FISH FUNGAL SPOILAGE
2021
https://doi.org/10.21786/BBRC/14.2.49…
7 pages
1 file
Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
The high nutritional value of fish makes it highly perishable because it provides favorable medium for the growth of microorganisms after catching. In addition, they can also act as carriers of several microbial and other health hazards. Many mould growth on foods stored at low temperature is common and recurring problem. Certain molds are known to be capable of producing mycotoxins at low temperature as low as (-2 to 10°) C. That encouraging us to perform this study which aimed to survey, isolation and perform different further genetic identification of fungal spoilage species of some marine fish from Saudi Arabia markets. 100 samples from 5 types of fishes; Salmon "Salmoniformes", Red sea Bream "Pagrus pagrus", Rabbitfish "Siganus rivulatus", Spanish mackerel "Scomberomorous commerson", Red mullet "Mullus surmuletus", collected from Jeddah fish markets, then prepared aseptically and plated on Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium incubated for 3-7 days/ 28±2 0 C and examined daily Macroscopically, microscopically and genetically. The results recorded 4 species of fungi; Aspergillus eucalypticola as one of (Black Aspergilli), Aspergillus oryzae as (white Aspergilli), Penicillium digitatum as (green fungi) and Byssochlamys spectabilis. This is the first report of Penicillium digitatum and Byssochlamys spectabilis in fish. Furthermore, the research identified each fungi gene cluster. More attention in fish rearing facilities, caution should be taken by consumers in preparation and applying perfect cooking in consuming fish and more education and efforts should be developed by fish farmers to avoid fishponds contamination. We recommended to further research should be done on fungal contaminations.
Related papers
Toxins, 2020
Periods of unfavorable storing conditions can lead to changes in the quality of fish feeds, as well as the development of relevant mycotoxins. In the present study, a commercial fish feed was stored under defined conditions for four weeks. The main findings indicate that even storing fish feeds under unsuitable conditions for a short duration leads to a deterioration in quality. Mycotoxin and fungal contamination were subsequently analyzed. These investigations confirmed that different storage conditions can influence the presence of fungi and mycotoxins on fish feed. Notably, ochratoxin A (OTA) was found in samples after warm (25 °C) and humid (>60% relative humidity) treatment. This confirms the importance of this compound as a typical contaminant of fish feed and reveals how fast this mycotoxin can be formed in fish feed during storage.
Introduction Part 1 1. Saprolegnia 2. Achlya 3. Aphanomyces 4. Branchiomyces Part 2 5. Dermocystidium 6. Sphaerothecum 7. Ichthyophonus 8. Lagendium 9. Haliphthoros 10. Halioticida 11. Halocrusticida 12. Atkinsiella 13. Aquastella 14. Pythium 15. Aspergillus 16. Fusarium 17. Exophiala 18. LCD 19. Ochroconis 20. Purpureocillium (Paecilomyces) 21. Phoma 22. Miscellaneous fungi 23. Yeasts 24. Mycotoxins
International Journal of Microbiology
The rapid population growth in developing countries has led to strong pressure on capture fisheries. However, capture fisheries have reached their maximal limits of fish production and are supplemented by farmed fish. The growth in aquaculture has led to high demand for fish feeds, which play a very important role in fish nutrition and health. Use of animal protein in fish feeds is expensive; hence, a majority of farmers from developing countries use local feed ingredients from plant origin as a source of dietary protein. However, these ingredients of plant origin provide the best natural substrates for fungi, which can be easily accompanied by mycotoxin development under suitable conditions. The locally made feed comprises ingredients such as soybeans, cottonseed cake, and wheat and maize bran which are mixed together and ground after which the compounded feed is pelleted and stored. Among the ingredients, maize and oilseeds are more susceptible for mycotoxigenic fungi compared to ...
Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences
Dried fishes are salted and sun dried fish products consumed by large population owing to their nutrient richness, flavor and long shelf life properties. Contamination of dried fishes by mycotoxin producing fungi pose serious threat to food safety and public health. A total of 27 samples belonging to three varieties of dried fishes collected in Chennai city, India were screened for the isolation of mycotoxin producing fungal contaminants. Mycological examination of samples revealed the prevalence of six types of fungi viz., A. parasiticus (27.27%), A. niger (22.72%), A. fumigatus (18.18%), Penicillium sp. (18.18%), Cladosporium sp. (9.09%) and Euratium sp. (4.54%). Detection using thin layer chromatography indicated that 18.18% of isolates belonging to A. parasiticus, A. fumigatus, Penicillium sp. were positive, while A. niger, Cladosporium sp., and Euratium sp. were negative for mycotoxin production. Further to the bioassay with Artemia larvae, substantial lethality was observed with the mycotoxin of A. parasiticus (100%), followed that of by A. fumigatus and Penicillium sp. (each 50%). The HPLC studies indicated that the mycotoxin produced by A. parasiticus was Aflatoxin G2. Need for proper hygienic practices during processing and handling of dried fishes in order to avoid fungal contamination and likelihood mycotoxicosis in consumers has been suggested.
Food Control, 2020
Dried fish are important dietary protein and income sources in Zhanjiang, China. Mycotoxins produced by pathogenic fungi that contaminate fish during processing can cause considerable hazard to consumer health. This study reports fungal diversity, total fungal counts and mycotoxin contamination of dried fish sold at the seafood market in Zhanjiang. Seven dried fish products (Hemibarbus maculatus, Pseudosciaena crocea, Lutjanus erythopterus, Thunnus thynnus, Scomberomorus niphonius, Eleutheronema tetradactylum, Trichiurus lepturus, n = 10) from seven retailers were analyzed for contaminated fungal species, occurrence frequency and residues analysis of four mycotoxins. Using potato dextrose agar (PDA) plate purification, morphology observation, internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequence analysis, 25 fungal strains representing 12 genera from dried fish were systematically isolated and identified. Three dominant genera in dried fish were Fusarium sp. (80.4%), Penicillium sp. (70.7%) and Aspergillus sp.(63.9%). Other fungal genera were Neoscytalidium sp.(38.1%), Cutaneotrichosporon sp. (38.1%), Trichoderma sp.(20.3%), Naganishia sp.(15.3%), Kodamaea sp. (10.8%), Phialemoniopsis sp.(9.2%), Nigrospora sp.(7.3%), Ceriporia sp.(6.3%), Phellinus sp.(4.5%). Aspergillus flavus contamination was the higher and ranged from 1.10 × 10 3 to 2.40 × 10 4 cfu/g. The mean fungal contamination of other fungal species in dried fish ranged from 1.07 × 10 2 to 4.58 × 10 4 cfu/g. The total fungal counts of Fusarium sp. ranged from 1.09 × 10 2 to 2.11 × 10 4 cfu/g, but the occurrence frequency is relatively high. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analyses showed that mycotoxin residues were present in 12 out of the 25 dried fish tested. Aflatoxin B 1 (AFB 1) was the most frequently detected and the concentration ranged from 0.03 to 3.52 μg/kg. T-2 toxin (T-2), ochratoxin A (OTA), and deoxynivalenol (DON) concentrations ranged from 0.21 to 1.53, 0.03-2.21 and 0.71 μg/kg respectively. High occurrence of fungal populations and mycotoxins in dried fish sold in the Zhanjiang market pose a potential threat to consumer health. It is recommended that in future, advanced processing methods and controlled storage condition need to be used to minimize and if possible eliminate fungal contamination during dried fish processing.
2017
Dried fish and stock fish are largely consumed as a source of nutrient by man. It has been established that fish food can act as vehicle for transmission of some mycological pathogens especially in immune compromised individuals. Sixteen (16) different samples of fish were bought from Ozoro central market in four different locations. The samples were labeled sample A (dried fish) and sample B (stock fish). A total of four (4) fungi species were isolated from the test samples: Aspergillus niger, Candida albican, Penicillium species and Rhizopus oryzae. Aspergillus niger has the highest plate count of 7.7x10, and 5.6x10 and 0.3x10 for both samples. While Penicillium species has the least plate count of 0.3x10 Aspergillus niger have the highest percentage (%) occurrence for both samples of 52.275%, while penicillium species have the least percentage (%) occurrence of 08.33%. The total mean cfu/g count for sample A is 10.08cfu/g while for sample B is 09.08cfu/g. the occurrence of Asperg...
International Journal of Agriculture and Biology
An investigation was conducted on fungal diseases of three imported freshwater ornamental fish Carassius auratus (L.), Xiphophorus maculates (Günter) and Poecilia reticulate (Peters). A total of 45 fish specimens, were dissected. Different body parts of fish were infected and showed clinical signs. Clinical picture of C. auratus showed that scales were eroded and haemorrhage and lesions were on abdomen. Dorsal and caudal fin were disintegrated. In X. maculatus eyes and mouth was covered with fungal hyphae. The clinical picture of P. reticulata showed that gills were whitish due to the presence of fungal hyphae and caudal fin also had cotton wool like margin. The fungi isolated from the infected areas on the fish were cultured on different media, Malt extract agar (MEA), Sabouraud dextrose agar (SDA) and Potato dextrose agar (PDA). The fungus was allowed to grow for 5-7 days at 28-30˚C. White, grey, black, brown, green and orange colors of colonies were observed. The slides were prepared and stained with 0.05% Trypanblue in lactophenol. The fungal infection in C. auratus, X. maculatus, and P. reticulatawere (80%), (80%) and (70%),respectively. Five genera of fungi were identified. Species of Aspergillus, Rhizopus, Mucor, Penicillium and Alternaria were isolated from C. auratus. Species of Aspergillus, Rhizopus, Mucor and Alternaria were isolated from X. maculatus. Species of Aspergillus, Mucor and Rhizopus were isolated from P. reticulata. Incidence of Aspergillus spp. was (47%), Rhizopus spp. (23.3%), Mucor spp. (10.3%), Penicillium spp. (8%) and Alternaria sp. (1.3%). Incidence of Aspergillus spp. was highest in the infected fish sample. Posterior part of the fishes had significantly higher(x²= 0.4, P=0.02) infection as compared to anterior part of the fishes. This study showed that fungi isolated from different freshwater ornamental fishes are considered as normal mycoflora but they can cause infection.
2010
This study was aimed at isolating and identifying the fungi associated with stockfish contamination in Jos Metropolis. A total of 100 stockfish samples were randomly purchased from four markets namely, Terminus, Kwararafa, Katako and Gada biu in Jos town, Plateau State, Nigeria. The stockfish samples were assayed for fungal contamination and moisture content using standard procedures. All the stockfish samples were contaminated with fungi. Seven different fungi were found to be associated with the stockfish samples sold in the four different markets. The associated fungi were Mucor Spp, Asergillus flavus, Trichophyton verrucosum, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus fumigatus, Penicillin Spp and Rhizopus Spp. It was observed that Mucor Spp had the highest rate of occurrence among the isolated fungi. The moisture content was between 6 -27%. Results from the study are useful in developing and establishing public health standards as consumption of these fungi exposes the consumers to the probable toxic metabolites produced by the fungi.
Fish has become an increasingly important source of protein and other elements necessary for the maintenance of human healthy. A total of 60 samples includes; (20 samples of each of Tilapia fish samples, water samples from water surrounding the collected fish and fish serum), were collected from ponds in El-Wadi-El-Gadid and El-Fayome governorates. Seven genera of molds were recovered from fish samples and four genera from water. Whereas, the Aspergillus spp. was recovered from fish and water samples at the rate of (90% and 40%) at the top of all isolated molds. While, the most identified Aspergillus spp. from fish and water were A. flavus (40% and 10%) and A. niger (20% and 15%) and A. ochraceus (20% and 5%). While, two genera of yeasts were recovered from fish samples and also from water namely, Candida spp. (70 % and 5%) and Rhodotorula spp. (70 % and 10%). The incidence rate of aflatoxin in fish was (25%), while, the maximum levels of aflatoxins was (24 ppb) with the mean levels of (13±2.0 ppb). Whereas, no any levels of AFT s were detected in water samples collected from surrounding water. On the other hand, the bacteria isolated from fish and water samples were identified as Pseudomonas spp. (22.5% and 25%), E. coli (15% and 35%), Proteus spp. (14.2% and 0%), then Klebsiella spp. (11.7% and 25%) and Citrobacter spp. (10% and 15%), respectively , while Salmonella spp. recovered at relatively lower incidence (1.6 and 0%). All species of isolated bacteria were identified biochemically. However, the biochemical examination of water samples indicated that it exhibited extremely high concentrations of iron and ammonia and negatively affected the quality of pond water which caused fish poisoning. The significant increase in AST, ALT, AlP and LDH levels in polluted fish indicates hepatic damage may be due to mycotoxin accumulation which in turn releases these enzymes into the bloodstream. Therefore, all hygienic measures must be performed during catching in clean water, handling, and processing, manufacturing, storage, transportation, marketing of fish to guard the fitness and its hygienic status for consumers.
Fish is a vertebrate animal, living in fresh and salt water. It is one of the main sources of animal protein foods available for human consumption. Fish is an important dietary component of people-. all around the world and represents a relatively cheap and accessible source of high quality protein for poorer households (Ikutegbe & Sikoki, 2014). In West Africa, fish has been reported to provide 40-70% of the protein intake of the population. Depending on consumer preference, there are several forms in which fish can be consumed; fresh, dried, frozen, fermented, brained, etc. In a study by Mafimisebi (2012), it was discovered that majority of the Nigerian people reported a preference for fresh fish; however limitations such as the low keeping quality of the fish after harvest and the distance between fishing grounds and marketing outlets make this very difficult. This results in' a higher reported consumption of smoke-dried fish, which has a longer shelf-life (Mafimisebi, 2012). In Nigeria, fish has an edge over meat because it is cheaper and relatively more abundant and constitutes about 40% of the animal protein intake. Because fish is highly perishable, a considerable effort has been directed to extend its shelf-like using preservation and processing techniques, such as refrigerating, freezing, canning, smoking, salting and drying (Nwachukwu & Madubuka, 2013). Beside this, some of these techniques can also be used to enhance the value of fish, such as smoked fish.
Peter C.
Microbiological Communication
Detection and Evolutionary Genetical Identification of Some Fungal Spoilage Fish Species from the Red Sea
Afra Mohammed Baghdadi 1, Nagwa T. Elsharawy 1,4, Wafa, A. Baabdullah 1 Ayman Sabry 3,5, Ali Alkaladi 3,4 and Salah E. M. Abo-Aba 2
1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
2 Biological Science Department, Faculty of Sciences, King Abdul-Aziz University, Saudi Arabia.
3 Biology Department, College of Science Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia.
4 Food Hygiene Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, New Valley University, Egypt.
5 Cell Biology Dept., National Research Center, Dokki, Giza Egypt.
ABSTRACT
The high nutritional value of fish makes it highly perishable because it provides favorable medium for the growth of micro-organisms after catching. In addition, they can also act as carriers of several microbial and other health hazards. Many mould growth on foods stored at low temperature is common and recurring problem. Certain molds are known to be capable of producing mycotoxins at low temperature as low as ( -2 to 10∘ ) C. That encouraging us to perform this study which aimed to survey, isolation and perform different further genetic identification of fungal spoilage species of some marine fish from Saudi Arabia markets. 100 samples from 5 types of fishes; Salmon “Salmoniformes”, Red sea Bream “Pagrus pagrus”, Rabbitfish “Siganus rivulatus”, Spanish mackerel “Scomberomorous commerson”, Red mullet “Mullus surmuletus”, collected from Jeddah fish markets, then prepared aseptically and plated on Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium incubated for 3-7 days/ 28±2∘C and examined daily Macroscopically, microscopically and genetically. The results recorded 4 species of fungi; Aspergillus eucalypticola as one of (Black Aspergilli), Aspergillus oryzae as (white Aspergilli), Penicillium digitatum as (green fungi) and Byssochlamys spectabilis. This is the first report of Penicillium digitatum and Byssochlamys spectabilis in fish. Furthermore, the research identified each fungi gene cluster. More attention in fish rearing facilities, caution should be taken by consumers in preparation and applying perfect cooking in consuming fish and more education and efforts should be developed by fish farmers to avoid fishponds contamination. We recommended to further research should be done on fungal contaminations.
KEY WORDS: ASPERGILLUS EUCALYPTICOLA, ASPERGILLUS ORYZAE, PENICILLIUM DIGITATUM, BYSSOCHLAMYS SPECTABILIS, GENETIC DIVERSITY, NCBI BLAST.
INTRODUCTION
Recently, the awareness about the nutritional and health benefits of fish consumption were developed due to its richness in; good quality protein with essential amino acids such as; lysine, with vitamin A, E, B- complex (B12, B6) and calcium, phosphorus fluorine, iodine which are needed development of strong teeth and the prevention of goiter in man, ω−3 and ω−6 fatty acids that known to support good health while, containing
Article Information:
Received: 15/03/2021 Accepted after revision: 10/06/2021 Published: 30th June 2021 Pp- 761-767
This is an open access article under CC License 4.0 Published by Society for Science ft Nature, Bhopal India. Online at: https://hbrc.in/ Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21786/bbrc/14.2.49
low saturated polyunsaturated fatty acids which are known to reduce the risks of coronary heart diseases. All that increased the dietary and health significance of seafood consumption (Adeyeye, et. al., 2015 and FAO, 2016, Neo 2019).
The coastal countries become capture about 50% of the world harvest and a large proportion of the catch are consumed internally, more than 30% of fish for human consumption comes from aquaculture. In many Asian countries over 50% of the protein intakes comes from fish while in Africa the proportion is 17.50% (Wogu ft Maduakor, 2010, Neo 2019). The high nutritional value of fish makes it highly perishable because it provides
favorable medium for the growth of micro-organisms after catching. In addition, they can also act as carriers of several microbial and other health hazards. The greatest risk to human health is due to the consumption of raw or insufficiently processed fish and fish products. Contamination is a very important aspect as this is the mode that most unwanted microorganisms may be transmitted onto seafood and other food products and may occur at various stages of handling and processing (Al-Ghabshi et al., 2012).
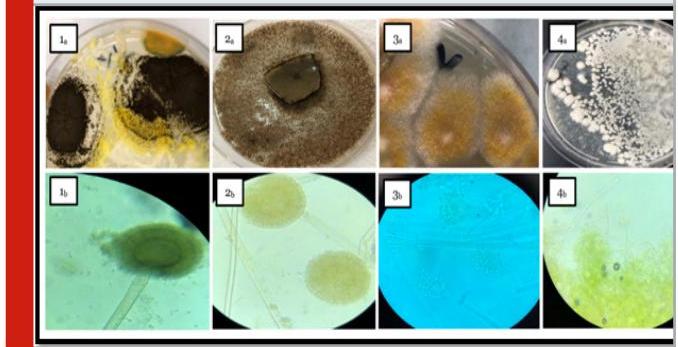
Figure 1: Macroscopic and Microscopic features of fungal genera isolated from tested fish spp. samples as following:
1)Pictures from (1a & 1b) group declared the macroscopic and microscopic view of Aspergillus eucalypticola cultureplates on PDA respectively.
2)Pictures from (2a & 2b) group viewed the macroscopic and microscopic view of Aspergillus oryzae cultureplates on PDA respectively.
3)Pictures group 3 (3a & 3b); showed the macroscopic and microscopic view of Penicillium digita tumplates on PDA respectively.
4)Pictures group 4 (4a & 4b); revealed the macroscopic and microscopic view of Byssochlamys spectabilis that cultured on PDA respectively
Fish is more likely to be spoiled by fungi than by bacteria. The occurrence of fungi and fungus-like organisms in water reservoirs is of great importance for sanitary and epidemiological reasons. Many mould growth on foods stored at low temperature is common and recurring problem. Certain molds are known to be capable of producing mycotoxins at low temperature as low as ( -2 to 10∘C ). Fungi and fungus-like organisms regarded as important etiological factors of mycotic infections are identified in fresh and saltwater. The most commonly encountered fungi in various ecosystems include such pathogenic species as Aspergillus sp, Penicillium sp. In the case of Penicillium species that can grow under refrigeration, spoilage of these products may happen more frequently during the colder months. Fluctuation of temperature in the packaging areas must be avoided since it can result in condensation.
The condensation on surfaces (walls, ceilings, overhead piping, etc.) can be conductive for mould growth. Furthermore, moisture condensation inside the package, due to packaging of the products prior to being
completely cooled, may accelerate mould growth and spoilage (Srinivasan & Saranraj, 2017). Aspergillus eucalypticola is one of (Black Aspergilli) which consider one of the food spoilage fungi in addition to their mycotoxin production in different food items (GilSerna, et. al., 2019). While, Aspergillus oryzae related to the Flavi species of Aspergillus (white Aspergilli) which produce very toxic compounds known as (aftatoxins) and highly spread among food elements. Furthermore, those microbes highly infected to immunocompromised consumers, causing “aspergillosis” (Kjærbølling, et. al., 2020).
Table 1. Results of ncbi BLAST query for the 11 fungi sequences isolated from Examined Fish Samples
| Isolate | Description | Query Coverage % |
Identity % |
|---|---|---|---|
| WA1 | Aspergillus oryzae | 98 | 97 |
| WA2 | Aspergillus eucalypticola | 97 | 97 |
| WA3 | Aspergillus oryzae | 84 | 97 |
| WA4 | Aspergillus eucalypticola | 97 | 97 |
| WA5 | no match was found | ||
| WA6 | Penicillium digitatum | 98 | 89 |
| WA7 | Aspergillus eucalypticola | 89 | 97 |
| WA8 | Aspergillus oryzae | 81 | 98 |
| WA9 | Penicillium digitatum | 89 | 96 |
| WA10 | Byssochlamys spectabilis | 84 | 98 |
| WA11 | Penicillium digitatum | 93 | 97 |
| WA12 | Aspergillus oryzae | 88 | 98 |
On the other hand, Penicillium digitatum is one mesophilic fungus from the most common blue and green “Penicillium” molds although this mold more common on fruits, this is one of the rarely report of this fungi in fish samples. Penicillium digitatum can causing mycosis or allergies for consumers and causing decaying of fish meat (Palou, 2014). Byssochlamys spectabilis able to spoil food and producing heat resistant ascospores and widely spread within food causing spoilage (Houbraken et al., 2008). Fungal spoilage of fish imposes significant annual global revenue for the food and beverage industries. Mould spoilage can also be a food safety issue due to the production of mycotoxins or allergens by these moulds. To avoid or reduce mould spoilage, several hurdles can be used: (1) reducing the water activity of the food, (2) thermal processing, (3) addition of preservatives, (4) reduction of oxygen in; the packaging using vacuum, oxygen scavengers or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), and (5) refrigerated storage. However, the addition of each of these hurdles will be selecting for a different group of spoilage fungi (Rico-Munoz, et al., 2019).
There were a surveillance shortage in fish spoilage fungus species in marine fish generally and marketed fish species in Saudi Arabia especially, In addition to nearly complete absence of studies on the genome sequences for this fungus specially in fish, which have
great importance on the fish quality and consumers’ health. All that encouraging us to perform this study which aimed to survey, isolation and perform different further identification of fungal spoilage species of some marine fish from Saudi Arabia markets.
Figure 2: Distribution of 11 fungyisolates

Table 2. Sequence length & GC content of 11 sequences
| Isolate | Length | GC% |
|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus eucalypticola | 1352 | 47 |
| Aspergillus eucalypticola | 1502 | 48 |
| Aspergillus eucalypticola | 1426 | 48 |
| Aspergillus oryzae | 1262 | 48 |
| Aspergillus oryzae | 1448 | 47 |
| Aspergillus oryzae | 1467 | 48 |
| Aspergillus oryzae | 1439 | 48 |
| Penicillium digitatum | 1361 | 47 |
| Penicillium digitatum | 1471 | 48 |
| Penicillium digitatum | 1411 | 48 |
| Byssochlamys spectabilis | 1306 | 47 |
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Study area, collection of samples: A total of one 100 samples from 5 types of fishes; Salmon “Salmoniformes”, Red sea Bream “Pagrus pagrus”, Rabbitfish “Siganus rivulatus”, Spanish mackerel “Scomberomorous commerson”, Red mullet “Mullus surmuletus”, 20 fish from each fish type. samples of different types of marine fish samples collected from Jeddah fish markets, about 150 g/ fish packaged in polyvinyl chloride films and transferred on ice box container as soon as possible to Faculty of science, University of Jeddah, on one of the postgraduate microbiology laboratories.
Examination of Samples: Collected samples were prepared aseptically according to the technique recommended by (USDA, 2012). 25 grams of the sample were transferred into a sterile plastic bag of the stomacher (Seward laboratory services, 400R Auckland) then 225 ml . of sterile 0.1% peptone water were added. The 2 minutes stomached sample was adequately dispersed to provide the homogenate; which represent the dilution of 1:10 (10-1) and plated in triplicate over plates containing on different culture media Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium incubated for 3-7 days/ 28±2∘C and examined daily. Macroscopic identification made by observing the colony colour and texture then prepared slides with lacto phenol cotton blue to detect fungal structures covered with a cover slip, identified microscopically according to the morphology of colony and spores.
Figure 3: Boxplot of Sequence of 11 isolates

Table 3. Distribution of 11 fungi isolates in 2 clusters
| Species | Cluster | |
|---|---|---|
| A.eucalypticola | 1 | 0 |
| A.eucalypticola (2) | 1 | 0 |
| A.eucalypticola (3) | 1 | 0 |
| A.oryzae | 1 | 0 |
| A.oryzae (2) | 1 | 0 |
| A.oryzae (3) | 1 | 0 |
| A.oryzae (4) | 1 | 0 |
| B.spectabilis | 0 | 1 |
| P.digitatum | 1 | 0 |
| P.digitatum(2) | 1 | 0 |
| P.digitatum(3) | 1 | 0 |
Serological examination: All the 11 sequences were subjected to ncbi BLAST search tool http:// blast.ncbi. nlm.nih.gov to detect non-chance sequence similarity. BLAST search was restricted to Reference genomic sequence and fungi database, where models ( XM/XP ) as well as unclultured/environmental samples were also filtered out, such that more reliable results would be attained. Each individual sequence was solely blastd, where blast hit with the lowest expect- value (which
indicate number of non-chance alignments) was picked. In order to ensure that Blast out puts were governed by expected-value (aka e-value), Blast algorithm parameter was decreased such the expected threshold was set to more stringent value of 1e−6.
Figure 4: Base frequencies of 11 isolates

Table 4. Estimated parameters of DNA polymorphism 11 fungi isolates
| No. | Haplotype | Nucleotide Average number of |
|---|---|---|
| Haplotype | diversity and diversity s | nucleotide differences 11 130.04 |
Alignment of the 11 sequence was carried out using version 2 of Clustalx (Larkin et al., 2007) Exploratory data and phylogenetic analyses were carried out under R Project for Statistical Computing (R Core Team, 2019). Where Exploratory data analysis was done using Seqinr (Charif & Lobry, 2007) R package. Phylogenetic analysis was carried out by ape package (Paradis et al., 2004). Re- construction of the phylogenetic tree was done using Neighbor joint method (Nei, 1987). DnaSP (Librado & Rozas, 2009) software was used to analyze the haplotype diversity (Hd), the average number of nucleotide differences, the average number of nucleotide differences, the nucleotide diversity (σ). The polymorphic site (S), the singleton variable sites (SP), and the parsimony informative sites (PIP) for each gene, and the average number of nucleotide substitutions per site between species (Dsy) (Tajima, 1983).
Statistical Analysis: The statistical program, SPSS version 16 for window, was used for determination of means, standard error and analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the one way (mean at significance level of ( P<0.05 ). Statistical significance was tested at the 5% level of significance in this study.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Phenotyping of the different fungal species in examined
fish samples Figure (1) shows the macroscopic and microscopic features of fungal genera isolated from tested fish spp. samples as following: (1a & 1b) pictures declared the macroscopic and microscopic view of Aspergillus eucalypticola culture plates on PDA respectively which belongs to black Aspergilli with their morphological feature as black colonies which roughen with maturity and black dark conidial heads with dark spores as almost members of Nigri family. While, Pictures group (2a & 2b) viewed Aspergillus oryzae on PDA as; pale grey to black colonies with coarsely wall of conidial heads and short column. Penicillium digitatum declared in (3a & 3b) as; woolly growth, velvety texture colonies. The white color firstly turns to yellowish green with white center or olive gray, microscopically appeared as; branched hyaline, with cup shape phialides and brush-like clusters which known as “penicilli”. Meanwhile morphological feature of Byssochlamys spectabilis in (42,46) as pale yellowbrown, smooth-walled irregularly branched cylindrical conidia.
NCBI Blast Query : Table (1) shows results of ncbi BLAST query for the 36 sequenced isolates. The criteria used for query sequence aimed to narrow down the search space (database), as the smaller the database the more likely to contain sequence of interest. For all the 11 queries zero E-values were attained indicated that all alignments were non-chance alignments. The percentages of query coverage ranged from 81 to 98%, where identity % were also high which ranged from 89 to 97%. The distribution of isolates/species/distribution is presented graphically in Figure (2). For the 11 isolates, the NCBI query resulted in 4 fungi species namely 4 isolates belonged to Aspergillus oryzae, 3 isolates belonged to Aspergillus eucalypticola and 3 isolates belonged to Penicillium digitatum oryzae and only one isolate belonged to Byssochlamys spectabilis.
Exploratory Data Analysis: The base frequencies of the 11 all species showed, no noticeable differences in the frequency of all 11 isolates, neither in GC content Table (2). Sequence length varied greatly among the 11 isolates. Sequence length ranged from 1262 to 1502 bp . The sequence length Byssochlamys spectabilis of species were also varied, for the range of sequence length 1306bp. While, Aspergillus eucalypticola ranged from 1352 to 1502 bp , where the range of sequence length of Aspergillus oryzae ranged from 1262 to 1467 bp . Meanwhile, Penicillium digitatum sequence length ranged from 1361-1471bp Figure (3) declared the boxplot sequence length of the fungi isolates.
Cluster Aphylogenetic Analysisnd: Cluster analysis was carried out as pre-processing step to glean an insight into the data distribution. Results of cluster analysis are shown graphically in Table (3) and figure (4). The resulted dendrogram of comprised 2 large clusters are shown, the first cluster merely includes only one species Byssochlamys spectabilis, where the rest of the 3 species were comprised in the second cluster. One of Aspergillus oryzae was clustered together with the other Aspergillus eucalypticola isolates in the same clade.
Figure (5) shows the evolutionary history of the 11 isolates was inferred based on Neighbor-Joining (NJ) method (Saitou ft Nei, 1987). The optimal tree with the sum of branch length =0.3 is shown. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method (Tamura et al., 2004) and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. This analysis involved 11 nucleotide sequences. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair (pairwise deletion option). There were a total of 1558 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analysis was conducted by ape package (Paradis et al., 2004).
Polymorphism and Genetic Diversity among species: The 11 sequences were also analyzed to characterize the sequence diversity. The results of the analysis are presented table (4) the haplotype diversity was 1±0.04
Figure 5: Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of 11 fungi isolates

0.02
Table 5. Estimated parameters of the polymorphic sites for 11 fungi isolates.
| No. Sites | No. monomorphic Informative sites |
No. Polymorphic sites |
Parsimony informative sites |
Singletone variable sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1564 | 1081 | 142 | 63 | 79 |
Figure 6: cluster analysis of 11 fungi isolates

and nucleotide diversity was only 0.04 where the average number of nucleotides diversity was 45.0 nly one conserved region was found among the 11 isolates in the region between 30 to 1017. Measurements of conservation (C)=0.97, homozygosity =0.99 and P -value <0.001. Conservation © is calculated as the proportion of conserved sites in the alignment region, where homozygosity is measured as 1- heterozygosity.
General information about the polymorphisms on the 11 fungi isolates is shown in table (5) the number of sites was 1564. The number of polymorphic sites was 142, number of parsimony-informative sites (i.e. sites that have a minimum of two nucleotides that are present at least twice) was 63 and the number of singletons was 79. The NJ tree declared in figure (6) where comprised from two large clusters. The P.digitatum species occupied
one cluster on its own, where the rest of the 3 species clustered in the second cluster. This second cluster involved two large clades; the first clade contains A.eucalypticola species along with one of A.oryzae species. The rest the A.oryzae species shared another clade with B.spectabilis. This inferred NJ tree is very similar to the cluster analysis except for that B.spectabilis did not has a separate cluster, this difference might be due to differences in the used algorithms.
Fungal spoilage of fish imposes significant annual global revenue losses due to the production of mycotoxins by moulds. The main fungal groups associated with spoilage are the xerophilic, heat-resistant, preservative-resistant, anaerobic and psychrophilic fungi (Rico-Munoz et al., 2019). Results recorded the percentages of query coverage ranged from 81 to 98%, where identity % were also high which ranged from 89 to 97%. The distribution of isolates/species/distribution is presented graphically for the 11 isolates, the NCBI query resulted in 4 fungi species namely 4 isolates belonged to Aspergillus oryzae, 3 isolates belonged to Aspergillus eucalypticola and 3 isolates belonged to Aspergillus oryzae and only one isolate belonged to Byssochlamys spectabilis. Different results have been reported by Donnenberg, (2005) who assessed the fish (Trachurus trachurus) and reported some spoilage moulds such as Apergillus flavus (33.3%), Penicillium sp. (16.7%) and Neurospora sp. (16.7%).
Aspergillus eucalypticola is one of (Black Aspergilli) which consider one of the food spoilage fungi in addition to their mycotoxin production in different food items (Gil-Serna, et. al., 2019). While, Aspergillus oryzae related
to the Flavi species of Aspergillus (white Aspergilli) which produce very toxic compounds known as (aflatoxins) and highly spread among food elements. Furthermore, those microbes highly infected to immunocompromised consumers, causing “aspergillosis” (Kjærbølling, et. al., 2020). from the other hand, Penicillium digitatum is one mesophilic fungus from the most common blue and green “Penicillium” molds although this mold more common on fruits, this is one of the rarely report of this fungi in fish samples. Penicillium digitatum can causing mycosis or allergies for consumers and causing decaying of fish meat (Palou, 2014). Byssochlamys spectabilis able to spoil food and producing heat resistant ascospores and widely spread within food causing spoilage (Houbraken. et. al., 2008).
According to Nishihara et al., (2008) and Samaha, et. al., (2015) fungal contamination of fishes prone in the field during; harvest, transport, marking and with the consumer. The most common moulds isolated were; Aspergillus species consist of Aspergillus flavus, A. niger, A. sydowii, A. wentii, and A. penicilloides. Several Penicillium spp. were also isolated, Iqbal & Saleemi, (2013) isolated four types of fungi from the fish; orange (37.83%), black (35.13%), grey (24.32%) and white ( 2.70% ) appeared on agar plates.
Three fungal genera; Aspergillus spp. (78.5%), Blastomyces sp. (7.5%), Penicillium sp. (3.5%) and unidentified fungal hyphae ( 10.5% ) were isolated from the fish. Recently Akwuobu, et. al., (2019) have reported different types of fungal agents associated with the contamination of fish sold in open markets in Makurdi, Benue State. A total of 100 randomly selected fish samples from the 3 major fish markets in the study area were used for the study. Fungi were detected in 74 of the 100 fish samples from the 3 markets surveyed with isolation rates ranging from 67.6% to 84.8%. A total of 77 fungal isolates were recorded from the 74 positive samples the predominant isolated fungi were; Aspergillus spp. (28.6%), Penicillium spp. (18.2%). The base frequencies of the 11 all species showed, no noticeable differences in the frequency of all 11 isolates, neither in GC content Table (2). Sequence length varied greatly among the 11 isolates. Sequence length ranged from 1262 to 1502 bp . The sequence length Byssochlamys spectabilis of species were also varied, for the range of sequence length 1306bp. While, Aspergillus eucalypticola ranged from 1352 to 1502 bp , where the range of sequence length of Aspergillus oryzae ranged from 1262 to 1467 bp . Meanwhile, Penicillium digitatum sequence length ranged from 1361-1471bp Figure (3) declared the boxplot sequence length of the fungi isolates.
Recntly, different results have been reported by Kjærbølling, et. al., (2020), who sequenced about 19 genomes for Aspergillus spp. which were isolated from spoiled food. However, the genome covered 99.78% and concluded that the size of Aspergillus spp. genome was an important aspect. They added that the average genome of A. oryzae was about ( 37.96Mbp). The branching of the tree about ( 100 straps in each branch) was present.
According to Houbraken, et. al., (2008) Byssochlamys spectabilis is heat resistance mould, producing heatresistant ascospores in raw food and can tolerate cooking temperatures and producing mycotoxins. There is a need to develop new antimicrobials to ensure food safety and extend shelf life. The use of antimicrobial agents directly added to foods or through antimicrobial packaging is one effective approach. In recent years, the use of inorganic antimicrobial agents in nonfood applications has attracted interest for the control of microbes (Wilcznski, 2000 and Tilman et al., 2011).
CONCLUSION
The presented study provides 11 new genomes, which have been added to the fungal genetic diversity. We identified the isolated fungi phenotypes macroscopically, microscopically and genetically. This study also was concerned with the isolation and proper identification of fungus in fish from Saudi Arabian markets. The results recorded 4 species of fungi; Aspergillus eucalypticola as one of (Black Aspergilli), Aspergillus oryzae as (white Aspergilli), Penicillium digitatum as (green fungi) and Byssochlamys spectabilis.
This is the first report of Penicillium digitatum which commonly found in citric fruit. The result also has the first report of Byssochlamys spectabilis as heterothallic mould species which causing food spoilage in fish. The four sequenced species compared with the already sequenced Aspergillus species and determined the genetic diversity. The phylogram constructed for whole-genome basis, showing the taxonomy tree of each isolated fungus genus. Furthermore, the research identified each fungi gene cluster. More attention in fish rearing facilities, caution should be taken by consumers in preparation and applying perfect cooking in consuming fish and more education and efforts should be developed by fish farmers to avoid fishponds contamination. We recommended to further research should be done on fungal contaminations.
REFERENCES
Akwuobu, C. A., Antiev, W. S. & Ofukwu, R. A.-P. (2019). Fungal Contaminants of Smoke-Dried Fish Sold in Open Markets in Makurdi, Benue State, North-Central Nigeria. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 10, 290-297.
Adeyeye, S., Oyewole, O., Obadina, A. & Omemu, A. (2015). Evaluation of microbial safety and quality of traditional smoked Bonga Shad (Ethmolosa frimbriata) Fish from Lagos State, Nigeria. Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 16, 286-294.
Al Ghabshi, A.; Al-khadhuri, H.; Al-Ahoudi, N.; AlGharabi, S.; Al-Khatri, A.; Al-Mazrooei and Sudheesh, P. (2012). Effect of the Freshness of Starting Material on the Final Product Quality of Dried Salted Shark. Advance journal of Food and technology. 4(2): 60-63. Charif, D., & Lobry, R. J. (2007). SeqinR 1.0-2: a contributed package to the R project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval
and analysis. Pages 207-232 of: Bastolla, U., Porto, M., Roman, H.E., &t Vendruscolo, M. (eds), Structural approaches to sequence evolution: Molecules, networks, populations. Biological and Medical Physics, Biomedical Engineering. New York: Springer Verlag. ISBN : 978-3-540-35305-8.
Donnenberg MS. Mandel GI, Bennet JE, John R, Mandel D (2005). Enterobacteriaceae, principles and practice of infectious diseases, 6th edition, pages 267 - 286.
FAO (2016). The State of World Fisheries Aquaculture Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All. FAO Rome.
Gil-Serna, J.; García-Díaz, M.; Vázquez, C.; GonzálezJaén, M. and Patiño, B. (2019). Significance of Aspergillus niger aggregate species as contaminants of food products in Spain regarding their occurrence and their ability to produce mycotoxins. Food Microbiology 82: 240-248.
Houbraken, J., Varga, J., Rico-Munoz, E., Johnson, S. &t Samson, R. A. (2008). Sexual reproduction as the cause of heat resistance in the food spoilage fungus Byssochlamys spectabilis (anamorph Paecilomyces variotii). Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 74, 1613-1619.
Houbraken, J.; Varga, J.; Rico-Munzo, E.; Johnson, Sh. and Samson, R. (2008). Sexual Reproduction as the Cause of Heat Resistance in the Food Spoilage Fungus Byssochlamys spectabilis (Anamorph Paecilomyces variotii). Applied And Environmental Microbiology, 74(5): 1613-1619.
Iqbal Z. and Saleemi, S. (2013). Isolation of Pathogenic Fungi from a Freshwater Commercial Fish, Catla catla (Hamliton) Sci. Int (Lahore), 25(4), 851-855.
Kjærbølling, I.; Vesth, T.; Frisvad, J.; Nybo. (2020). A comparative genomics study of 23 Aspergillus species from section Flavi. Nature Communications. 11:1106. Larkin, M.A., Blackshields,G.,Higgins D.G. (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23: 2947-2948.
Librado, P., &t Rozas, J. (2009). DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25: 25, 1451-1452.
Nei, M. (1987). Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. New York: Columbia Univ.
Neo P (2019) Protein powerhouse: Asia the key protein market by 2025 with China and India leading the charge
Nishihara, M., M. Kamata, T. Koyama and K.Yazawa. (2008). New phospholipase A1-producingbacteria from
a Marine Fish. Marine Biotechnology, 10: 382-387
Palou, L. (2014). Penicillium digitatum, Penicillium italicum (Green Mold, Blue Mold). Postharvest Decay. 45-102.
Paradis, E., Claude, J., &t Strimmer, J. (2004). APE: analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics, 20, 289-290.
R Core Team. (2019). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Rico-Munoz, E., Samson, R. A. &t Houbraken, J. (2019). Mould spoilage of foods and beverages: Using the right methodology. Food microbiology, 81, 51-62.
Saitou, N., &t Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 4, 406-425.
Samaha, I. A., Amer, A. A., Abd-Elshahid, Y. S., &t Elbialy, S. M. (2015). Mycological Evaluation of Imported Frozen Fish. Alexandria Journal for Veterinary Sciences, 45.
SPSS Inc. (2011). IBM SPSS Software for Windows, 20.0, Chicago
Srinivasan, T. &t Saranraj, P. (2017). Isolation and identification of spoilage causing microorganisms in an Indian mackerel fish (Rastrelliger kanagurta). International Advanced Research of Biological Science. 4(7): 1-7.
Tajlma, F. (1983). Evolutionary Relationship of DNA Sequences In Finite Populations Fumio. the Genetics Society of America. 437-460.
Tamura, K., M., Nei, &t Kumar, S. (2004). Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (USA), 101, 11030-11035.
Tilman, D.; Balzer, Ch.; Hill, J. and Befort, B. (2011). Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. PNAS. 108 (50): 20260-20264.
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), (2012). Food Safety and Inspection Service. Introduction to the Microbiology of Food Processing, Small Plant News Guidebook Series. 1-60.
Wilczynski, M. (2000). Anti-microbial porcelain enamels. 62nd Porcelain Enamel Institute Technical Forum. Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings.
Wogu, M. &t Maduakor, C. (2010). Evaluation of microbial spoilage of some aquacultured fresh fish in Benin City Nigeria. Ethiopian Journal of Environmental Studies and Management, 3.
References (22)
- Akwuobu, C. A., Antiev, W. S. & ofukwu, R. A.-P. (2019). Fungal Contaminants of Smoke-Dried Fish Sold in open Markets in Makurdi, Benue State, north-Central nigeria. Food and nutrition Sciences, 10, 290-297.
- Adeyeye, S., oyewole, o., obadina, A. & omemu, A. (2015). evaluation of microbial safety and quality of traditional smoked Bonga Shad (Ethmolosa frimbriata) Fish from lagos State, nigeria. Pacific Journal of Science and Technology, 16, 286-294.
- Al ghabshi, A.; Al-khadhuri, h.; Al-Aboudi, n.; Al- gharabi, S.; Al-Khatri, A.; Al-Mazrooei and Sudheesh, P. (2012). effect of the Freshness of Starting Material on the Final Product Quality of Dried Salted Shark. Advance journal of Food and technology. 4(2): 60-63.
- Charif, D., & lobry, R. J. (2007). SeqinR 1.0-2: a contributed package to the R project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval and analysis. Pages 207-232 of: Bastolla, u., Porto, M., Roman, h.e., & vendruscolo, M. (eds), Structural approaches to sequence evolution: Molecules, networks, populations. Biological and Medical Physics, Biomedical engineering. new york: Springer verlag. ISBn : 978-3-540-35305-8.
- Donnenberg MS. Mandel gI, Bennet Je, John R, Mandel D (2005). enterobacteriaceae, principles and practice of infectious diseases, 6th edition, pages 267 -286.
- FAo (2016). The State of World Fisheries Aquaculture Contributing to Food Security and nutrition for All. FAo Rome. gil-Serna, J.; garcía-Díaz, M.; vázquez, C.; gonzález- Jaén, M. and Patiño, B. (2019). Significance of Aspergillus niger aggregate species as contaminants of food products in Spain regarding their occurrence and their ability to produce mycotoxins. Food Microbiology 82: 240-248.
- houbraken, J., varga, J., Rico-Munoz, e., Johnson, S. & Samson, R. A. (2008). Sexual reproduction as the cause of heat resistance in the food spoilage fungus Byssochlamys spectabilis (anamorph Paecilomyces variotii). Appl. environ. Microbiol., 74, 1613-1619. houbraken, J.; varga, J.; Rico-Munzo, e.; Johnson, Sh. and Samson, R. (2008). Sexual Reproduction as the Cause of heat Resistance in the Food Spoilage Fungus Byssochlamys spectabilis (Anamorph Paecilomyces variotii). Applied And environmental Microbiology, 74(5): 1613-1619.
- Iqbal z. and Saleemi, S. (2013). Isolation of Pathogenic Fungi from a Freshwater Commercial Fish, Catla catla (hamliton) Sci. Int (lahore), 25(4), 851-855.
- Kjaerbølling, I.; vesth, T.; Frisvad, J.; nybo. (2020). A comparative genomics study of 23 Aspergillus species from section Flavi. nature Communications. 11:1106. larkin, M.A., Blackshields,g.,higgins D.g. (2007). Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics, 23: 2947-2948.
- librado, P., & Rozas, J. (2009). DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DnA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25: 25, 1451-1452.
- nei, M. (1987). Molecular evolutionary genetics. new york: Columbia univ. neo P (2019) Protein powerhouse: Asia the key protein market by 2025 with China and India leading the charge nishihara, M., M. Kamata, T. Koyama and K.yazawa. (2008). new phospholipase A1-producingbacteria from a Marine Fish. Marine Biotechnology, 10: 382-387
- Palou, l. (2014). Penicillium digitatum, Penicillium italicum (green Mold, Blue Mold). Postharvest Decay. 45-102.
- Paradis, e., Claude, J., & Strimmer, J. (2004). APe: analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics, 20, 289-290.
- R Core Team. (2019). R: A language and environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, vienna, Austria.
- Rico-Munoz, e., Samson, R. A. & houbraken, J. (2019). Mould spoilage of foods and beverages: using the right methodology. Food microbiology, 81, 51-62.
- Saitou, n., & nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and evolution, 4, 406-425.
- Samaha, I. A., Amer, A. A., Abd-elshahid, y. S., & el- bialy, S. M. (2015). Mycological evaluation of Imported Frozen Fish. Alexandria Journal for veterinary Sciences, 45. SPSS Inc. (2011). IBM SPSS Software for Windows, 20.0, Chicago
- Srinivasan, T. & Saranraj, P. (2017). Isolation and identification of spoilage causing microorganisms in an Indian mackerel fish (Rastrelliger kanagurta). International Advanced Research of Biological Science. 4(7): 1-7.
- Tajlma, F. (1983). evolutionary Relationship of DnA Sequences In Finite Populations Fumio. the genetics Society of America. 437-460.
- Tamura, K., M., nei, & Kumar, S. (2004). Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proceedings of the national Academy of Sciences (uSA), 101, 11030-11035.
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, Ch.; hill, J. and Befort, B. (2011). global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. PnAS. 108 (50): 20260-20264. united States Department of Agriculture (uSDA), (2012). Food Safety and Inspection Service. Introduction to the Microbiology of Food Processing, Small Plant news guidebook Series. 1-60.
- Wilczynski, M. (2000). Anti-microbial porcelain enamels. 62nd Porcelain enamel Institute Technical Forum. Ceramic engineering and Science Proceedings. Wogu, M. & Maduakor, C. (2010). evaluation of microbial spoilage of some aquacultured fresh fish in Benin City nigeria. ethiopian Journal of environmental Studies and Management, 3.
 Dr N
Dr N