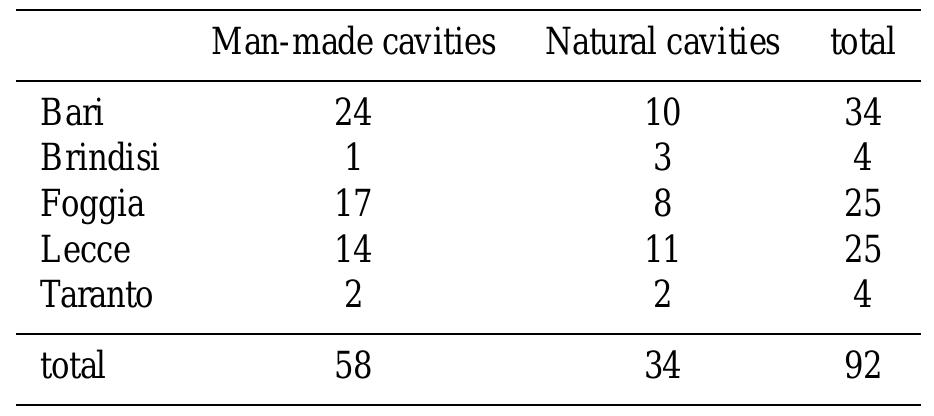
Sinkholes of both natural or anthropogenic origin are widespread phenomena in Italy, and locally constitute the main hazard. Notwithstanding the potential threat they represent to the built-up environment, sinkholes are rarely considered...
moreSinkholes of both natural or anthropogenic origin are widespread phenomena in Italy, and locally constitute the main hazard. Notwithstanding the potential threat they represent to the built-up environment, sinkholes are rarely considered in the assessment of the geological hazards, and are generally underrated when compared to other hazards such as floods and landslides. Using a variety of information sources we have recently compiled a chronological catalogue of about 700 events that occurred in Italy. Mandatory for including a sinkhole in the catalogue is the knowledge of the date of occurrence. This is considered to be complete when hour/day/month/year of the event are all available, which corresponds to high accuracy of the record. When the information about time of occurrence is more limited (for instance, comprising only month and year, or a few generic information), the accuracy is considered of progressively lower degree (medium, medium-low or low). The documented sinkholes in the catalogue cover a time span from 276 B.C. to the present day. For any event the location (precise or approximate) is also included, ranked in different levels of certainty, according to the information provided by the sources or derived from our direct surveys. More than 50 % of the sinkholes in the catalogue are related to man-made cavities, excavated in different rock types, including limestones, calcarenites, and volcanic rocks. This is due to the complex history of the country, and the many phases of underground constructions that had occurred during the different epochs, with a variety of purposes (working places, rupestrian settlements, hydraulic works, quarries, worship sites, etc.). Location of these cavities often got lost in time, so that they were later on included in the expansion of newly developed towns, thus increasing the related risk. Natural sinkholes, on the other hand, are generally located in areas where soluble rocks (carbonates, evaporites) crop out, or where alluvial sediments are present; they definitely have a lower impact on the built-up environment, mostly affecting rural areas. Trigger of the sinkholes can be due to rainfall or seismic events, or to man-made works (realization and/or maintenance of pipelines, quarrying activities, etc.). Further, other important features of sinkholes are shown in the catalogue, covering morphometric characters (width and depth), lithologies involved, and occurrence as first collapse or as a re-activation of a former sinkhole. The regions with the highest number of documented sinkholes are: Campania (246), Sicily (117), Latium (107) and Apulia (88). Only two Italian regions (Molise and Valle d'Aosta) so far are not present in the catalogue with any documented sinkhole. Sinkholes have repeatedly caused in Italy heavy damage to the society. Water supply systems, sewer systems, roads and other communication routes were often damaged; in addition, damage and/or collapse of buildings, with the deriving casualties, had also to be registered in several circumstances. In the time span covered by the catalogue, casualties (which include deaths, missing persons, and injured people) are reported in 3.5 % of the events, whilst damage are documented in 32.6 % of the cases. The numbers above are underestimated, because most of the sources typically provide generic information, that often simply refer to the occurrence of an unspecified number of deaths and injured people (especially as regards the oldest reports). This, together with the ancient date of many events, is at the origin of the difficulty in precisely quantifying the intensity of the sinkholes, in terms of their effects on the society. Most of the damage was registered in central-southern Italy, and in particular in the aforementioned regions. This is partly due to the geological setting of these territories, and to availability of specific studies on sinkholes carried out in these regions (especially in the towns of Palermo, Naples and Rome) as well. The documented damage are described in this work, subdivided in different categories, according to the type of damage, number of casualties, geographic distribution, recurrence time of the sinkhole events in the different regions. Eventually, some preliminary considerations on the quality of the used sources is also provided.