Real-Time Operating Systems for Small Microcontrollers
2009, IEEE Micro
Abstract
AI
AI
Real-time operating systems (RTOSs) are essential for embedded systems requiring timely responses, particularly in small microcontrollers. Unlike generic operating systems, RTOSs utilize preemptive scheduling, predictable synchronization, and fixed-size memory allocation to ensure deterministic behavior. Despite perceptions that small-scale embedded systems do not need an RTOS, the advantages include enhanced software productivity, better task management, and improved synchronization, significantly reducing bugs and development time.
Key takeaways
AI
AI
- RTOSs provide preemptive, priority-based scheduling, enhancing task execution efficiency in embedded systems.
- Deterministic behaviors in RTOSs ensure predictable task synchronization and latency, unlike generic operating systems.
- Developers increasingly favor open-source RTOSs, rising from 16% to 19% between 2006 and 2007.
- Time management functions in RTOSs simplify timing-related tasks, reducing complexity in embedded system development.
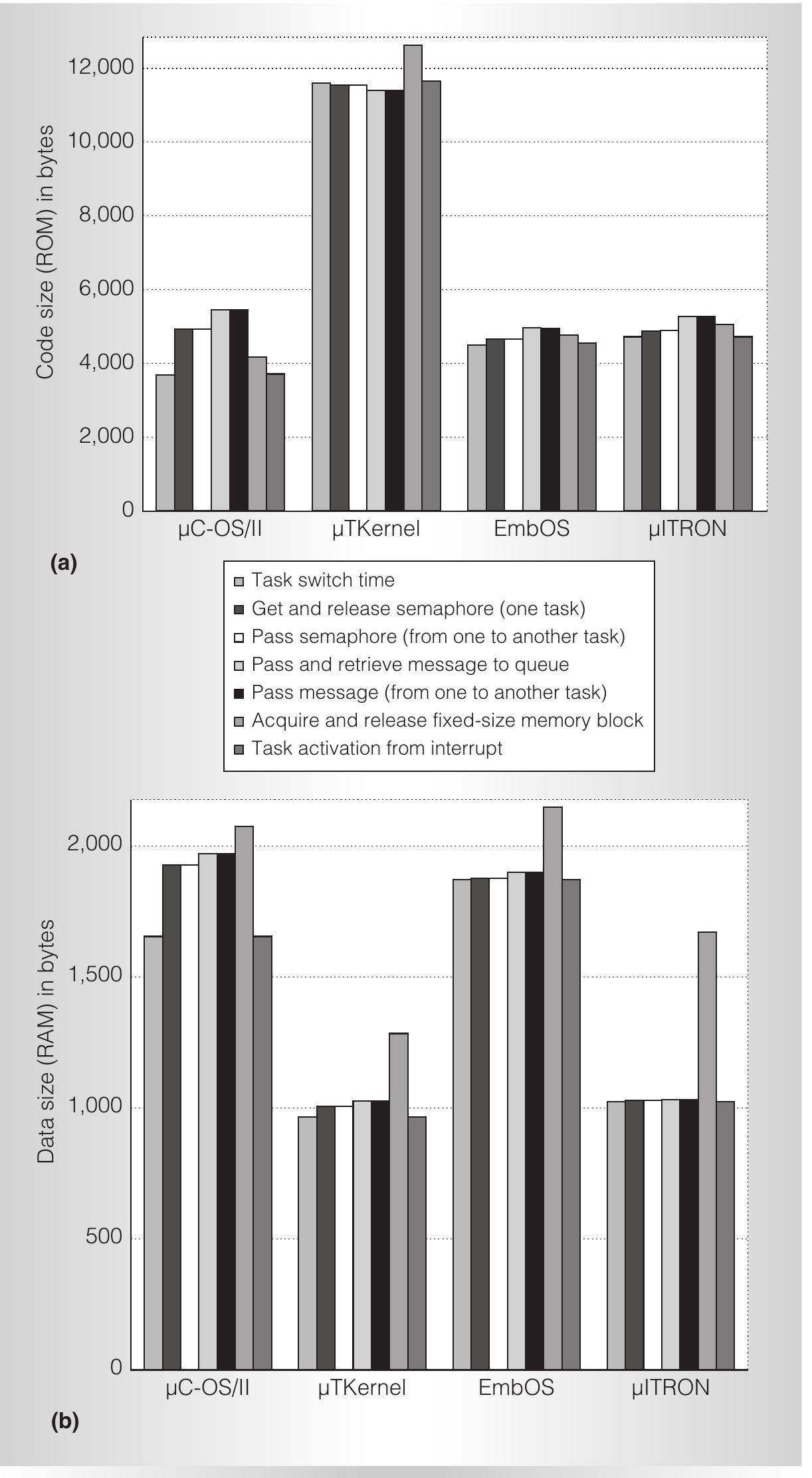
- mITRON and mTKernel offer the best performance in task switching and semaphore operations among evaluated RTOSs.
Figures (13)
References (26)
- D. Kalinsky, ''Basic Concepts of Real-Time Operating Systems,'' Linux Devices, Nov. 2003; http://www.jmargolin.com/uavs/jm_ rpv2_npl_16.pdf.
- K. Sakamura and H. Takada, ''mITRON for Small-Scale Embedded Systems,'' IEEE Micro, vol. 15, no. 6, Nov./Dec. 1995, pp. 46-54.
- J. Ganssle, ''The Challenges of Real-Time Programming,'' Embedded System Pro- gramming, vol. 11, July 1997, pp. 20-26.
- R. Nass, ''Annual Study Uncovers the Em- bedded Market,'' Embedded Systems Design, 2 Sept. 2007; http://www.embedded.com/ design/opensource/201803499;jsessionid= NGMOMOIGE5ZNNQE1GHOSKHWATMY 32JVN?printable=true.
- K. Baynes et al., ''The Performance and En- ergy Consumption of Embedded Real-time Operating Systems,'' IEEE Trans. Com- puters, vol. 52, no. 11, 2003, pp. 1454-1469.
- J.J. Labrosse, MicroC/OS-II: The Real-Time Kernel, R&D Books, 1999.
- T-Engine Forum, ''mTKernel specification, 1.00.00,'' Mar. 2007; http://www.t-engine.org.
- R. Barry, ''A Portable, Open Source Mini Real-Time Kernel,'' Oct. 2007; http://www. freertos.org.
- K. Curtis, ''Doing Embedded Multitasking with Small Microcontrollers, Part 2,'' Embedded System Design, Dec. 2006; http://www. embedded.com/columns/technicalinsights/ 196701565?_requestid=242226.
- A. Garcia-Martinez, J. F. Conde, and A. Vina, ''A Comprehensive Approach in Perfor- mance Evaluation for Modern Real-Time Operating Systems,'' Proc. 22nd EuroMicro Conf., IEEE CS Press, 1996, p. 61.
- R.P. Kar and K. Porter, ''Rhealstone: A Real- Time Benchmarking Proposal,'' Dr. Dobb's J. of Software Tools, vol. 14, no. 2, Feb. 1989, pp. 14-22.
- K.M. Sacha, ''Measuring the Real-Time Operating System Performance,'' Proc. 7th EuroMicro Workshop Real-Time Systems, IEEE CS Press, 1995, pp. 34-40.
- K. Sakamura and H. Takada, mITRON 4.0 Spec- ifications, TRON Assoc., 2002; http://www. ertl.jp/ITRON/SPEC/FILE/mitron-400e.pdf.
- EmbOS Real-Time Operating System, User & Reference Guide, Segger Microcontroller, 5 2008; http://www.segger.com/cms/admin/ uploads/productDocs/embOS_Generic.pdf.
- A.J. Massa, Embedded Software Develop- ment with eCos, Prentice Hall, 2002.
- P. Gai et al., E.R.I.K.A.: Embedded Real-tIme Kernel Architecture; ERIKA Educational User Manual, Realtime System (RETIS) Lab, Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna, Italy, 2004; http://erika. sssup.it/download.shtml#Doc.
- G.C. Buttazzo, ''Hartik: A Hard Real-Time Kernel for Programming Robot Tasks with Explicit Time Constraints and Guaran- teed Execution,'' Proc. IEEE Int'l Conf. Robotics and Automation, IEEE Press, 1993, pp. 404-409.
- R. Chrabieh, ''Operating System with Prior- ity Functions and Priority Objects,'' Tech- Online, Feb. 2005; http://www.techonline. com/learning/techpaper/193101942.
- G. Hawley, ''Selecting a Real-Time Operat- ing System,'' Embedded System Design, vol. 12, no. 3, 1999, http://www.embedded. com/1999/9903.
- M. Timmerman and L. Perneel, ''Understand- ing RTOS Technology and Markets,'' Dedicated Systems RTOS Evaluation proj- ect report, 2005; http://www.dedicated- systems.com/vpr/layout/display/pr.asp?PRID= 8972.
- R. Bannatyne and G. Viot, ''Introduction to Microcontrollers, Part 2,'' Northcon Conf. Proc., IEEE Press, 1998, pp. 250-254.
- B. Millard, D. Miller, and C. Wu, ''Support for ADA Intertask Communication in a Message-Based Distributed Operating Sys- tem,'' Computers and Comm. Conf. Proc., IEEE Press, 1991, pp. 219-225.
- M16c/62P Group Hardware Manual, Renesas Technology, 2006; http://documentation. renesas.com/eng/products/mpumcu/ rej09b0185_16c62pthm.pdf.
- Renesas Technology, ''mTKernel for M16C Source Code and Documentation,'' 2007; ht tp://www.superh-t ker nel.org/eng/ do wnload/misc/software/M30626FJPGP_ micro_tkernel/software/index.html.
- I. Ripoll et al., ''RTOS State of the Art Anal- ysis,'' tech. report, Open Components for Embedded Real-time Applications (OCERA) project, 2002.
- D. Kalinsky, ''Asynchronous Direct Message Passing Rapidly Gains Popularity,'' Embedded
 Duc-4D-18 Tran Thi Phuong Anh
Duc-4D-18 Tran Thi Phuong Anh