Key research themes
1. How does the Andrew File System (AFS) balance large-scale distributed file sharing with UNIX compatibility and local caching strategies?
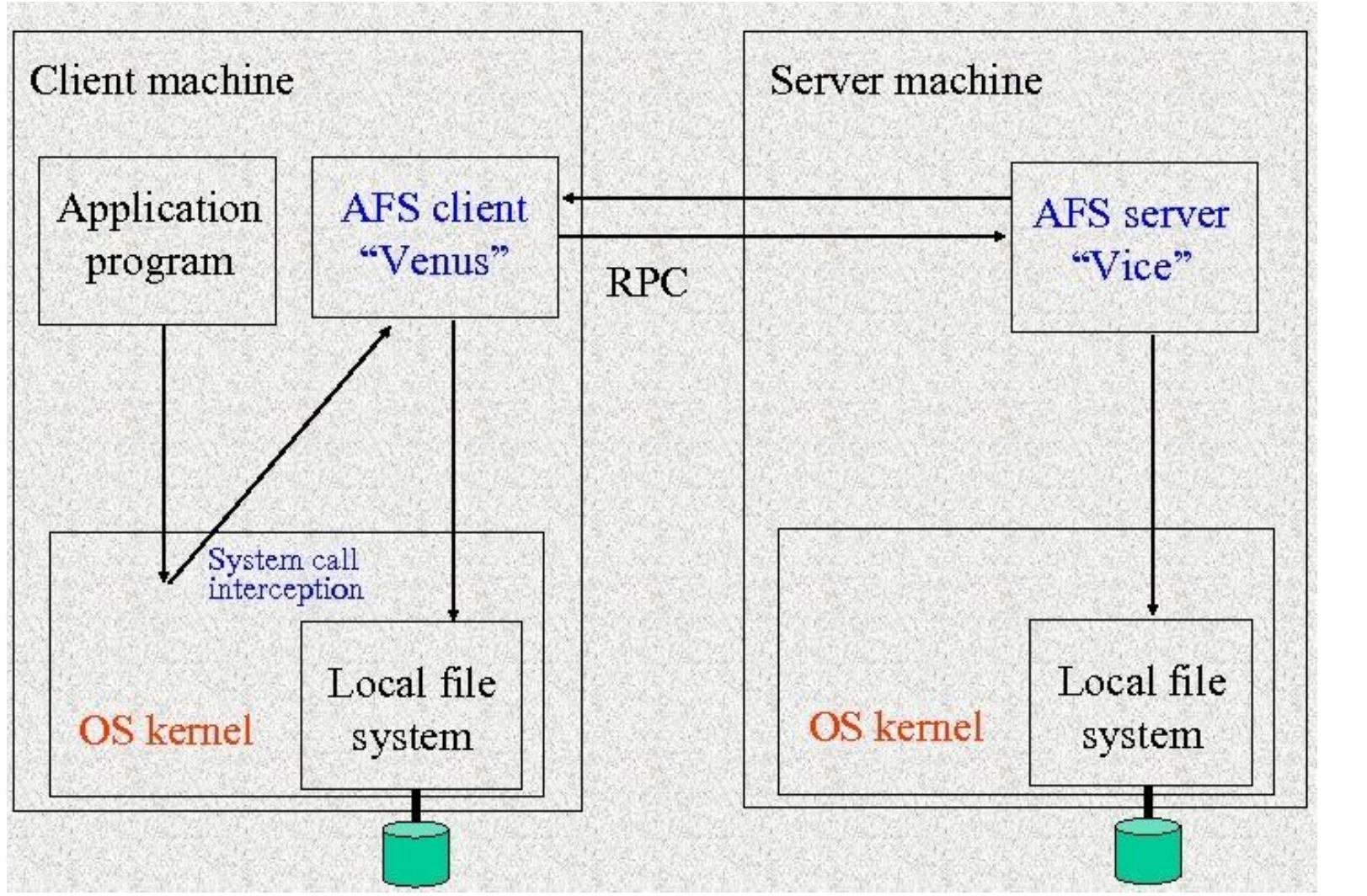
This theme investigates how AFS was designed to provide a campus-wide distributed file system supporting thousands of workstations with performance and availability considerations. It specifically looks at the design decisions around UNIX compatibility, whole-file caching on local disks, and server architecture to balance scalability, network efficiency, and user experience.
2. What architectural and protocol innovations enable high-performance network-attached storage in file systems like AFS and its successors?
This theme explores how newer file system designs, including those influenced by AFS, address client overhead and data transfer efficiency through innovations in network protocols (e.g., RDMA) and user-level file system integration. The focus is on architectural adaptations that minimize kernel involvement, optimize caching and locking, and integrate with high-speed networks to support demanding workloads.
3. How do distributed file systems manage data durability, replication, and fault tolerance across large-scale, multi-node environments?
This theme covers mechanisms for ensuring data survival and fault tolerance in distributed file systems, including replication strategies, erasure codes, and methods to handle node and network failures. It emphasizes resilience techniques crucial for systems like AFS that scale to thousands of nodes and explore variations in centralized versus decentralized storage management.