The main goal... more
As the web is increasing exponentially, so it is very much difficult to provide relevant information to the information seekers. While searching some information on the web, users can easily fade out in rich hypertext. The existing... more
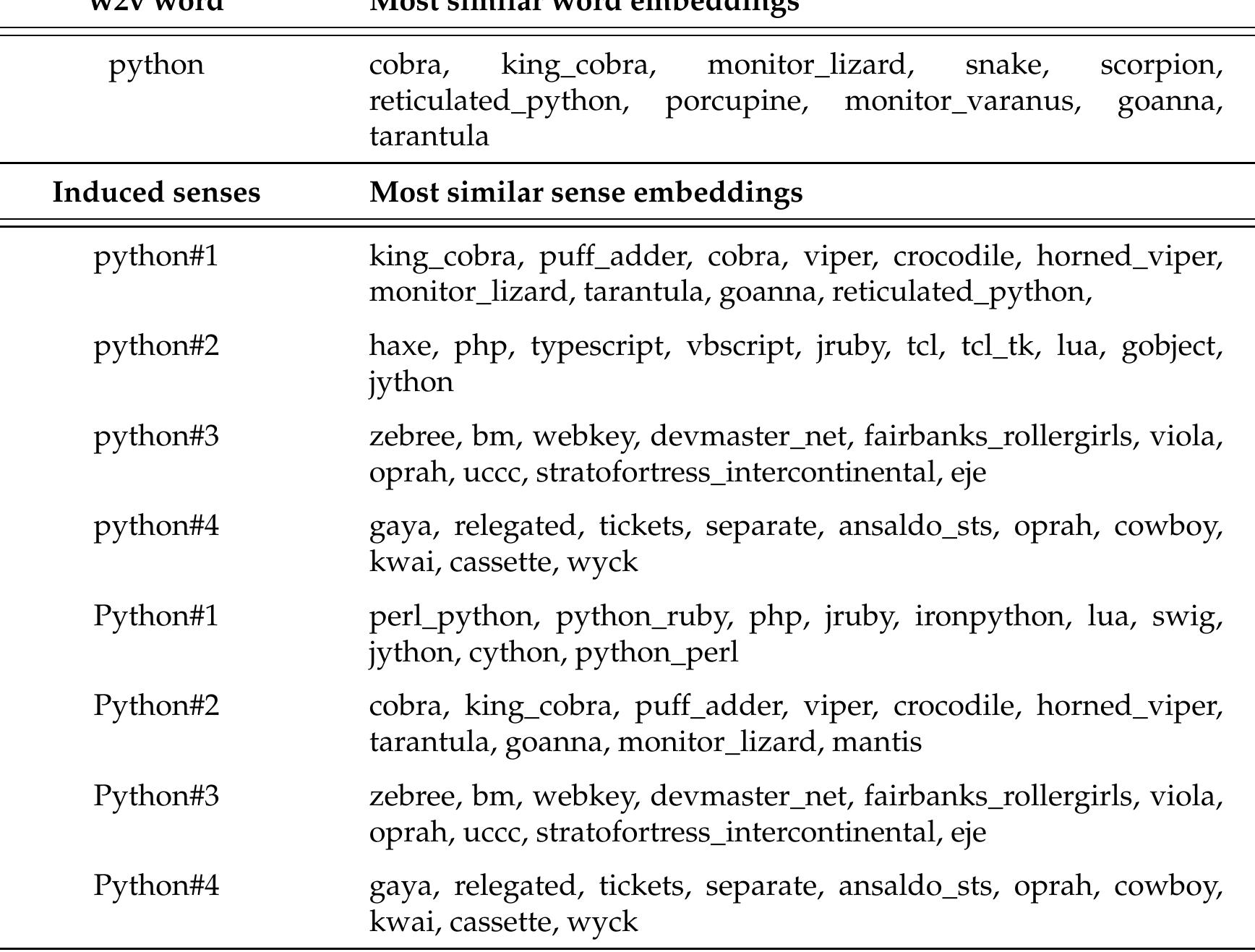
There has recently been a lot of interest in unsupervised methods for learning sense distributions, particularly in applications where sense distinctions are needed. This paper analyses a state-of-the-art method for sense distribution... more
The process of identifying the meaning of a polysemous word correctly from a given context is known as the Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) in natural language processing (NLP). Adapted Lesk algorithm based system is proposed which makes... more
We provide a comparative study between neural word representations and traditional vector spaces based on cooccurrence counts, in a number of compositional tasks. We use three different semantic spaces and implement seven tensor-based... more
In natural language processing (NLP), word sense disambiguation (WSD) is defined as the task of assigning the appropriate meaning (sense) to a given word in a text or discourse. Natural language is ambiguous, so that many words can be... more
An attempt is made in this paper to report how a supervised methodology has been adopted for the task of Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) in Bengali with necessary modifications. At the initial stage, four commonly used supervised methods,... more
This paper investigates techniques for knowledge injection into word embeddings learned from large corpora of unannotated data. These representations are trained with word cooccurrence statistics and do not commonly exploit syntactic and... more
As mentioned in our Introduction, one of the first thorough analyses of ambiguity in IR is that performed in Reference 24. Of the several comments made by Krovetz and Croft 24 when concluding their study, we especially retain the one... more
Over the last two decades, numerous algorithms have been developed that successfully capture something of the semantics of single words by looking at their distribution in text and comparing these distributions in a vector space model.... more
Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) is a significant issue in Natural Language Processing (NLP). WSD refers to the capacity of recognizing the correct sense of a word in a given context. It can improve numerous NLP applications such as... more
Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) is a significant issue in Natural Language Processing (NLP). WSD refers to the capacity of recognizing the correct sense of a word in a given context. It can improve numerous NLP applications such as... more
Poster: Aiming for more objectivity in creativity assessment - Applying word vectors on creativity data
In this paper we study unsupervised word sense disambiguation (WSD) based on sense definition. We learn low-dimensional latent semantic vectors of concept definitions to construct a more robust sense similarity measure wmfvec. Experiments... more
When clustering together synonyms, complications arise in cases of the words having multiple senses as each sense’s synonyms are erroneously clustered together. The task of automatically distinguis ...
This paper develops a compositional vector-based semantics of relative pronouns within a categorical framework. Frobenius algebras are used to formalise the operations required to model the semantics of relative pronouns, including... more
This paper develops a compositional vector-based semantics of subject and object relative pronouns within a categorical framework. Frobenius algebras are used to formalise the operations required to model the semantics of relative... more
Count-based distributional semantic models suffer from sparsity due to unobserved but plausible co-occurrences in any text collection. This problem is amplified for models like Anchored Packed Trees (APTs), that take the grammatical type... more
In this paper, we investigate whether an a priori disambiguation of word senses is strictly necessary or whether the meaning of a word in context can be disambiguated through composition alone. We evaluate the performance of off-the-shelf... more
Count-based distributional semantic models suffer from sparsity due to unobserved but plausible co-occurrences in any text collection. This problem is amplified for models like Anchored Packed Trees (APTs), that take the grammatical type... more
The process of identifying the meaning of a polysemous word correctly from a given context is known as the Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) in natural language processing (NLP). Adapted Lesk algorithm based system is proposed which makes... more
This paper develops a compositional vector-based semantics of relative pronouns within a categorical framework. Frobenius algebras are used to formalise the operations required to model the semantics of relative pronouns, including... more
Despite the incremental nature of Dynamic Syntax (DS), the semantic grounding of it remains that of predicate logic, itself grounded in set theory, so is poorly suited to expressing the rampantly context-relative nature of word meaning,... more
Despite the incremental nature of Dynamic Syntax (DS), the semantic grounding of it remains that of predicate logic, itself grounded in set theory, so is poorly suited to expressing the rampantly context-relative nature of word meaning,... more
Change and its precondition, variation, are inherent in languages. Over time, new words enter the lexicon, others become obsolete, and existing words acquire new senses. Associating a word’s correct meaning in its historical context is a... more
Researchers working on distributional semantics have recently taken up the challenge of going beyond lexical meaning and tackle the issue of compositionality. Several Compositional Distributional Semantics Models (CDSMs) have been... more
Much as the social landscape in which languages are spoken shifts, language too evolves to suit the needs of its users. Lexical semantic change analysis is a burgeoning field of semantic analysis which aims to trace changes in the... more
Consider the meanings of the following phrases: “red apple,” “red hair,” and “red state.” The meaning of the word “red” in each of these examples interacts with the meaning of the noun it modifies, applying a different color to the first... more
The Practical Lexical Function (PLF) model is a model of computational distributional semantics that attempts to strike a balance between expressivity and learnability in predicting phrase meaning and shows competitive results. We... more
The Practical Lexical Function model (PLF) is a recently proposed compositional distributional semantic model which provides an elegant account of composition, striking a balance between expressiveness and robustness and performing at the... more
For many decades researchers in the domain of NLP (Natural Language Processing) and its applications like Machine Translation, Text Mining, Question Answering, Information Extraction and Information retrieval etc. have been posed with a... more