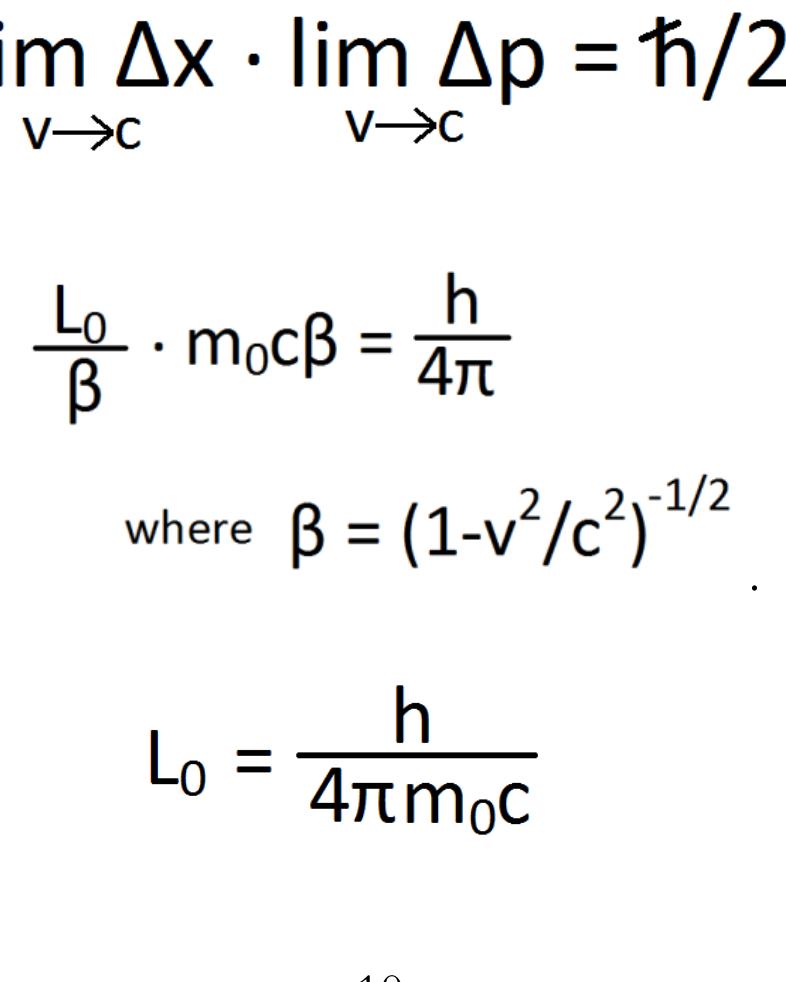Key research themes
1. How do fundamental field structures and modulation mechanisms explain the origin and precise properties of elementary particles in theoretical physics?
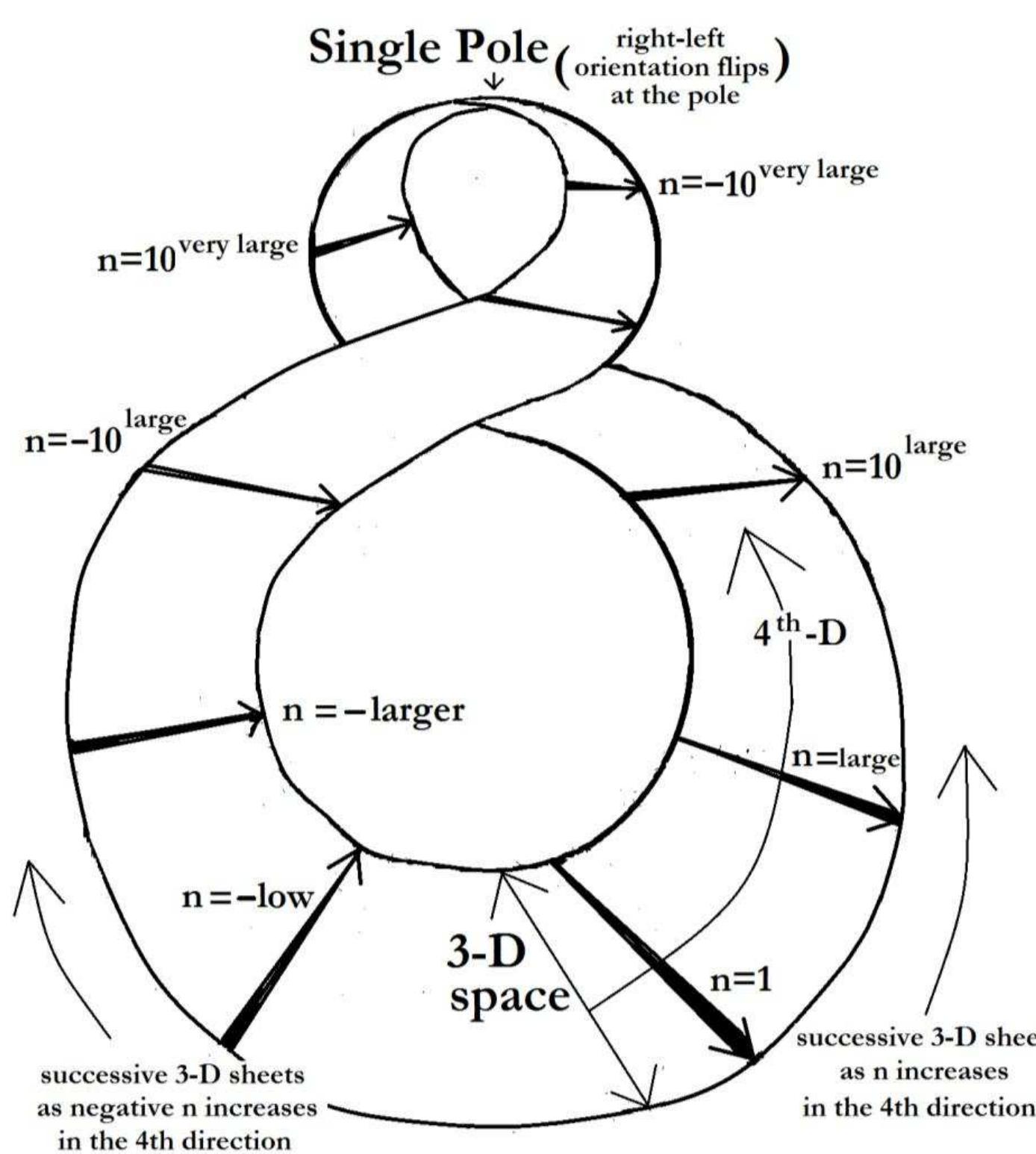
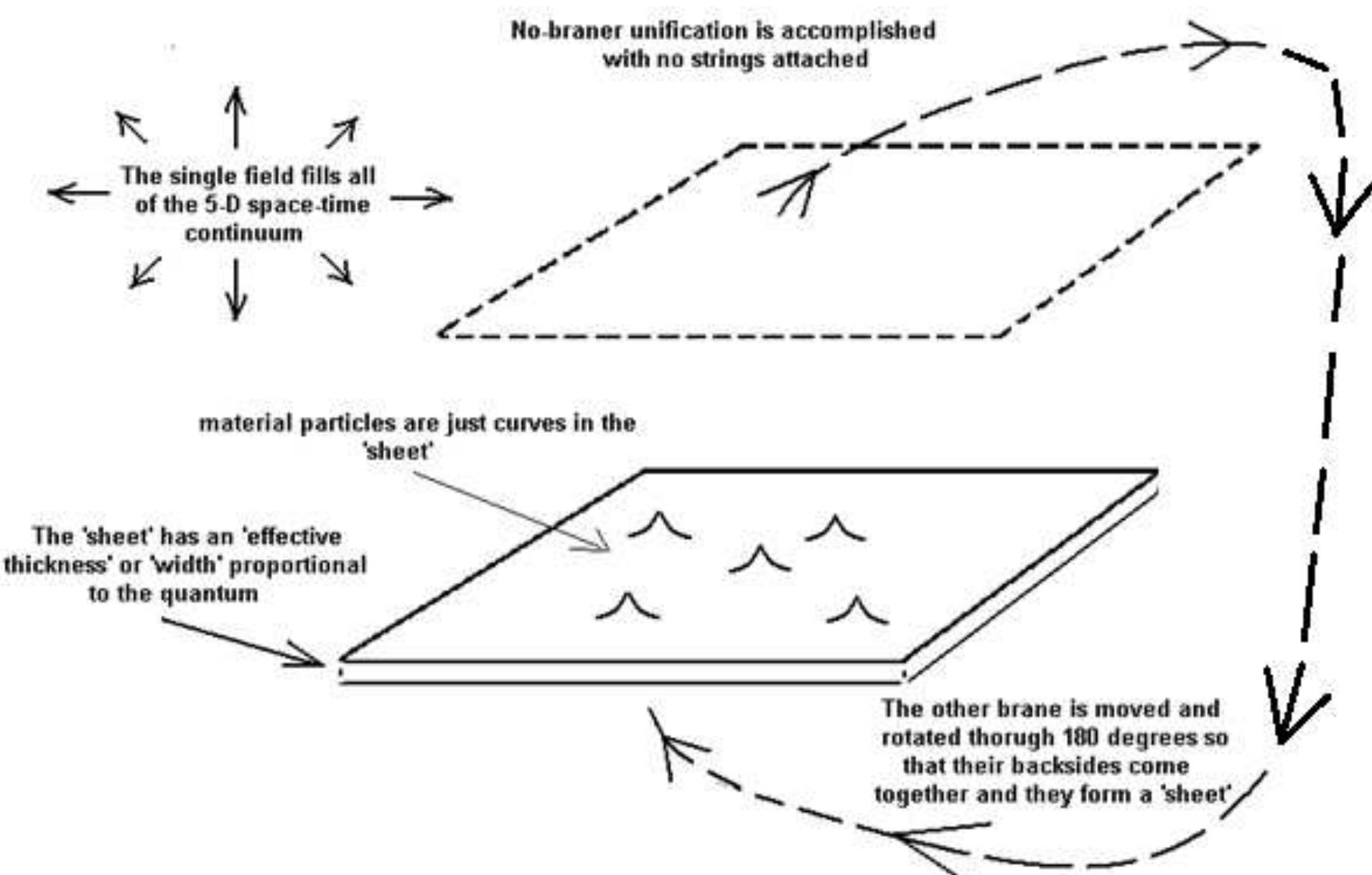
This theme explores the foundational mathematical framework and physical mechanisms underlying particle genesis from continuous fields, focusing on how modulation resonance criteria and field configurations yield discrete particle properties such as mass, charge, spin, and statistics. It addresses the century-old wave-particle duality problem through deterministic and geometrical interpretations and aims to derive fundamental constants and particle hierarchies from first principles, providing a comprehensive theoretical basis surpassing standard quantum field and particle models.
2. What are the current conceptual and ontological challenges in interpreting the Standard Model and quantum field theories with respect to particle reality and theoretical unification?
This theme investigates the foundational philosophical and conceptual issues surrounding the Standard Model's ontological commitments, contrasting interaction theories like the Standard Model with the broader quantum field theory frameworks. It addresses debates about the reality of particles versus fields, the interpretation of quantum mechanics inherited measurement problems, and the challenges in unifying quantum theory with relativity. It also reflects on evolving perceptions of what constitutes a particle given experimental constraints and theoretical limits.
3. How can quantum physics education be designed to effectively integrate Nature of Science (NOS) concepts and address the challenges of teaching foundational quantum mechanics at the secondary school level?
This theme focuses on physics education research analyzing secondary curricula internationally to identify core quantum physics topics taught and how NOS concepts—such as the role of uncertainty, probabilistic nature, and epistemological aspects—are integrated. It studies curricular differences in presenting quantum theory to improve student comprehension and proposes teaching resources that connect conceptual quantum phenomena with NOS to bridge gaps in physics instruction that prepare students for modern scientific thinking.