Fire Fighting Robot Using GSM
Abstract
AI
AI
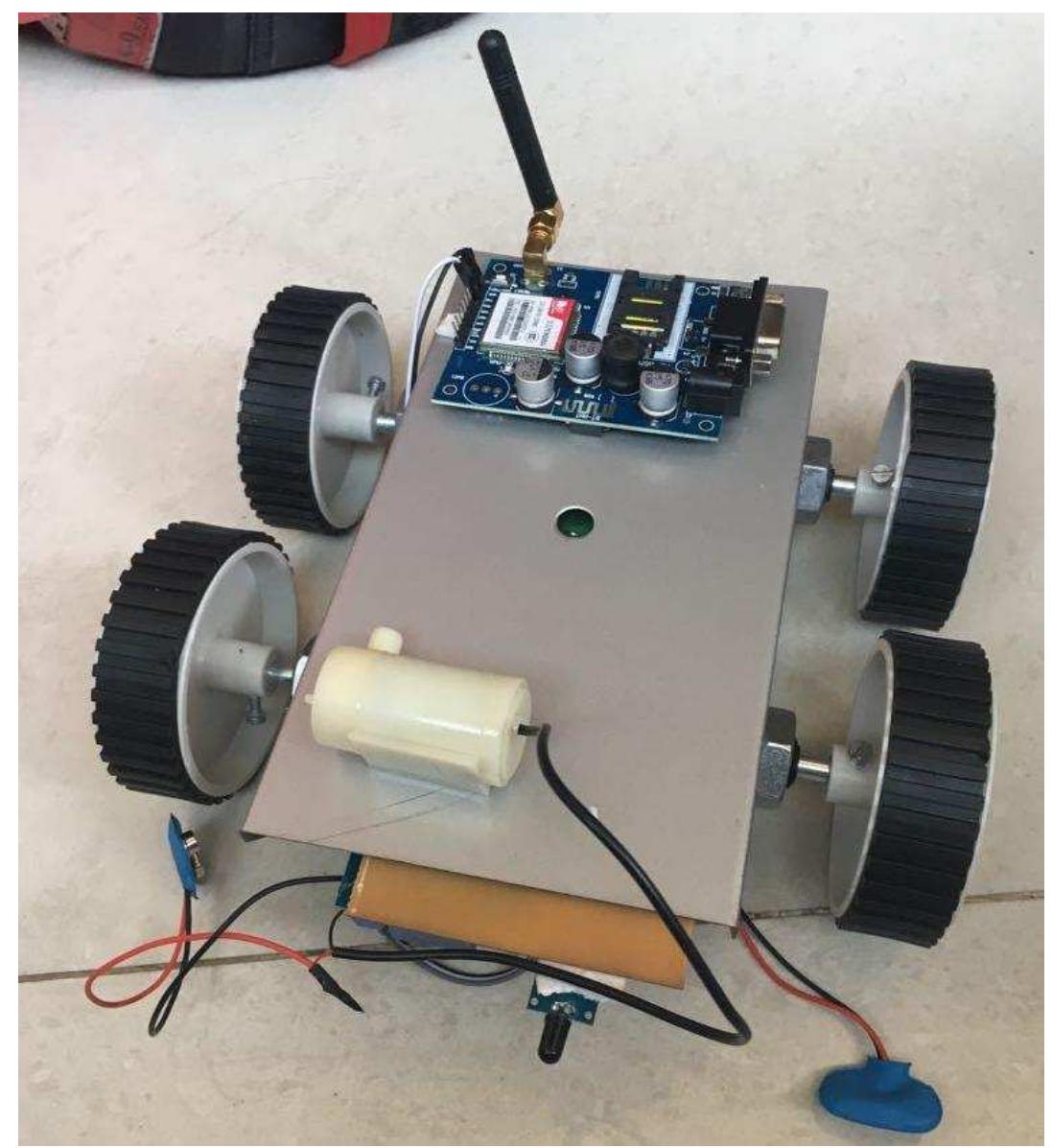
This paper presents the development of a fire fighting robot controlled via GSM technology. The robot is equipped with a water tank and pump, allowing for remote operation through a smartphone or tablet interface. It utilizes an ARDUINO microcontroller for movement and water discharge operations, offering a robust solution to enhance fire safety and reduce the risks associated with traditional fire fighting methods.
FAQs
AI
What are the main advantages of using GSM for remote fire fighting robots?
The research shows that utilizing GSM for control allows extensive range and quick command execution, facilitating real-time intervention in emergencies. This system significantly enhances the operational efficiency of fire-fighting robots compared to traditional wired controls.
How does the robot detect and extinguish flames effectively?
The robot employs a combination of ultrasonic sensors and flame detection sensors to identify and target flames accurately. Once identified, the Arduino-controlled water pump activates to extinguish flames from a safe distance.
What components are essential for controlling the robot's movement?
The system integrates an Arduino microcontroller with a motor driver IC (L293D) to manage the robot's two driving motors. This setup ensures precise directional control and speed regulation during operation.
How does the flame sensor function in the robot's design?
The flame sensor operates within a detection range of 760nm to 1100nm, identifying flames by their signature wavelengths. Its output is processed by the microcontroller to activate the extinguishing mechanism upon detection.
What safety features are included in the robot's design?
The robot is designed to operate from a remote location, reducing the risk of human injury during fire emergencies. Additionally, it can send SMS notifications regarding fire detection, enhancing situational awareness for operators.
References (20)
- W. Budiharto, Membuat Robot Cerdas, Jakarta: Gramedia, 2006.
- Ratnesh Malik, "Fire Fighting Robot: An Approach", Indian Streams Research Journal Vol.2, Issue.II/March; 12pp.1-4
- Kristi Kosasih, E. Merry Sartika, M. Jimmy Hasugian, danMuliady, "The Intelligent Fire Fighting Tank Robot" , Electrical Engineering Journal Vol. 1, No. 1, October 2010
- H. P. Singh, Akanshu Mahajan, N. Sukavanam, VeenaBudhraja ,"Control Of An Autonomous Industrial Fire Fighting Mobile Robot", DU Journal of Undergraduate Research and Innovation
- Swati A. Deshmukh, Karishma A. Matte and Rashmi A. Pandhare, "Wireless Fire Fighting Robot", International Journal for Research in Emerging Science and Technology
- Lakshay Arora, Prof.AmolJoglekar, "Cell Phone Controlled Robot with Fire Detection Sensors", (IJCSIT) International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies, Vol. 6 (3) , 2015, 2954- 2958 Websites:
- "MECHATRONICS" ALPHA I (FIRE FIGHTING ROBOT)" -IJESAT 2012.
- Trinity College, Fire-Fighting Home Robot Contest, http://www.trincoll.edu/~robo
- E. Krasnov and D. Bagaev, "Conceptual analysis of firefighting robots' control systems," 2012 IV International Conference "Problems of Cybernetics and Informatics" (PCI), Baku, 2012, pp. 1-3.
- K. L. Su, "Automatic Fire Detection System Using Adaptive Fusion Algorithm for Fire Fighting Robot," 2006 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Taipei, 2006, pp. 966-971.
- Sharma, Aman. "A FULLY AUTOMATED FIRE FIGHTING ROBOT." Irnetexplore. Dronacharya College of Engineering. Web. 28 Oct 2013.
- Xu, James. "Industrial Systems Design and Integration." Fire Fighting Robot. (2009): n. page. Web. 10 Nov. 2013, 1989.
- Gupta, Rishi, and Sandeep Saini. "Fire Righting Robot." gobookee. N.p.. Web. 28 Oct 2013.
- K-Team Mobile Robotics. n.d. K-Junior V2 Super Educational Pack. [online] Available at: http://www.k-team.com/mobile-robotics- products/k-junior/edu-pack [Accessed: Oct 2013]. Serial.println("AT+CMGF=1"); delay(1000);
- Serial.print("AT+CMGS=\"");
- Serial.print(pn);
- Serial.println("\""); delay(1000);
- Serial.write(0x1A);
- Serial.write(0x0D);
- Serial.write(0x0A);
 imran ansari
imran ansari