Behavioral contingency analysis
2008, Behavioural Processes
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BEPROC.2008.01.013…
22 pages
1 file
Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution and sharing with colleagues. Other uses, including reproduction and distribution, or selling or licensing copies, or posting to personal, institutional or third party websites are prohibited. In most cases authors are permitted to post their version of the article (e.g. in Word or Tex form) to their personal website or institutional repository. Authors requiring further information regarding Elsevier's archiving and manuscript policies are encouraged to visit: http://www.elsevier.com/copyright







Related papers
Revista latinoamericana de psicología
Filosofiya osvity. Philosophy of Education
A historical review was conducted on Fred Fiedler’s Contingency Model to determine how this model has been used over the past 30 years since 1980. Fred Fiedler’s Contingency Model was created in 1967 to move the field of organizational research from analyzing traits and personal characteristics of leaders to assessing leadership styles and behaviors. The premise of the model is that the individual’s leadership style is the result of their life experiences, making it a fixed characteristic that is extremely difficult to change. Over the years, this model has been used with the aim of improving its validity and reliability in a multitude of national and international organizational settings. The article begins with a brief review of Fiedler’s background, progresses with a detailed description of Fiedler’s Contingency Model, and chronicles Fiedler’s Contingency Model’s use in the past and the present from 1980 to 2022. As a result, two major implications were found. The first implicati...
1980
issue of Behavioral Science, which was devoted entirely to research done under the auspices of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis. This issue is the second one of this sort to appear, since the May 1979 issue of this journal was also devoted to IIASA work. We are greatly indebted to James Grier Miller , the Editor of Behavioral Science, for suggesting and organizing these special issues and devoting space to them, to Larry W. Dybala, its Managing Editor, for helping with the arrangements for bringing them to completion, and to the General Systems Science Foundation, the copyright holder, for permission to reproduce this special issue as an IIASA Research Report .
American Journal of Research in Business and Social Sciences , 2023
This study is premised on contingency theory. It looks at it from a holistic point of- a critical study. Proponents of this theory, chief amongst them is Fred Fielder, are of the view that, there exist a plethora of ways to getting things done. There is no one best way. This theory is also referred to as the situational theory. It is of the argument that, whatever approach cum style a leader or manager adopts, is a function of several factors viz a viz size of the organization, leader-follower relationship, influence of the leader and the overall working condition of the organization. In a very large organization, management would tilt towards the Max Weber bureaucracy that is highly characterized by specialization, formal authority, hierarchy, and what have you. Whilst a relatively small organization would definitely fail, if it tries to follow the precept of the former. Managers cum leaders of the smaller organization would have to be less formal and establish a close rapport with the staffs and all that.
2017
The effectiveness and sustainability of behavioral insights, which characterize contemporary evidence-based public policymaking and social regulations, are dependent on the establishment of a functional relationship between a desired behavior and its beneficial consequences. We address two fundamental concepts in the science of behavior analysis, namely contingencies of reinforcement and schedules of reinforcement, in order to contribute to the multidisciplinary discussion on tackling large-scale behavior change. As for many other disciplines, different conceptual frameworks may define the same phenomena. The behavioral perspective unites several disciplines. The focus of the paper is to contribute to the growing field of behavioral solutions by focusing on the consequences of behavior. Behavioral economics has contributed largely by offering the design of choice architecture: deliberately manipulating the antecedents for appropriate behaviors. This is accomplished by changing the d...
This chapter reports data from a longitudinal exploratory case study of two strategic alliances with the aim of achieving a better understanding of interpartner dynamics. Combining insights from the response strategy perspective and interpersonal theory, we propose that response strategies are organized along the circumference of a circle in a two-dimensional space. In such a circumplex structure the complimentarity principle, explaining how partners respond to each other, is composed of two rules: the rule of reciprocity and the rule of correspondence. The objective of this chapter is to explain when and why alliance partners follow or deviate from these rules. Evidence from the two strategic alliances indicates that the response behaviors derived from interpersonal theory can be identified at the inter-organizational level in a strategic alliance. Moreover, partners often use a complementary behavior. The findings, however, also provide insights into three mechanisms that trigger partners to use non-complementary behavior. This study provides a fine-grained explanation for alliance partner interaction and offers a tentative first step in building an integrative model of interpartner dynamics in strategic alliances.
We pre sent the concep t o f organiz ational misfit as a complement to multi-co ntingenc y theory fit concepts for organizational performance. Firms with misfits have o ppo rtunit y losses t hat firms without misfits do not suffer. Using data from 232 small and medium sized Danish firms, we confirm the hypotheses that firms with either or both situat ional and contingency misfits have lower performance increases than firms without misfits. Furthe r, a firm may not obt ain increased performance from the eliminat ion o f misfits piecemeal, but will obtain significant nonlinear p ositive increases when misfits are fixed within a holistic or systems approach.
Journal of Business & Economics Research ( …, 2011
Journal of Business & Economics Research (JBER). Font Size. Journal Help. Subscription Login to verify subscription. Journal Content Search. All. Browse: ...
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 1991
Neither Flexser (1991) nor Gardiner (1991) convincingly refutes demonstration and argument regarding limitations of contingency analyses in successive testing experiments. By describing supposedly analogous thought experiments and conclusions, Flexser tries to show indirectly that the argument leads to absurdity. The relation between the manipulation and conclusions in these thought experiments, however, fails to parallel that of Hintzman and Hartry in a crucial respect. Gardiner argues that contingency analyses produce replicable findings. However, the repeated failure to find dependence when one or both tasks involves implicit memory may reflect the small amount of priming relative to other sources of variance. Moreover, the supposed lawfulness of recognition-failure results can be understood in terms of variance sources that either contribute toward the contingency or suppress it, and in terms of inherent mathematical constraints.
Establishing change readiness may be one of the key factors in determining whether a given change intervention will ultimately be successful or not. Unfortunately, there is a good deal of conceptual confusion in the literature surrounding the term, illustrated by the sheer number of terms that are used to capture the construct (e.g., openness, receptivity, commitment, attitudes toward change) and the varying theoretical foundations that have been proposed. To arrive at a more conceptually sound notion of change readiness, the current article advocates moving beyond statebased conceptualizations toward a process model of change readiness. This process model has the advantage of serving as a framework against which to synthesize extant theorizing on change readiness, incorporating the influences of context and environment over time on an individual's cognitive and affective evaluations and subsequent positive and proactive responses to change, and capturing readiness as a recursive and multidimensional process.

This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution and sharing with colleagues.
Other uses, including reproduction and distribution, or selling or licensing copies, or posting to personal, institutional or third party websites are prohibited.
In most cases authors are permitted to post their version of the article (e.g. in Word or Tex form) to their personal website or institutional repository. Authors requiring further information regarding Elsevier’s archiving and manuscript policies are encouraged to visit:
http://www.elsevier.com/copyright
Behavioral contingency analysis
Francis Mechner*
The Mechner Foundation, 200 Central Park South, 18E, New York, NY 10019, United States
Received 4 September 2007; accepted 17 January 2008
Abstract
This paper presents a formal symbolic language, with its own specialized vocabulary and grammar, for codifying any behavioral contingency, including the complex multiparty contingencies encountered in law, economics, business, public affairs, sociology, education, and psychotherapy. This language specifies the “if, then” and temporal relationships between acts and their consequences for the parties involved. It provides for the notation of the probabilities, magnitudes, positive or negative valences, or time delays of the consequences for the parties, and for the parties that would perceive, misperceive, not perceive, predict, mispredict, or not predict events. The language’s fractal-like hierarchical and recursive grammar provides for the flexible combination and permutation of the modifiers of the language’s four nouns: acts, consequences, time intervals, and agents of acts; and its four verbs: consequate, prevent, perceive, and predict-thereby giving the language the ability to describe and codify various nuances of such complex contingencies as fraud, betting, blackmail, various types of games, theft, crime and punishment, contracts, family dynamics, racing, competition, mutual deterrence, feuding, bargaining, deception, borrowing, insurance, elections, global warming, tipping for service, vigilance, sexual overtures, decision making, and mistaken identity. Applications to the management of practical situations and techniques for doing so, as well as applications in current behavior analysis research and neuroscience, are discussed.
© 2008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Keywords: Formal contingency language; Behavioral economics; Competition and cooperation; Cognitive-behavior therapy; Neuroscience; Behavior notation and codification; Social interaction codification; Operations research; Simulation
1. Behavioral contingencies
1.1. What are they?
Behavioral contingencies 1 are the ubiquitous “if, then” situations that influence what people do and do not do. The “if” part specifies some behavior; the “then” part some consequence for the involved party(ies): if you drop a glass (the behavior), it may break (the consequence), and a price label on a product in a store states that if you pay that price, you get the product. The price label contingency might have effects on customer behavior, sales of that product, and competitive pricing by other stores. Further contingencies may be implicit, e.g., if you wait too long, the product may no longer be available.
[1]Behavioral contingencies exist independently of any behavior or dynamics that may occur as a result of their existence. The dropped glass would break if dropped even if no one ever dropped it or picked it up, and the price label contingency is in effect even if no one ever sees the price label or buys anything. In general, however, a behavioral contingency is of practical interest because of its possible behavioral effects.
1.2. Behavioral contingencies in human affairs
Behavioral contingencies, often rather complex ones, are a common element of all the behavioral sciences and are at the root of the behavioral phenomena that are of concern in such diverse realms as law, business, education, economics, management, public affairs, therapy, the social sciences, child management and everyday interactions between people.
1.2.1. Prominent examples
- Laws consist, in general, of “if, then” statements of the form, "If a person does or doesn’t perform certain
- Tel.: +1212765 7899/718 5442001.
E-mail address: fmechner@panix.com.
1 B.F. Skinner (1969) applied the term behavioral contingency to the “if, then” conditional relationship, “If a response, then a consequence” originally to describe the basic paradigm of operant conditioning, “If a response, then a consequence.” The more traditional usage - temporal contiguity regardless of conditionality - is not the sense in which the term is used here. ↩︎
- Tel.: +1212765 7899/718 5442001.
E-mail address: fmechner@panix.com.
1 B.F. Skinner (1969) applied the term behavioral contingency to the “if, then” conditional relationship, “If a response, then a consequence” originally to describe the basic paradigm of operant conditioning, “If a response, then a consequence.” The more traditional usage - temporal contiguity regardless of conditionality - is not the sense in which the term is used here. ↩︎
acts, certain consequences for that person shall follow". Laws are, in essence, behavioral contingency statements intended to regulate, modify, or influence behavior in a society.
- Education systems involve the behavioral contingencies that govern the interactions of students, teachers, parents, administrators, unions, textbook publishers, and members of the community.
- When business managers seek to improve operations by means of incentive compensation systems, work flow systems, and safety practices, they operate on the behavioral contingencies involved.
- The rules of games, ranging from tic-tac-toe to baseball, bridge, poker, or chess, are behavioral contingencies that determine how the games are played.
- Many everyday interactions between people involve behavioral contingency statements of the general type “If you do A, I will do B,” including promises, requests, enticements, and threats, sometimes with reference to other parties, time periods, probabilities, or other qualifications.
Unlike the other major determiners of behavior - the personal histories of the involved parties and the immutable realities of physics and biology - behavioral contingencies can be modified and designed.
1.3. The roles of signals and experience
The effects of a prevailing behavioral contingency depend on the individual’s history or previous experience with that contingency or with related ones.
Example. The effect of a price tag depends on ability to read and on prior exposure to the product and to price tags. For verbal individuals, a contingency can be communicated by verbal descriptions, including “rules”. For non-verbal individuals, a contingency can be communicated by other kinds of signals 2 and the information conveyed about a contingency can be accurate or inaccurate, complete or incomplete, well understood or only partially understood.
1.4. The value of a formal behavioral contingency language
The present paper presents a formal language, with its own specialized vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, for the systematic codification and analysis of any behavioral contingency. The practical application of this language falls into the province of behavioral technology, 3 but given the central place of behavioral contingencies in behavioral science and its applications,
[1]behavioral contingencies are also worthy of study in their own right. 4
It is true that formal codifications of behavioral contingencies can often also be expressed, sometimes with less effort, by means of natural language, as can the codifications of other formal symbolic languages like those of mathematics or symbolic logic. But in the case of complex behavioral contingencies, formal codification, with the attendant identification of key variables and features, is often a necessary precondition for their systematic study and analysis, whether by means of experiments with living subjects, computer simulation, operations research, or other methods.
Formal symbolic languages, including the present one, also provide the advantage of cutting across all natural languages (universality), with codifications that are succinct and avoid ambiguity. They can reveal relationships among elements that would not be revealed as clearly by natural language descriptions, and in science they can aid in the development of classification systems and theories.
While the antecedent of the present language (Mechner, 1959) was developed as a tool for the specification of independent variables and experimental procedures (Mechner and Latranyi, 1963; Mechner et al., 1963), and has found pedagogic uses like those cited in Section 1.5, the present expanded language is designed for the codification of any behavioral contingency, including complex multiparty contingencies. The language is also well suited for the specification of the situations and contingencies that are the subject matter of behavioral economics (Camerer and Lowenstein, 2003; Becker, 1976, 1995, 1997), including some (described in Section 5) that have become the subject of current behavior analysis research.
Clearly, this type of language cannot generate new knowledge about behavior or make empirical assertions of any kind. Behavioral contingencies do not describe or predict what behavior will actually occur-they only specify consequences for the parties involved if some specified behavior occurs. From the standpoint of experimental science, behavioral contingencies have the status of independent variables, and if used as such in experiments, their empirically observed behavioral effects would have the status of dependent variables.
1.5. Related work
While this paper may be the first effort to develop a general language for codifying any behavioral contingency, specialpurpose notation systems for behavioral contingencies have been proposed in the past. 5 The original language and notation sys-
2 The technical term for “signal” is “discriminative stimulus.” The term “stimulus” is avoided here because of its connotation of stimulus-response and reflex phenomena.
3 The application of behavioral contingencies is key in such applied areas as educational technology, behavior management, clinical interventions, and business applications. Sidman (2004) pointed out that the application of behavior analysis to human affairs has still fallen far short of the potential. ↩︎4 The distinction between independent and dependent contingencies proposed in Weingarten and Mechner (1966), and hierarchical contingency structures, may be examples of types of issues that a science of contingencies might address.
5 Some behavioral notation systems or paradigms (e.g., Chisholm and Cook, 1995; Findley, 1962; Goldwater and Acker, 1995; Keller and Schoenfeld, 1950; Malott et al., 1993; Mattaini, 1995) have been used to codify behavior analysis principles for instructional purposes and for describing behavioral phenomena that actually occur, as opposed to behavioral contingencies as defined here. These behavioral notation systems have no direct relevance to the theme of the present paper. ↩︎
tem for codifying behavioral contingencies (Mechner, 1959) dealt with examples drawn mainly from the experimental psychology literature on schedules of reinforcement, escape and avoidance behavior, discrimination learning, and maze learning. Weingarten and Mechner (1966) took an initial step in extending the language to contingencies involving multiple parties.
Skinner (1958) proposed a notation for describing certain specific schedules of reinforcement graphically. Snapper adapted “state notation” (Snapper et al., 1982; Stephens and van Haaren, 1977; Tanaka and Nomura, 1993) for the computer control of certain types of behavioral experiments. In a detailed comparison of the Mechner (1959) notation system and state notation, Michael reported his use of the Mechner language in the undergraduate and graduate courses he taught at Arizona State University (Michael and Shafer, 1995). Michael also used the Mechner (1959) language for his laboratory manual (Michael, 1963), and it was used in the textbook Behavior Analysis and Learning (Pierce and Epling, 1995). A strippeddown version of it was used in a laboratory instruction manual (Millenson and Leslie, 1979).
2. The language’s vocabulary, grammar, and syntax
2.1. The elements of the language
This paper attempts to show how the proposed language’s sparse vocabulary and simple grammar can describe a wide range of complex behavioral contingencies in diverse domains.
The units of any formal symbolic language reflect the conceptualizations of its field: the basic units of chemical notation are atoms; those of musical notation are notes; and those of the present language are acts A,6 time intervals T, consequences C,7 and the involved parties (designated here by arbitrarily chosen lower case letters).
These are the language’s six basic elements:
- A→, read as, “If act A occurs then …”. Thus, every A is understood to be preceded by an implied “If”.
- Agent of the A : The agent(s) of an act A are designated by arbitrarily chosen letters placed in front of the A (e.g., aA, bcA).8
- T→, read as “upon termination of time T……”. The time period T is part of the situation, as opposed to a property of the behavior.
- A consequence C is any situation or event resulting from an A→ or a T→. The term refers broadly to all relevant aspects of the prevailing environment.
[1]5. Prevention of a consequence: A consequence is prevented when a horizontal arrow leading to it is cut by a vertical arrow originating from another A or T, like this: □9.
6. Simultaneity of onset: A bracket enclosing vertically listed As,Ts, or C s indicates simultaneity of onset of the listed conditions. For instance, C would be read as “When C is present then if A, then …”. The order in which the conditions are listed has no significance.
Only A s or T s can consequate 9C s or further A→ or T→ contingencies. Thus, arrows can never emanate from a C, only from an A or a T.
2.2. Architecture of the grammar: the four quadrants
Every element of the language can have up to four modifier categories, as shown in the four quadrants of each symbol in Fig. 1. Each quadrant is allocated to one of the four modifier categories in a consistent way. The modifiers can, in turn, have the same modifiers in the corresponding quadrants, in a theoretically infinite hierarchical and recursive regress, fractal mode. 10
The subscript (lower right quadrant, e.g., the numeral 5 in aA5 ) is an arbitrary numeral indexed to a legend where the referenced entity is described (see Section 2.3).
The superscript (upper right quadrant) is allocated to the entity’s attributes, which can be viewed as the language’s adjectives and adverbs-probability, magnitude, valence, 11 duration, or variability, as explained in more detail in Section 2.4.
The pre-subscript (lower left quadrant) of an entity indicates the party(ies) that would perceive 12 the entity (see Sections 2.5-2.8), and the pre-superscript (upper left quadrant) indicates the party(ies) that would predict 13 the entity (see Section 2.9). One of the theses of this paper is that the verbs perceive and predict are a unique (necessary and sufficient) and parsimonious key to the generality of the language’s applicability.
2.3. Subscript: indexing to a legend
Arbitrary subscripts (usually numerals) can index the diagram’s symbols to descriptions in a legend. They can also provide differentiation between different As,C s, or other enti-
6 The term “act” is used here, rather than “response,” which has the undesired connotation of a stimulus-response reflex, and usually of a brief response performed by a single individual.
7 The term “consequence” is used in favor of the traditional term “stimulus,” again to avoid the “stimulus-response” connotation. Consideration was given to using 5 for “situation,” but the term consequence conforms better to behavioranalytic thinking.
8 The term “agent” or “party” refers to an individual, group, team, company, populace, or country that would perform the designated act. ↩︎9 The verb conseguate has been used in behavior analysis and is useful in the present context. The alternative verbs “produce,” “generate,” “result in,” or “cause” tend to carry undesired epistemological baggage.
10 These are also characteristics of such formal languages as symbolic logic and mathematics, as well as of most natural languages.
11 A C 's valence indicates whether the C is rewarding or punishing, desirable or undesirable, beneficial or harmful, positively or negatively reinforcing.
12 The verb “perceive” is understood to encompass all of the learned or genetically encoded discriminative responses to the stimuli or situation comprised by the perceived entity.
13 The verb “predict,” as used here, refers only to the behavioral effects of the party’s prior contact and experience with the contingency involved, or with the signals (verbal or non-verbal discriminative stimuli) that were previously associated with the contingency. No other connotations are implied. ↩︎

Fig. 1. Diagrammatic representation of the hierarchical/recursive quadrant-based grammar of the behavioral contingency language. The center box containing the language’s four nouns has four quadrants, shown as shapes that represent modifier entities (e.g., perceive, predict, attributes, index numbers to the legend), each of which in turn has its own analogous quadrants.
ties. For example, to indicate that the duration of C1 is T, a new consequence C2 is shown replacing C1⋅C1
When descriptions consist of one or two words, it may be convenient to show those words in the subscript positions within the diagram, while lengthier descriptions can be provided in the legend. In a7A5, the legend might describe the nature of party a as a particular individual, team, population, or government under the arbitrary numeral 7, and the nature of act A under the numeral 5. Without subscripts and legends, every diagram would represent the infinite number of contingencies that have the same structure. Specificity is achieved only by the use of descriptive subscripts.
2.4. Attributes of entities
2.4.1. Valence
The notation Ca+ or Ca− means that C has a positive or negative valence for party a.Ca+,b− means that the valence is positive for a and negative for b, and Cab− means that the negative valence applies to both. Cat,t,1 means that the valence for a can be either positive or negative.
2.4.2. Magnitude M
The magnitude attribute for act A, as in AM, can refer to such intensive dimensions as effort, force, loudness, duration, or an amount of money. When M refers to the act’s duration, a lower case t replaces the M. The duration t of an act is measured from its beginning to its termination. In Astart →Aend t,At is read as “end of act A’s duration.” The term Astart can be omitted, since every act that ends must also have started.
The duration attribute is particularly significant when an act is repetitive and can continue or end at any time. Examples of such acts, often called activities, are walking, running, waiting, foraging, working, or practicing a skill. In behavior research, a latency or inter-response time would be codified as an act whose terminating event is At.
The magnitude of a C would usually refer to the magnitude of its positive or negative valence, but can also refer to any scalable dimension like value or amount of money, or to some qualitative dimension.
For time periods, TM refers to the duration of T.
A magnitude of a consequence or of a valence that changes as a function of some variable x can be represented
by M=f(x) ) shown in the attribute position of the consequence.
2.4.3. Probability
A lower case p, or an actual value of a probability shown in an entity’s upper right quadrant, indicates the probability, in the analyst’s view, that the entity would occur.
2.4.4. Variability
Tc or Mc indicate that the modified entity is variable.
2.4.5. Negation
The tilde sign ∼, representing the negation attribute “not”, is placed above the entity’s symbol. 14
Although these attributes are fully sufficient for codifying the wide and diverse range of situations analyzed in this paper, additional attributes may, in the future, be required to meet challenges presented by specialized applications in other fields like law, business, economics, sociology, public affairs, or psychotherapy. 15
2.5. The notation of perception
In A→abC, the lower left quadrant of C indicates that both parties a and b would 16 perceive the consequence C of act A. To show that party a would not perceive C but that b would, the notation is A→abC, with the a having a tilde sign above it meaning "not a ".
aA→abT→abC is read as, “If party a does A, then C occurs after time lag T. The C would be perceived by both a and b, and the time lag would be perceived by b but not by a.” The T would be shown without any pre-subscripts if the analyst considers perception of the time lag not relevant to his focus.
The contingency aA1→bA2→ is read as “If aA1→ then if bA2→ then …”. In the case where the desired meaning is “If aA1→ then bA2 would occur,” the bA2 term would have the status of a consequence C.
2.6. The notation of misperception
aC implies that party a 's perception of C would be “correct” in the sense that it corresponds to the analyst’s belief, that being the sense in which the terms “correct” or “actual” will be used throughout. If the analyst wishes to show that the perception would be a “misperception” or idiosyncratic, 17 the misperceiving party’s designator, still shown in the lower left quadrant, would have the letter x in its own upper right (attribute) quadrant. For example, axbC means that a would misperceive C and that b would perceive it correctly. To elaborate on the misperception, the analyst could explain under, say, the legend’s numeral 5,a5bbC that a would, for example, misperceive a neutral comment as hostile. The term “misperceives” is used broadly here for any perception that is idiosyncratic or “subjective,” in the sense that it deviates from the analyst’s belief.
When time is an attribute of an act (i.e., its duration) rather than a feature of the situation, the party’s perception, misperception, or non-perception of the act’s duration would be shown as the pre-subscript of the t, like this: aAattor aAat. The latter diagram could mean " a not keeping track of how long its act A was taking."
2.7. Perception, misperception, and non-perception of valences
If a party would perceive (or misperceive or not perceive) a consequence C, would that party then also perceive (or misperceive or not perceive) that same C 's valence? The answer is that it would, based on the distributivity rule which states that any perception, non-perception, or misperception of the C applies also to that C 's valence and any of its other attributes.
Example. aA→abCb⋯a+ could mean that a would harm b and benefit himself, with both a and b perceiving this consequence and its valences. If either a or b would not perceive either or both of these valences, that party’s designator would be shown with a tilde over it, in the lower left quadrant of the non-perceived valence term, to override the distributivity rule. For example, to show that a would not perceive the C 's valence b− in spite of perceiving the C itself, the b− valence symbol would need the pre-subscript a~,abCa~b,a+abCb− would mean that a would perceive neither C nor its valence.
To show that a party would misperceive a C 's valence but not the C itself, that party’s designator, with the letter x in its upper right quadrant, is shown in the valence’s lower left quadrant. Familiar examples are Adam and Eve, or Snow White, who might have perceived the apple correctly but misperceived its valence.
14 It is more convenient to place it above the entity than in its upper right quadrant, which is where it would be placed based on the placement rule for attributes. In symbolic logic it is usually placed in front of the character, but here this placement would have the drawback of the multiplicity of meanings (including “approximately”) that such a placement has in various other contexts.
15 It may be possible, for example, to extend the language to the description of the environmental contingencies that result in speciation and evolution-the adaptation of species to contingencies imposed by the environment. The consequences would then be characteristics like camouflage or immunity, and the valences might pertain to competitive advantages or disadvantages related to reproduction and survival. The language may also be applicable to the contingencies involved in the evolution of cultural practices (Glenn and Madden, 1995; Glenn, 2003, 2004), and perhaps to any system involving conseqation with feedback.
16 The term “would” or “will” is used throughout, to maintain consistency with the conditional “if, then” logic of contingency statements, e.g., “If act A, then party(ies) a,b,c would or will perceive or predict a designated entity.” A statement of the form that a,b, or c actually do perceive or predict an entity, without the qualification of conditionality, would be inconsistent with the definition of a behavioral contingency statement. ↩︎17 In behavior analysis terminology, misperception or idiosyncratic perception means responding to a stimulus (here termed consequence) as if it were a different stimulus. ↩︎
The valence shown is the one the analyst considers the real one. The precise nature of the misperception he has in mind can be described in a legend. Here are some combinations (remember that the C 's pre-subscript applies not only to the C but also to its attributes):
aCa− a perceives both the C and its negative valence for itself.
aCaa− a perceives the C and misperceives its negative valence.
aaaCa− a misperceives both the C and its negative valence.
aCaCa− a perceives the C but not its negative valence.
a^Ca−a does not perceive either the C or its negative valence.
2.8. Misperception of a party: who done it?
baAmeans that b perceives that a is the agent. baaA means that b misperceives the fact that a is the agent. This distinction could come up in false accusations or in criminal law where there can be divergent assertions regarding the agent of an act. Again, the nature of the misperception could be described in a legend. Analogously, the notation aT means that a would misperceive T, and the notation aT means that a would not perceive T at all.
2.9. Prediction
The term “predict,” as used here, encompasses all of the behavioral effects of the party’s prior experience with similar contingencies, or with signals (called verbal or non-verbal discriminative stimuli by behavior analysts) that were previously associated with similar contingencies. Signals consisting of verbal statements of contingencies are sometimes called rules. When the analyst indicates that a party would predict a consequence, he therefore reflects his beliefs regarding the party’s relevant history.
A signal that might occasion a party’s prediction of a consequence has the status of a C.
2.10. The notation of “predict”
The party(ies) that would predict a C are designated in the C 's upper left quadrant, like this: aC.aA→aaC means that a would perceive C when it occurs and would also predict it. aA→aaCmeans that a would predict C but would not perceive it (note the a^ in C 's lower left quadrant).
Examples. Committing suicide, predicting the consequence of sending a letter without perceiving that consequence when the letter reaches its destination, predicting the consequences of issuing an order without perceiving the order being carried out, dropping a bomb on a target. The reverse, aA→aaC, means
that a would perceive C when it occurs but would not have predicted it. Here one might say that C would surprise a.
Depending on the desired emphasis and focus, the analyst may or may not indicate the party(ies) that do or do not perceive or predict a particular consequence.
2.11. Perceiving or predicting another party’s perception or prediction
aA→bCa− means that party b would predict that a would hurt himself. The notation aCa− means that a would mispredict it. To show that b would also perceive that a was mispredicting Ca−, the b would be shown in the lower left quadrant of the ax, like this aaCa−. The diagram aa,ba would show that b would, in addition, predict correctly that a 's act would be hurtful to a.
When the verb predict is applied to a probability, the meaning is similar to that of the verb “estimate.” The expression ap1, for instance, would be read as “party a’s prediction/estimation of p1.”
2.12. Nuances of meaning involving probabilities and predictions
This diagram could mean that if a asks (aA1)b for a favor, then if b complies (bA2) with the request bC4, the consequence aA1→bbC4→C3
would be C3. The analyst can express the following nuances regarding bA2 :
(bA2)p: The probability of bA2 occurring is less than one.
baA2:p is the probability that b (rather than another party) would do A2.
a(bA2):a would predict bA2. Replacing the a with ap would mean that the analyst considers the probability to be p that a would predict bA2.
2.13. Why the terms “aware,” “intend,” and “expect” are not used
The term “aware,” when applied to a contingency, is imprecise in that it could apply equally to the act only, to the consequence only, or to the party’s prediction of the consequence only, and when applied to the act or to the consequence it does not distinguish between its perception and prediction. The terms perceive and predict, on the other hand, are precise in that they can be applied with pinpoint precision to acts, consequences, and attributes, and unlike the term “aware,” they can be modified by a probability or as a misperception or misprediction.
The terms “intend” or “expect” 18 are also imprecise in that they do not tell us if an intent or expectation is still present if the consequence is modified by a probability or delayed by a time interval. The contingency language avoids such ambigu-
18 For other discussions of related terminological issues see Chisholm (1957), Baum and Heath (1992), Foxall (2007) and Hineline (2003). ↩︎
ity. It is able to express these concepts fully, along with their many possible nuances of meaning, by specifying that the act’s agent predicts, mispredicts, or does not predict the act’s consequence, with further nuances provided by recursively assigned modifiers.
2.14. Vertical arrows that terminate and change contingencies
A vertical arrow (initiated by an A or a T ) cutting a horizontal arrow, like this, □ terminates the contingency represented by that horizontal arrow. This diagram could describe the contingency involved in catching a plane or train or in meeting a deadline.
To show that a vertical arrow not only prevents a consequence but also creates a new one, the vertical arrow is shown pointing to the new consequence C2, as in the diagram on the left.

Note that at the intersection of the arrows, only the contingency represented by the horizontal arrow is terminated or changed. The horizontal arrow does not cut or affect the contingency represented by the vertical arrow.
2.15. Recycling contingencies
To show that a contingency remains in effect and can repeat, a recycling arrow is used. For example, when a CD has been played, it can be played again. To indicate that an act can recycle n times, the n is written above the recycling arrow: n A→nC.
3. Other features of the contingency language
3.1. Distributivity relations among the quadrants
The default rule is that an entity’s subscript (the numeral that indexes a legend item) is distributive across all of the entity’s modifiers, but the analyst may sometimes want to use separate subscripts for individual modifiers.
The verbs perceive and predict also extend to the modified entity’s attributes (shown in the upper right quadrant)-i.e., any entity that is perceived or predicted includes all of that entity’s attributes, these being similarly perceived or predicted.
For example, bab^Ca+
means that b would perceive that p is the probability that a would perceive C and C 's valence.
All other relations are non-distributive. For example, in a0C a would not also perceive the fact that b would predict C, that is, the perception by a would not be distributive to the upper left quadrant, and vice versa. To show that a would also perceive that b would predict C, the a would have to be shown again in the b 's lower left quadrant.
3.2. The grammar of consequences
A general default feature is that only one consequence C is present at one time, because every C is presumed to include all of the relevant features of the prevailing situation. Thus, any change of C is a new, again all-inclusive, C produced by a further A or T.
Suppose, for instance, that A1 consequates Ctone , and C2 A1→ T→C2
Ctone is a light coming on subsequently. C2 then replaces Ctone (tone alone), and may then consist either of both the light and the tone together or of the light alone. The legend would state which, if the analyst considers the distinction relevant. In either case, Ctone (tone alone), having been replaced by C2, is no longer present.
3.3. When all consequences are represented by one C
The analyst would always narrow his analysis to those consequences that are relevant to his focus and would represent these with a single C, notwithstanding the fact that all real-life acts have multiple and innumerable consequences, in the sense of the proverbial wing flap of the butterfly in China ultimately affecting the weather on the other side of the earth. A party performing an act would never perceive or predict all of the act’s consequences.
A mundane example. If I open the refrigerator and pour myself some juice, I would probably predict that I would be drinking juice in a few seconds and then perceive it. I would probably not perceive or predict all of the physical, chemical, and thermal consequences of opening the refrigerator or of the juice on my stomach chemistry.
A weightier example. If a company’s directors close down a factory, they would predict and/or perceive certain of the consequences and their time lags, but not numerous others.
3.4. Diverse consequences: when more than one consequence is shown
On the other hand, when the modifiers of the consequences are heterogeneous and yet relevant to the analyst’s focus, a single C cannot always represent all of them. The analyst would then represent them with more than one C :
←aA1→←bC2
Examples. (1) Party a introduces parties b and c to each other. The result would be two consequences −bC2 ( b 's perception of the situation that includes party c ), and cC3 ( c 's perception of the situation that includes party b ). Also, C2 and C3 may have different valences for the three parties a,b, and c, which may also have different predictions or perceptions of those valences; (2) a business executive a assigns a task to b and c. When b and c divide the work and each takes a different part of the job, the consequence for each of them would necessarily be different.
In some cases, the analyst may want to distinguish between diverse consequences of a single act.
Example. Shooting at a target and hitting it. In this case, A1 is pulling the trigger, C1 is the gun firing, and C2, is the bullet’s point of impact. A party could perceive and/or predict either of these consequences and not the other.
There are also cases where the analyst may want to aA1D2⋅bC2a4
bA2→C4 assign different probabilities to the performance of the act and to its consequence occurring (e.g., to the act of shooting at a target and to the probability of hitting it).
In the real world, the flow of acts and their consequences is continuous and seamless. In codifying a situation, exactly where in that flow the analyst chooses to draw the demarcation line between an act and its consequence depends on the desired focus. When the consequence of aA1 serves as the cue for party b 's act, this cue can be just the sight or some other consequence of a performing the act.
3.5. Consequation by external agencies
A situation C may be consequated by an external agency e as well as by one of the parties involved in the contingency proper.
Examples of externally consequated C s. The hand that a bridge player is dealt, a test item presented to a test taker, or any situation presented by the physical environment. In these cases, the external agency would be the card dealer, the presenter of the test item, or the physical environment. Acts by such external agencies eA would be shown only if the analyst considers this aspect of the contingency relevant to his intended focus.
The diagram at the left shows that a would perceive that he has an e-mail, eC3, sent by an unknown external agency eA1.
eA1⋅aA2⋅bC4
aC3aA5→bC6a If a opens the e-mail (aA2),a will predict and perceive its display C4 on the screen, including an attachment. The a shown in C4 's upper left quadrant means that a would predict that opening the e-mail would consequate the screen image eC4. This a pertains only to C4 and has no bearing on the $a A_{5} \rightarrow C_{6}^{a_{-}}$contingency, namely on whether a would also perceive or predict that if aA5 (clicking on the attachment), the computer would be infected with a virus C6a−. The a˘ designator in the upper left quadrant of aC6a− indicates that a would not predict that opening the attachment would incur a virus. To show that a would predict it, the a would need to be shown in the upper left quadrant, like this, aC6a−, without the tilde.
3.6. The notation of uncertainty
Uncertainty is indicated by a question mark after the entity to which the uncertainty applies. The specific nature of the uncertainty, or the reason for it, can be elaborated in the legend. The numeral indexing the legend can be shown in the question mark’s lower right quadrant: b?5.
aC means that the analyst is uncertain that a would predict C.(a?b means that the analyst is uncertain as to whether a would perceive the C. When a party, rather than the analyst, is uncertain, the party’s designator is shown in the question mark’s attribute quadrant: (a→a)bC. (The logic underlying this rule is that the uncertain party is like an attribute of the uncertainty.) To show that the analyst is uncertain regarding the correctness of a perception or prediction, the question mark is shown in the party’s attribute quadrant: aC. To show that it is a who is uncertain about the correctness of a 's own prediction, an additional a is shown in the question mark’s attribute quadrant: apaC. To indicate that the analyst is uncertain as to the valence for b but not for a, the notation is Ca+,b(+,−) ?
3.7. Uncertainty and probability
When to use the question mark and when to use the probability notation: a question mark indicates the lack of some existing information where the uncertainty would be eliminated if that information were provided. An indication of a probability, on the other hand, suggests that the event depends on an external process like the tumbling of dice, the order of the cards in the deck, or the results of decision processes of others. In such cases, a second branch of the consequating arrow can show the consequence for the 1−p complement of the probability, if doing so is relevant to the focus. A probability can have as a modifier a party’s prediction/estimation (shown as the p 's pre-superscript), but an uncertainty cannot.
Notations of uncertainty or probability are used only when they are relevant to the analyst’s focus. Although all consequences would necessarily be probabilistic to some degree, relatively small uncertainties are usually unimportant in relation to the focus, and the analyst may therefore not indicate them.
3.8. Simplifying assumptions and abbreviations
Formal symbolic statements are inherently stripped down to presumed essentials through the use of simplifying assumptions intended to eliminate features that might mask the intended focus. With that intent, the analyst simplifies the contingencies being represented by selecting some features and omitting others. The result bears the same type of relationship to reallife contingencies that a drawing of an object bears to the real object.
A common simplifying assumption is the omission of the T s representing the time lags between all acts and their consequences. When the time lag is relevant, the contingency might be shown as A→T→C.
Abbreviations provide another way to simplify diagrams. For example, the symbol Co+ is an abbreviation. If the analyst considers the specific reasons for the valence being positive for a important, he can elaborate them in the diagram proper or in a separate diagram indexed to the point of insertion.
Examples of reasons. Upon the occurrence of C,a might be able to avert an impending negative consequence or procure a positive consequence by certain further acts.
3.9. “And” relationships: cooperation, contracts, agreements
When a consequence depends on the occurrence of all of two or more events, the symbolic logic symbol ∩ for the intersection of sets (the “and” relationship) is used. 19
Example. Mother says to child, "I will read you a story (C+) in 5min(T3) if you have brushed your teeth (A1) and gotten into bed (A2) in those 5 min":(A1∩A2∩T3)→C+. The ∩ s mean that all three conditions must be met.
The ∩ symbol is also used in codifying cooperation, as when a and b perform separate acts aA1 and bA2 when they cooperate.
Example. If a and b make an agreement (aA1∩bA2) by exchanging promises, undertakings, signatures, or money, and agree to perform further acts (aA3∩bA4), namely the undertakings stated in the agreement, presumably for the parties’ mutual benefit Cab+, this would be represented as (aA1∩bA2)→(aA3∩bA4)→Cab+. The specific terms of the agreement can be elaborated in the legend. If aA1 and bA2 are thought of as a single act rather than as separate acts, the notation abA would be used instead of the expression with the ∩ symbol.
3.10. Durations of acts
In many contingencies the consequence is a function of the amount of time that has elapsed or that is consumed by an act. A Chinese proverb relates the contingency of being afraid to dismount the tiger that keeps getting hungrier. Here t is the duration of aAdismounts (time since mounting), and M and/or p are direct functions of t, where M is the magnitude of the negative consequence and p is its probability.

Examples. Procrastinating having a dental or medical problem taken care of, fear of reporting a worsening business situation to one’s shareholders, fear of confessing a crime, delaying paying a tax penalty, or not fixing a leaky roof.
In the analogous contingency where the valence is positive, patience is rewarded, or the magnitude or probability of the reward increases the longer one waits.

[1]Foraging, too, can be described by this general contingency, where finding food may depend on the time t spent foraging.
3.11. Repetitive recycling of an act: learning and practicing
Familiar examples of possible behavioral effects of such recycling contingencies are the progressive decrease in t (i.e. an increase in the speed of the act) LdTAdTC seen in learning and practicing, or an increase in t seen in fatigue or drug effects. Such observed effects can then be described by the function t=f(ni).
3.12. Behavioral history factors
Some aspects of a behavioral contingency description are independent of the histories of the involved parties, and some are not. The specification of the acts, the time periods, the consequences, the parties, and certain of the entities’ attributes like probabilities and magnitudes, reflect the analyst’s beliefs about the situation’s objective or physical features, without consideration of the parties’ histories. But such modifiers as perceive, predict, and the valences of consequences do depend on the parties’ histories and reflect the analyst’s beliefs about the effects of those histories. For example, the glass will break if dropped regardless of any party’s history, but a party’s prediction of that consequence, and its valence for that party, would depend on the party’s history. Thus, parties’ histories can be part of the contingency. The representation of any given situation would therefore depend not only on the analyst’s focus and analytic intent but also on his beliefs regarding the parties’ histories and motivations, and would, accordingly, be different for different parties, and for the same party(ies) at different times.
4. Examples of applications
4.1. Wrong predictions: getting swindled, wrong number, “friendly fire”
A party might mispredict the consequence of its act A.
Examples. Dialing an incorrect phone number in error, paying a swindler for nonexistent real estate, and a soldier shooting one of his own men. These situations would all be represented as aA→acCa. The ac in the C 's upper left quadrant shows that a would mispredict Ca−. These examples make the point that only consequences that would actually occur (i.e., in the analyst’s view) - calling the wrong party, obtaining an invalid deed, and shooting a comrade - can be codified, in this case represented by the a−. Consequences that would not occur (e.g., “expectations”), cannot. Only the legend would state what the parties may have intended or expected-calling the desired party, obtaining a valid deed, and shooting an enemy. The diagram can show only
19 As explained in Mechner (1959), the “and” symbol is an abbreviation for a diagram that would show the possible occurrence of any of the permutations of the sequence of the events in question, with reciprocal vertical arrows showing that the occurrence of each sequence prevents the subsequent occurrence of the others. ↩︎
that the party would have predicted a consequence that differs from the actual one. 20
To show that a would also perceive the actual consequence if and when it occurred in each of the above examples, the a would also be shown in the lower left quadrant of the C, as in aA→aaCa−.
4.2. Unpredicted effect on another party’s behavior
When a party a misuses a word in an unfamiliar language or gives someone faulty driving instructions, the consequence would be an unpredicted effect on the behavior of another party. When a word is misused, the consequence might be puzzlement by the other party. When faulty driving instructions are given, it might be the other party getting lost and complaining. In both cases, the actual consequence is negative for a.
If aA is uttering the wrong word and
aAutterm ∣baAwuth aa+aCwound of "huh" a−
Cwrong word is the utterance of that word perceived (heard) by b, it is b 's puzzled reaction “huh?” to the word that would constitute the negative consequence for a, not Cwrong word .
If the listener b nods in spite of puzzlement (see diagram)
aAutterm ∣baAwuth aa right of nod Cnigh a+
as indicating that b understood. The consequence of the nod is positive for a because of a 's misperception of it. If b predicted a 's misperception, as indicated by the b in the upper left of the aa, the nod would constitute a form of deception by b.
4.3. When nuances determine the meaning: setting a trap
In this diagram, C3 's valence is negative for b.
aA1→bA2→abC3b−
The two negation symbols bˉ show that b would not predict C3 or perceive the warning signal C4. This could be described as a setting of a trap for b. The a in the upper left of C3 shows that a would predict that bA2 would consequate C3b− and would therefore have set the trap “intentionally,” as one might say. Additional nuances or emphases could be indicated by showing a 's in the upper left quadrants of either or both bˉ s (in C4 and C3 ), to show that a would predict b 's non-perception of C4 and non-prediction of C3b−. Nuances like these can assume great significance in legal matters.
4.4. Probability of a consequence: creating a hazard
The assignment of probability p to C3b−, as an additional attribute, defines the contingency as a hazard.
aA1→baA2→bbC3b−,p
The a in the upper left quadrant of b means that a would predict that b would be the agent. The a in the upper left quadrant of A2 means that a would predict A2 regardless of who does it. The b in the upper left quadrant of C3, in addition to the a, means that both a and b would predict that A2, if it occurs, will consequate C3 and its attributes, which include p. Would a and b then also be predicting that C3 's probability is p ? The distributivity rule (that the modifiers perceive and predict apply also to the entity’s attributes) says that they would. An ap in C3 's attribute quadrant would override the distributivity rule, meaning that a would then not predict p.abp would mean that b still would.
4.5. Theft
If b takes the cookie out of a 's lunch box (bA4) before a does (aA3),a would be prevented (vertical cutting arrow) from doing so.

(The fact that the cookie is in a 's lunch box in the first place (C1) would have been consequated by the act of an external agent, eA, not shown.) Since only b would predict that b will end up with the cookie (C2), and since aˉ shows that a would not perceive that the cookie is in b 's possession, bA4 would represent a theft. This example makes the additional point that a rigorous definition of the concept of theft, especially from a legal standpoint, requires specification of the perceptions and predictions of both parties, and the valences of the consequences.
4.6. Applications in therapy
To achieve desired results, therapists (psychotherapists, psychoanalysts, behavior therapists, cognitive-behavior therapists, coaches, or counselors) often seek to understand the contingencies involved in the patient’s interactions with others (Erickson and Achilles, 2004; Wachtel, 1997). Such contingencies can be generated in part by the interactions themselves, including their reverberations at higher levels of the recursion hierarchy.
Family therapy in particular is an area where modifiers of modifiers can be important. In dealing with family dynamics, the therapist may analyze the contingencies that parents, siblings, and related parties create for each other. These often involve multiple levels of regress of each other’s perceptions, mis-/nonperceptions, predictions and mis-/non-predictions of acts and their consequences, as well as of their valences and magnitudes. Since all of these are the result of the parties’ histories, one of the therapist’s challenges is to modify the effects of such histories,
20 When the act’s agent would also predict the act’s consequence, one might say that the consequation is intentional. However, as was explained in Section 2.13, terms relating to intentionality, as well as expectations, hopes, visualizations, goals, etc., are not needed. ↩︎
an endeavor in which a detailed behavioral contingency analysis can be useful.
4.7. Consequence of omitting an act: failure to pay a bill
There are situations where failure to perform an act has a significant consequence. In such cases C would be consequated by a T→ or an A→ or by another (sometimes external) party. For example, if a phone bill is not paid by the end of time T,
the phone company will shut off service.
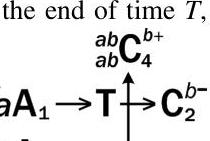
Here, b would be the agent of the preventive act. The vertical arrow shows that bA3 would avert C2 by terminating the T→C2 contingency. Non-performance of bA3 would permit C2 to occur.
The legend indexed to the subscripts might read:
- If phone company a threatens to cut off service after time T.
- Service would be cut off.
- (If) customer b pays the phone bill within time T.
- Service would continue.
The consequence C of the termination, with all of its modifiers, can be shown at the end of the terminating arrow.
4.8. Reciprocal vertical arrows: decision making and competition
When each of two consequences prevents the occurrence of the other, as in decision making and certain types of competition, reciprocal vertical arrows are required (see diagram).

taking a multiple choice test,

the student may be confronted with a question C together with simultaneously available choices (acts), as in the above diagram. The external agency e that presents (consequates) the C may be a teacher, a computer, or the student himself turning a page. The reciprocal vertical arrows show that each of the three acts terminates the availability of the others.
4.10. Two interrelated time intervals: the roast in the oven
The diagram shows a situation where a put a roast in the oven and left the house without turning the oven off (aA1). The roast will burn (C5a−), unless the oven is turned off (A8) within time T4.

If the oven is turned off (A8) after T7 and before T4, the roast will be done. But the oven will get turned off only if a asks (aA6) her neighbor b to do so before T4.T7 and aA6 therefore have an “and” relationship.
Legend:
aA1: If a leaves the roast in the oven on leaving home ... aC5: The roast would be in the oven with the oven on. T4: Time after which the roast would burn. T7: Time after which the roast would be done. C5a−: Burnt roast. aA6: If a calls her neighbor b and leaves her a message ... abC9: Message to turn off the oven after time T7. bA6→: If b turns off the oven after T7 and before T4…C5a+: The roast is done and C5a− is averted.
The b in abC9 's lower left quadrant implies that b got the message. The ap attributes of A8 and C3 represent a 's
prediction/estimation of the probability that b will actually do bA8 and that the roast will therefore be taken out in time.
4.11. Types of “or” relationships: achieving priority, putting out a fire
One kind of “or” relationship is where either one of two or more acts can result in a given consequence. Another is where a single act can result in either one of two or more consequences. Both can in turn be divided into exclusive (either, or, but not both) and inclusive (either, or, or both) “or” relationships.
[aA1bA2]→Cpriority aA1∪bA2→Cfire out
Diagram on the left: an exclusive “or” relationship shown by a merging of the horizontal arrows. The consequating entities in such diagrams can be A s and/or T s. This diagram could represent two parties competing to consequate C, where whoever gets there first obtains the only available C (as when parties compete for priority in applying for a patent or in reaching the South Pole).
Diagram on the right: either one of two parties or both together can put out the fire-the inclusive “or,” represented by the union symbol ∪.
(aA1∪bA2)→(aA3∩bA4)→Cab+ would be read as, “If either a or b or both (note the inclusive “or” symbol ∪ ) create a situation in which cooperation between a and b (note the ∩ symbol for “and”) can occur, the consequence would be Cab+.”
4.12. Probabilities of alternative consequences: Russian roulette
Another type of “or” situation is where a single act A (e.g., the tossing of dice) consequates two or more possible outcomes with different probabilities. In “Russian roulette” there is a 1/6 probability of the consequence “bullet in chamber” occurring. If the focus is on the two alternative scenarios, the arrow can be shown as branching, with the other branch consequat-

ing the complementary probability 5/6.
In general, contingencies involving alternative consequences are represented by a multi-pronged fork with two or more arrows pointing to the different possible Cs.
The analyst may sometimes wish to show that a modifier like perceive and predict, or a valence, has an “if” in front of it. For example, he may want aC to be read as “If a would perceive C " rather than the standard " a would perceive
C.” He would then show the two possibilities
as the branches of an “or” fork. For example, when considering whether or not to commit a crime (Becker, 1976, 1995, 1997) a party might weigh the consequences of the crime being perceived (p) or not perceived (1−p) by society. (For a fuller analysis, see Mechner, 2008).
4.13. Sequential multiple discriminations: traffic lights, naming people
In a sequential multiple discrimination, signals appear one at a time.
Example. We stop when the traffic light is red and proceed when it is green, and call different people by their respective names.
To codify this type of contingency we first ask how the circumstances for the acts are consequated. Traffic lights are controlled by timers, and telephone equipment transmits the voices of people we may want to name when they call us. In both cases external agencies e consequate the situations in an “or” manner-the traffic light is either red or green, and we receive phone calls from one person or another.

Again, the “or” relationship is represented by a fork. When the multiple discrimination involves more than two signals, the fork would have correspondingly more branches.
4.14. Misperception of C : mistaken identity
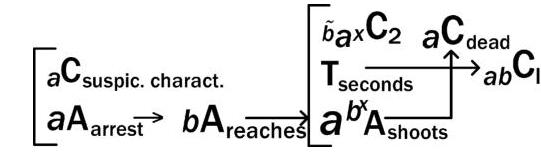
If policeman a sees a suspicious character b, he may try to arrest him. If b, claiming mistaken identity, reached into his pocket (bAreaches ) for his identification (abCID ), then in T seconds this might take, the policeman could misperceive the visual consequence ( aaC2 ) of (bAreaches ) as pulling out a gun, and shoot b dead, mispredicted by b. The b term means that b would not predict a 's misperception.
4.15. Misperception of a missile test
A similar diagram could describe a misperception by country a in response to a missile test by a hostile power b, and the associated mispredictions by b.

Here, aaa^aCtest shows a 's non-prediction and misperception of the test. If a responds with aAattacks , the consequence would be negative for both parties. The bx in the upper left quadrant of the ax shows that b would mispredict a 's misperception of the test. The bx in the upper left of Aattacks shows that b would mispredict the attack by a. If it were desired to show that b would not predict rather than mispredict a 's misperception, b^ would replace bx in ax 's upper left quadrant.
Many types of situations that involve misperception, and misprediction of misperceptions, are of great concern to societies and nations, as well as in interpersonal relationships. Behavioral contingency analysis helps identify the critical variables whose effects can then be studied by various methods.
4.16. Concatenated probabilities in systems analysis: the Trojan horse
If Homer had been the analyst, he might have shown Odysseus - the general of the besieging Greeks - as party a scheming the following contingency:
“If we build a giant hollow wooden horse and leave it for the Trojans to find ( aAoffers ), the Trojans (b) may misperceive the horse (as being empty rather than filled with soldiers). If the Trojans thereupon take the horse into their city ( bAtakes in ), our soldiers hidden inside the horse may be able to emerge from the horse during the night ( aAemerge ) and open the gates for the rest of us to enter and sack the city, thereby winning the war.”
The b^ in the upper left quadrant of Chorse shows Odysseus’s bet that the Trojans would not predict this “gift.” The bx in the lower left quadrant of Chorse shows b 's possible misperception, and the ap1 in bx ‘s attribute quadrant shows Odysseus’ prediction/estimation of the probability of this misperception. Odysseus might also have predicted/estimated the probabilities of various subsequent events- ap2 for the act bAtakes in , and ap3 for aAemerge (e.g., the Trojans might discover the ruse, or the horse’s door might jam). The b^ symbols in the two verb quadrants of aAemerge show that b would not perceive or predict aAemerge . The attributes quadrant of Csucked shows that this consequence would be negative for b, positive for a, and that a would have predicted/estimated its probability as p4.
If Odysseus had indeed performed this analysis and considered the product of the four probabilities, he might have concluded that his scheme was very (too?) risky.
4.17. Vigilance 22 and the analysis of interrelated probabilities
If (p1)e plants a bomb ( eAplants ) that has probability p7 of going off after unknown time TM7, and if ( aAvigilance ) shows that
[1]a is probably (p2) engaged in vigilance/detection activity, then a will detect (perceive) aCbomb with probability p3. If a thereupon alerts ( aAalerts ) the bomb squad b (probability p4 ) with a signal (abCalert ), the bomb squad will probably (p5) attempt to disarm the bomb ( aAdisarm ), with p6 being the probability of doing so successfully.

4.18. Modification of contingencies: mitigating a danger
This diagram shows a situation in which two or more parties cooperate to avert a threat. Again, Cab− can come after an unpre-
dictable time TM7 with probability p. [Tat(aA∩bA)T]→Cat−p
By acting cooperatively (aA∩bA) (e.g., by exercising vigilance, building levees, or storing provisions), a and b can prevent Cab−.
To show that (aA∩bA) merely reduces the probability of Cab− from p1 to p2, rather than to zero, the changed contingency would be shown at the end of the vertical arrow with the new probability p2, as in the diagram.

Here (aA∩bA) would change both the timing and the probability of the terminated contingency. If the new contingency requires a bracket, the arrow would point to the bracket.
4.19. Risky choices: thinking ahead in a game
The risks that a chess, checker, or go player takes when choosing between moves are the uncertainties regarding (1) how accurately or completely he identified the opponent’s possible responses, (2) which of these the opponent will actually choose, and (3) the valence of the outcomes of these possibilities.
If a considers two possible moves aA1 and aA9, and thinks two moves ahead in considering b 's possible responses, a would be uncertain as to whether, in response to aA1,b would choose bA3 (say, a particular identified move) or bA5 (say, a possible

unidentified move),

C12 or whether in response to aA9,b would choose bA7 (say, another particular identified
22 Experimental studies of vigilance and observing behavior and the associated contin gencies include Dinsmoor (1983), Dinsmoor et al. (1972), Case and Fantino (1989); and Nevin et al. (2005). ↩︎
move) or bA10 (say, another possible unidentified move). Furthermore, a would be uncertain regarding the valences of the resulting situations (note the a s in the attribute quadrants of the question marks).
4.20. Divergent contingencies for two parties: a sexual overture
If a makes a sexual overture aA1 to b, the two possible outcomes, from a 's point of view, are that b would accept (probability p ) and that b would decline (1−p). The reciprocal vertical arrow is needed to show that b 's accepting and declining
are mutually exclusive.

From b 's point of view the issue is whether to accept or decline, rather than a probability issue. This type of examination of two divergent perspectives can be useful in fields like law, business (see Section 6.7), economics, or public affairs, where the differences in the contingencies for each party can be important.
4.21. Game theory situations and bluffing: blackmail and kidnapping
If blackmailer a threatens to harm b unless b pays, the probability of the harm actually occurring, even if aAexecutes , might be p2. If aAdemand stated that b can avert harm by bApays , then the probability that a would do no harm if b pays is p4, and

the probability that a would actually execute the threat if a does not pay is p1, that is, a is bluffing. The probability that bApays would consequate a recycling of the entire contingency is p3. When a contingency recycles, all components of that contingency are restored for the next cycle, including ones terminated by vertical arrows in the preceding cycle.
The same diagram could also describe hostage taking or kidnapping. This example and many of those that follow illustrates how behavioral contingency analysis can serve as a tool for identifying the variables and their relationships, including utility, that would be considered in the types of economic analyses proposed by G.S. Becker (1976, 1992, 1995).
4.22. Predictions/estimations of p : the basis for a wager
Here aAM1 and bAM2 represent bets that a and b can place in situation abC5 on, say, the outcome of a ball game. The external agency e could be two ball teams producing one of the two possible consequences.

The attributes M1 and M2 of the bets can be the amounts of money a and b would be betting. The symbol ∩ indicates the “and” relationship of the bets, as in a contract. The notations (a,b)p1 and (a,b)p2, with commas between the a and b, show that a and b have different predictions/estimations of p1 and p2 (they would not be betting unless they did). If there were no comma, just ab, it would mean that a and b have a joint prediction/ estimation.
4.23. Perceptions of M : tipping a service provider
If customer b has received a service (aA1) from a (say, a waiter), the magnitude M of the tip b gives (bAM) may be M1, M2, or M3. The three tips are C3,C7, and C11, and a may have subjective/idiosyncratic perceptions of their magnitudes.

The magnitudes are attributes of the three C s and the idiosyncratic perceptions of the magnitudes (indicated by ax s in the M s’ lower left quadrants), are shown in the three references, a technique used because if these attributes were scaled to the size of the main diagram and inserted, they would be hard to read.
The fact that the two sets of three M s have the same (lower right) subscripts means that they represent the same amounts of money. (The three-way reciprocal vertical arrow shows that these three possible consequences are mutually exclusive.) The legend might elaborate that a would idiosyncratically perceive M1 as too small, M2 as acceptable, and M3 as generous. These three idiosyncratic perceptions have probabilities p1,p2, and p3, respectively, which b might predict/estimate, as shown by the b s in the upper left quadrants of the three probabilities.
a 's possible reactions aA4 and aA9 would consequate C5 or C10, which b would perceive and whose respective probabilities b would predict/estimate as p4 and p5. C5 might be an insult and C10 might be an expression of gratitude.
These and many other intricate social and cultural variables at play in many tipping situations have been discussed by Green et al. (2003), and a brief review of the relevant literature is presented in Lin (2007).
4.24. Misperception of the M of a C: perpetration of a fraud
If seller a offers (aA1) to sell b a counterfeit painting, C3,a would perceive the value of the painting to be M4 (as indicated by the a in the lower left quadrant of C3, which is distributive to C3 's attribute M4 ),
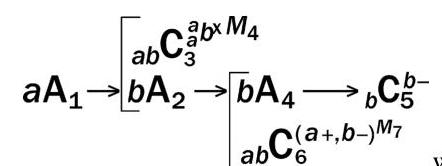
its value, indicated by the bx in M4 's lower left quadrant. Note that both a and b perceive the painting, but only b misperceives its value. The a 's in the two left quadrants of the bx indicate that a would perceive and predict b 's misperception of the value, which is what makes the transaction a fraud. The description of aA1 in the legend might include history events responsible for b 's misperception.
If b accepts a 's offer aA1 and buys the painting (bA2), paying a the asking price M7 (an attribute of C6 's valence), then a+ would be a receiving the M7 and b− would be b parting with it. If b subsequently gets the painting appraised (bA4) and consequently learns its true value bC5b−, the valence of that information would be negative for b. If a third party c witnessed the fraud and stood to benefit from it, c would face the choice of warning b, or letting the fraud occur, thereby becoming an accomplice.
4.25. Symmetrical reciprocal recycling contingencies: feuding
This diagram represents a feud where parties a and b alternate

hurting each other.
The crossing diagonal recycling arrows show the symmetry of this type of contingency. Attempts to end the feud can be made at any point by A1 or A6 (peace overtures) that have probabilities p1 and p2 of being effective.
Other examples of contingencies that have symmetrical recycling structures: bargaining, where two parties take turns making each other offers and counteroffers; situations where two parties take turns assisting each other; or a chess game that uses a chess clock where each player’s move Ai stops his own clock and starts the other player’s. If a player exceeds his limited allotted time, he loses (see Mechner, 2008).
4.26. Mutual deterrence and first strike
Mutual deterrence is another type of symmetrical recycling contingency rife with game theory dynamics that can occur in military confrontations and other situations where there can be standoffs. Two factions, a and b, both have the option of launching a first strike. If a attacks first, b will retaliate unless a 's attack terminates b 's ability or willingness to do so.
The protagonists will usually differ in their perceptions and predictions/estimations regarding the magnitude of any damage inflicted as well as the various probabilities that (a) the other party will execute a first strike, (b) that there will be retaliation for each attack, © that the first strike will avert retaliation, and (d) that any given retaliation will end the cycle of exchanges. Each party would also consider the other party’s prediction/estimation of its own predictions/estimations of the various probabilities and magnitudes, and the predictions regarding possible misperceptions, mispredictions, and uncertainties regarding the modifiers of these entities at several levels up the recursion hierarchy (see Mechner, 2008).
These types of complex interactive situations can be addressed by operations research or computer simulation, with behavioral contingency analysis helping to identify and confront relevant variables that could easily be overlooked.
5. Behavioral contingency analysis as a research tool
5.1. Widely studied contingencies: schedules, the “matching law”
The basic contingencies for the widely studied fixed or variable interval schedules and fixed ratio schedules (Skinner, 1938) would be codified as $\overbrace{\mathrm{T} \rightarrow \mathrm{A}^{\perp}}^{\mathrm{C}^{\perp}} \mathrm{C}^{+}and\overbrace{\mathrm{C}}^{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{C}^{+}$$\mathrm{C}^{+}$, respectively, where the n represents the number of consecutive A s rather than the agent of A (Mechner, 1959). 23
In the contingency shown at the right, there is a limited time window T1 during which A→C can recycle T1A⊥→CC (e.g., “Make hay while the sun shines”), or be allowed to occur only once (termed “limited hold” in Ferster and Skinner, 1957). T2 is the parameter that distinguishes a free operant situation from a trial situation. The usual possible modifiers of the A s, C s, and T s can suggest independent variables in experimental analyses of this general contingency.
Another widely studied contingency is the one to which the “matching law” applies (Herrnstein, 1970; Baum, 1979), which states the observed relationship (often hyperbolic, e.g., Mazur, 2001) between measures of behavior and measures of consequences. The diagram represents a generic “matching law” experiment-one that studies behavior allocation or other manifestations of choice as a function of the magnitude or probability of consequences. The contingencies represented by this diagram are seen in most situations that involve choice or decision making, and in many that are the subject of behavioral economics research (Herrnstein et al., 1997; Camerer and Lowenstein, 2003; Becker, 1976, 1995, 1997).
23 The number n could also be shown as an attribute of the A. Either notation is an abbreviation for the notation that shows the A as recycling n times with the consequence of $C^{+}$depending on the C register (see Section 6.2 ©) having reached n. ↩︎

C4 represents the two manipulanda or physical facilities for the two choices A3t and A5t. The t attributes of the choices can refer to the amount of time allocated to each of the two choices or to their rates, inter-response times, or latencies. M8 and M9 represent the magnitudes of the valences of the two consequences (e.g., amount of reinforcement), and p10 and p11 represent their probabilities (e.g., reinforcement probability or frequency). A1 can be a changeover response (as when a switches from A3t to A5t or vice versa) and T2 is the amount of time the changeover takes up.
5.2. Temporal discounting research
Temporal discounting research deals with the relationships between the behavioral effects of the magnitude of a consequence and its delay (e.g., Commons, 1987; Lattal, 1987; Mazur, 1987; Critchfield and Kollins, 2001; Green et al., 2004, 2007; Rachlin, 2006). In many situations, less/sooner can be equivalent to more/later for certain values of time and consequence magnitude, with the equivalence contour often described by a hyperbolic function (e.g., Mazur, 1987). The trade-off between delay and magnitude of reward in this type of research has sometimes been associated with “delay of gratification” or “selfcontrol” (Rachlin, 1995).
The diagram below is a generic representation of temporal discounting experiments that would use real, as opposed to verbally described, delays and consequences.
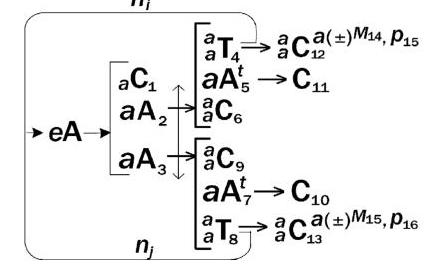
One delay-magnitude combination is T4/M14, and the other is T8/M15. The two choices are aA2 and aA3. The diagram provides a road map for identifying this research area’s potentially operative variables besides the basic ones of delay, valence magnitude, and probability of the consequence. For instance:
- C6 and C9 signal the two delay intervals (which can be “filled or empty,” MacInnis, 2007).
- The acts aA5t and aA7t indicate the possibility of filling the delay intervals with alternate behavior maintained by various possible contingencies.
- The ± valences show that the consequences can be positive or negative.
- The probabilities p15 and p16 of the consequences are shown as a possible alternative or supplement to the valence magnitude variable.
- All of the time intervals and consequences are shown as modifiable by perceptions and predictions that could be a function
of signaled or experiential history variables (e.g., number of repetitions).
- Not shown in the diagram but also possible variables are misperceptions or mispredictions and non-perceptions or nonpredictions of any of the entities.
The diagram also highlights the issue of using, as the independent variables, real delays and consequences (as Mazur did with rats and pigeons, Mazur, 1987) versus verbally described (sometimes termed “hypothetical”) consequences and/or time delays (e.g., Kowal et al., 2007; Johnson and Bickel, 2002). When the independent variable is embodied in a verbal statement, aC1, presented simultaneously with the choice contingency, and the consequences of the choices are also verbal statements, C4 and C5, the diagram reduces to the one at the right. In this type of experiment, a description of aC1 in the legend would explain the experimenter’s assumptions regarding the subjects’ behavioral and verbal histories with respect to the described delays and consequences. A key issue here would be the assumed correlation between the behavioral effects of (a) real delay/consequence combinations and (b) verbal descriptions of these, given certain verbal histories. Some of these issues are discussed in Hertwig and Ortmann (2001), Johnson and Bickel (2002), and Fantino et al. (2007).
5.3. Research on the prisoner’s dilemma
This class of behavioral contingencies, which is of sweeping importance in the social sciences, is very well explained in the Wikipedia article entitled “Prisoner’s dilemma,” (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prisoner’s_dilemma). The central theme of such situations is the decision on the part of a party to “cooperate or defect” (Rapoport and Chammah, 1965). This dynamic is present to some extent in many social situations, especially choice situations that relate to short-term versus longterm self-interest (sometimes termed “selfish versus altruistic”) (Rachlin et al., 2001), in situations involving predictions as to choices that others will make (e.g., Yi and Rachlin, 2004), and in many types of game-theoretic situations that involve social acts like voting in elections, coalition formation (Gelman, 2003), or behavior related to global warming (e.g., Clemons and Schimmelbusch, 2007).
The generic prisoner’s dilemma diagram that follows shows four combinations of a and b cooperating or defecting, with four possible consequences.

Every act and the probability of every act is subject to prediction by the other party, and every possible consequence and its M and/or p for each party can be perceived and predicted by both parties, with all predictions being subject to further prediction by the other party at an indeterminate number of levels up the recursion hierarchy. Not shown in the diagram (due to graphical limitations) is that every prediction can also be a misor non-prediction, and can be further modified by an uncertainty on the part of the predicting party.
As in the case of temporal discounting research, behavioral contingency analysis of these types of situations helps identify the numerous operative variables that can be studied experimentally or used in simulations, and that can easily escape notice absent such analysis. Some of these are:
- The number of times the contingency has recycled with resulting learning history effects, as seen in studies that showed stabilization of choice behavior (e.g., Thomas and Feldman, 1988).
- Effects of other types of experimentally imposed learning histories.
- Different numbers of recyclings for different choices and consequences.
- Differences in the possible positive or negative consequences for each party (the consequences need not be symmetrical for the parties).
- The effects of the magnitudes of the valences, which can also be asymmetrical.
- The probabilities of the consequences, as distinct from those pertaining to the choices, that is, the same sets of choices need not always result in the same consequence, or in consequences that have the same modifiers.
Also, as in the case of temporal discounting research, this analysis highlights the issue of using “real” versus verbally described consequences.
5.4. Specifying independent variables in neuroscience research
Some neuroscience experiments on the mapping of neural functions require an operationally specified independent variable that is under the experimenter’s control. Behavioral contingencies meet this requirement (See Mechner, 2008).
6. Progressive changes and registers
6.1. Pumping water into a bucket
There are important contingencies in which a consequence keeps changing as a function of recyclings or other variables. The codification of such contingencies requires the use of a register that shows the changing magnitude of the consequence.
This diagram describes the water level in a bucket being


increases the water level by one increment ΔL. The ∑ expression in the Cregister 's magnitude position (attribute quadrant) shows the amount of water in the bucket after every ni such As, calculated as the cumulative number of times (ni) the A has recycled at every point times the change in the water level ΔL with each cycle.
6.2. Other registers of progressive changes

This diagram shows the generic representation of contingencies that involve progressive changes as a function of i,f(ni,ti).
Examples.
(A) When f=∑(ni/ti), the register represents the rate at which act A would be occurring at any given value of i, for a desired range. Instances: response rate in experiments, proficiency assessment when practicing a skill.
(B) When f=∑(ti/ni), the register could show the act’s average duration after every ni repetitions, within a desired range. Instances: indicator of speed when learning to do a job faster or practicing a skill, keeping track of the average time between contractions during labor.
© When f=∑(ni), the register shows the total number of acts that have occurred at every value of i. Instances: points scored in a game, money saved up so far, number of votes so far during election coverage.
(D) When f=∑(ti), the register shows the total elapsed time value of i. Instances: watching the clock, concern that a job is taking too long.
(E) Exponential functions could show progressive effects of various kinds of growth or proliferation, of exponential decay, or of other asymptotic functions.
6.3. Short-term and long-term contingencies: global warming
When sustained repetition of a type of act has a cumulative long-term negative effect at individual, societal, or national levels, such acts are often maintained by their short-term positive consequences. There are also acts whose sustained repetition has short-term negative and long-term positive consequences (e.g., IRA savings accounts, doing aversive work to accumulate money).
The diagram at the right shows some of the behavioral dynamics of global warming-the cumulative consequence
of many individual acts like coal burning or burning of vegetation that are maintained by their short-term positive consequences with possible resulting long-term temperature change.

In this diagram, there is no identified end point of the process, unlike in the case of filling a bucket with water. The register Ctemperature register is shown as having the magnitude M of its negative valence (again represented by the formula in the exponent position) being cumulatively and progressively incremented as a function of the number i of repetitions. This type of analysis can help identify the roles of some of the variables that may affect global warming (e.g., Clemons and Schimmelbusch, 2007).
Other familiar examples of this same contingency structure are the possible long-term effects of smoking and the entire gamut of addictive behaviors, of consuming excessive sugar on health, or of dumping chemicals and wastes into waterways. All such contingencies involve repetitive behavior with positive short-term and negative long-term consequences, and differ only in the descriptions of the A s and C s and of the variable that is changing (e.g., Δh for health or Δ temp for temperature, as above). In all these cases, the Cregister would show the cumulative effect at every interim point.
6.4. Competitive depletion of a limited supply
If two parties concurrently and incrementally consume a limited supply, the ultimate consequence is depletion of the supply.
Examples. Cats lapping milk from the same bowl, overfishing in a body of water, overlogging a forest.

In the diagram, the initial magnitude Minit of the limited supply Csupply would be progressively reduced by the amounts consumed by the two parties-a representing one party and b all the others. Every ni th of a 's n consumption acts reduces the supply by an additional ΔiMinit , and each mj th of b 's m consumption acts reduces the supply by an additional ΔjMinit . 24 The t attributes of the consumption acts can represent rates or dura-
[1]tions. When the M of the supply has thus reached zero or some other threshold, the external agency e terminates (eAMedt) the consumption cycles. The description of the effects of this contingency can be tuned by the usual perceive and predict modifiers of the three C s and by the values of their M s or ΔM s.
6.5. Registering points in a game: keeping score and communicating it
In many kinds of games, like basketball, soccer, or football, the winner is the player or team that scored the most points, often by the end of a certain time period. In the diagram, every aA and bA represents the scoring of a point, and the register Cscore register shows the scores of the two teams during the game. The score, shown by the summation formula, is a magnitude dimension

of the Cscore register -
perceiving it are not shown in the diagram.
6.6. Feedback regarding progress in races
Most games, races, or contests end when one of the parties has crossed a finish line, scored more points than the other party at the end of time T, or has met some other definition of the goal whose achievement determines the winner. The contestants’ acts that consequate progress toward the goal can consist, for example, of a runner’s strides or a rower’s oar strokes. The two progress registers would show each contestant’s progress after any particular number of such acts, as the summation of all progress increments up to that point. The pre-subscripts of the progress registers would show whether each party has access to their own and/or each other’s progress indicators, information that is usually important in such contingencies.
Examples of races or contests where each party knows only its own state of progress. Two research teams racing to be first to publish an important discovery; two corporations competing to be first to bring a new product to market (see Mechner, 2008).
6.7. Divergent points of view: loans and insurance
When a loan reaches its term, the interest payment cycle is terminated and the borrower b either repays the loan or defaults. From lender a 's point of view, these consequences would have probabilities p and 1−p. In the case of a default, a then has a choice between several acts, each having a different consequence. From b 's point of view, the possible consequences of a 's decision process would have probabilities p and 1−p. A register could display the accumulated interest payments as the loan approaches maturity (see Mechner, 2008).
24 The term M could obviously be any function defining the magnitude of the change at each decrement. ↩︎
A similar example is an insurance contract, which usually involves the payment of insurance premiums on a time cycle analogous to that for interest payments. Here, a register for the accumulated premium payments reflects the perspective of the insurer. The diagram for the full contingency (see Mechner, 2008) shows an external agency e that unpredictably generates possible mishaps against which the beneficiary is insured. The beneficiary’s point of view shows the possible acts of the insurer in case of such a mishap (e.g., paying the award, disputing the entitlement, undertaking a study of circumstances), as alternative consequences with different probabilities, and the insurer’s point of view shows them as a choice or decision.
6.8. Elections
In elections, the campaigning acts of each party are assumed to consequate votes for it. A summation term in the two registers could show the presumed number of votes each party has accumulated up to any point in time. The winner is determined by the difference in the number of votes accumulated by the two parties by Election Day (see Mechner, 2008).
7. Applying behavioral contingency analysis
7.1. The value of behavioral contingency analysis
The behavioral contingency language can be used to address practical problem situations in diverse fields of human affairs. If the behavioral outcomes of a situation are important - potentially very valuable or very threatening - the time and effort involved in analyzing the contingencies may be justified.
In practical applications, the analyst’s goal would usually be to gain a better understanding of the contingencies that are at play in the situation so as to increase his ability to modify them and thereby come closer to achieving the desired behavioral outcomes. The result of the analysis may reveal that the contingencies are different from what they were thought to be or that there are some at play that were not noticed, especially when the situation is complex and involves multiple parties. A systematic behavioral contingency analysis may also expand the list of the parties that could be considered, their possible acts and the consequences of those acts, the probabilities and magnitudes of those consequences, and the parties’ relevant perceptions, predictions, misperceptions, and mispredictions regarding aspects of the situation. In research applications, the value resides in a clearer and more complete understanding of the behavioral contingencies, and in their objective and operational specification when they constitute independent variables.
7.2. Using prompts as an algorithm
The prompts listed below constitute an algorithm for guiding the process of performing a behavioral contingency analysis of any situation. These prompts help the analyst register every relevant thing he knows or assumes about the situation being analyzed. Each prompt is understood to be qualified by the words “where relevant to the analyst’s desired focus.” In practice, the
answers to most of the listed prompts would not be relevant to the desired focus and therefore not needed.
- Identify and list the parties involved in the situation.
- For each party, indicate its possible act(s) A.
- For each act, indicate its possible consequence C.
- Indicate the valence of each C for each party.
- Indicate the magnitude M of each valence.
- For each act (where relevant) indicate a duration variable.
- For each C, indicate its probability p.
- For each p, indicate the party(ies) that might have a prediction/estimation of it.
- For each C, indicate the time lags T.
- For each T, indicate any A or T that may change or terminate it.
- For each C, indicate any A or T that might prevent or change it.
- For each termination, indicate the replacing C or contingency.
- For each p, indicate any A or T that might change it.
- For each A,C, agent of A, and their modifiers indicate the party(ies) that perceive, predict, misperceive, mispredict, or do not perceive or predict it.
- For each M, indicate the party(ies) that misperceive or idiosyncratically perceive it.
- Indicate all A s and T s that may initiate recycling arrows, and the termination points of these arrows.
- For each recycling arrow, indicate n where it has significance.
- Define any consequence that changes as a function of n.
- If the change in that quantity has an end point, define that end point, and the consequence C of it being reached.
When responding to prompts that involve time, magnitude, or probability, the analyst may initially just note the variable, and only when known would he indicate actual or relative values.
Just going through the process of responding to these prompts would tend to improve an analyst’s understanding of the operative contingencies, the parties to be taken into account, and the factors and variables to be considered. The analyst would also be prompted to identify and confront areas of ignorance or uncertainty about the situation.
7.3. The role of behavioral science
The contingency structures that an analyst produces when analyzing any given situation 25 would flow directly from the information, beliefs, and assumptions he registered and entered
25 In practice, large and intricate diagrams are difficult to display in two dimensions. The analyst can bypass the need to do so by using the prompt method, which permits full use of the language’s hierarchical/recursive features to express any desired nuance without the constraints of printed diagrams. The creation of more complex diagrams will require computer software that can convert the registered information into multi-dimensional behavioral contingency structures. While these would exist only in the computer memory, two-dimensional diagrams of particular portions could be printed out for use in checking and debugging. The development of software with these capabilities is in progress at the time of writing. ↩︎
in response to the prompts. To predict the resulting behavioral outcomes, he would draw upon his knowledge of the behavioral effects of various types of contingencies, of various types of behavioral histories, of signaling positive or negative consequences having various relative magnitudes and probabilities, of cues regarding contingencies, and of time factors. The contingency diagrams themselves obviously do not embody such knowledge and therefore cannot generate predictions of behavioral outcomes. Such predictions require the application of knowledge provided by the behavioral sciences.
The analyst can iteratively revisit and readjust the contingency information he entered in response to the prompts when he sees a discrepancy between the predicted behavioral outcomes and his expectations. The modification and design of contingencies by this general method could become one of the practical uses of contingency analysis in operations research, computer simulation, and the management of behavioral contingencies in any area of human affairs. As the database of knowledge provided by the behavioral sciences continues to expand, the usefulness of behavioral contingency analysis can be expected to increase correspondingly.
7.4. The pedagogic value of behavioral contingency analysis
The sometimes heard comment that behaviorism has limited relevance to complex human behavior or to practical concerns can be answered by pointing to the sweeping applicability of behavioral contingency analysis. Students who learn to use the present behavioral contingency language, and make efforts to apply it, quickly become persuaded of the great and general relevance of behavior analysis to human affairs. 26
Acknowledgements
The author expresses his deep appreciation for the valuable and substantive contributions to this work made by M. Jackson Marr, Alliston K. Reid, Murray Sidman, and Lanny Fields, for the helpful comments of Prof. Giulio Bolacchi, Sigrid Glenn, Richard Malott, Parsla Vintere, and Claire Poulson, for Philip N. Chase’s encouragement to submit the paper to SQAB, for the feedback from the AILUN university students who made the effort to learn the contingency language and for the valuable editorial assistance of Laurilyn D. Jones and Karyn Slutsky, and posthumously for the encouragement of this project that Donald A. Cook and Thom Verhave provided almost fifty years ago. The author welcomes communications with researchers interested in using the contingency language or in extending the range of its applications.
References
Baum, W., 1979. Matching, undermatching and overmatching in studies of choice. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 32, 269-281.
Baum, W.M., Heath, J.L., 1992. Behavioral explanations and intentional explanations in psychology. Amer. Psychologist 47, 1312-1317.
Becker, G.S., 1976. The Economic Approach to Human Behavior. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, 320 pp .
Becker, G.S., 1995. Crime and punishment: An economic approach. In: Febrero, R., Schwartz, P.S. (Eds.), The Essence of Becker. Hoover Institution Press, Stanford, CA, pp. 463-517.
Becker, G.S., 1997. The economic way of looking at life: Nobel lecture. In: Persson, T. (Ed.), Nobel Lectures, Economics 1991-1995. World Scientific Publishing Co, Singapore, pp. 38-58.
Camerer, C.F., Lowenstein, G., 2003. Behavioral economics: past, present, future. In: Camerer, C.F., Lowenstein, G., Rabin, M. (Eds.), Advances in Behavioral Economics. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp. 3-51.
Case, D.A., Fantino, E., 1989. Instructions and reinforcement in the observing behavior of adults and children. Learning and Motivation 20, 373-412.
Chisholm, R.M., 1957. Perceiving: A Philosophical Study. Cornell University Press, Oxford, England, 203 pp .
Chisholm, D.C., Cook, D.A., 1995. A model of cause-effect relations in the study of behavior. Behav. Anal. 18, 99-111.
Clemons, E.K., Schimmelbusch, H., 2007. The environmental prisoners’ dilemma. At http://opim.wharton.upenn.edu/clemons/blogs/prisonersblog. pdf.
Commons, M.L., 1987. Preface. In: Commons, M.L., Mazur, J.E., Nevin, J.A., Rachlin, H. (Eds.), The Effect of Delay and of Intervening Events on Reinforcement Value Quantitative Analyses of Behavior, vol. 5. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale, NJ.
Cricchfield, T.S., Kollins, S.H., 2001. Temporal discounting: basic research and the analysis of socially important behavior. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 34, 101−122.
Dinsmoor, J.A., 1983. Separating the effects of salience and disparity on the rate of observing. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 40, 253-264.
Dinsmoor, J.A., Browne, M.P., Lawrence, C.E., 1972. A test of the negative discriminative stimulus as a reinforcer of observing. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 18,79−85.
Erickson, S.J., Achilles, G., 2004. Cognitive behavioral therapy with children and adolescents. In: Steiner, H. (Ed.), Handbook of Mental Health Interventions in Children and Adolescents: An Integrated Developmental Approach. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, pp. 525-556.
Fantino, E., Gaitan, S., Kennelly, A., Stolarz-Fantino, S., 2007. How reinforcer type affects choice in economic games. Behav. Processes 75, 107−114.
Ferster, C.F., Skinner, B.F., 1957. Schedules of Reinforcement. AppletonCentary-Crofts, New York.
Findley, J.D., 1962. An experimental outline for building and exploring multioperant behavior repertoires. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 5, 113-166.
Foxall, G.R., 2007. Explaining consumer choice: coming to terms with intentionality. Behav. Processes 75, 129-145.
Gelman, A., 2003. Forming voting blocks and coalitions as a prisoner’s dilemma: a possible theoretical explanation for political instability. Contrib. to Econ. Anal. Policy, 2, Article 13.
Glenn, S.S., 2003. Operant contingencies and the origin of cultures. In: Lattal, K.A., Chase, P.N. (Eds.), Behavior Theory and Philosophy. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp. 223-242.
Glenn, S.S., 2004. Individual behavior, culture and social change. Behavior Analyst 27, 133-151.
Glenn, S.S., Madden, G.J., 1995. Units of interaction, evolution and replication: Organic and behavioral parallels. Behavior Analyst 18, 237-251.
Goldwater, B.C., Acker, L.E., 1995. A descriptive notation system for contingency diagramming in behavior analysis. Behav. Anal. 18, 113-121.
Green, L., Myerson, J., Schneider, R., 2003. Is there a magnitude effect in tipping? Psychon. Bull. Rev. 10, 381-386.
Green, L., Myerson, J., Holt, D.D., Slevin, J.R., Estle, S.J., 2004. Discounting of delayed food rewards in pigeons and rats: Is there a magnitude effect? J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 81, 39-50.
26 A PowerPoint tutorial on the behavioral contingency language and its applications can be downloaded from the website http://www.mechnerfoundation.org. Estimated completion time: 3−15 h, depending on time spent on the exercises. The course received a dry run at AILUN University in November of 2007 under the auspices of Prof. Giulio Bolacchi. ↩︎
Green, L., Myerson, J., Shah, A.K., Estle, S.J., Holt, D.D., 2007. Do adjustingamount and adjusting-delay procedures produce equivalent estimates of subjective value in pigeons? J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 87, 337-347.
Herrnstein, R.J., 1970. On the law of effect. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 13, 243-266.
Herrnstein, R.J., Rachlin, H., Laibson, D.I., 1997. The Matching Law: Papers in Psychology and Economics. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Hertwig, R., Ortmann, A., 2001. Experimental practices in economics: A methodological challenge for psychologists? Behav. & Brain Sci. 24, 383−451.
Hinelner, P.N., 2003. When we speak of intentions. In: Lattal, K.A., Chase, P.N. (Eds.), Behavior Theory and Philosophy. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 422 pp.
Johnson, M.W., Bickel, W.K., 2002. Within-subject comparison of real and hypothetical money rewards in delay discounting. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 77, 129−146.
Keller, F.S., Schoenfeld, W.N., 1950. Principles of Psychology: A Systematic Text in the Science of Behavior. Appleton-Century-Crofts, East Norwalk, CT.
Kowal, B.P., Yi, R., Erisman, A.C., Bickel, W.K., 2007. A comparison of two algorithms in computerized temporal discounting procedures. Behav. Processes 75, 231-236.
Lattal, K.A., 1987. Considerations in the experimental analysis of reinforcement delay. In: Commons, M.L., Mazur, J.E., Nevin, J.A., Rachlin, H. (Eds.), The Effect of Delay and of Intervening Events on Reinforcement Value Quantitative Analyses of Behavior, vol. 5. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale, NJ, pp. 107-123.
Lin, T., 2007. Economic behavior of restaurant tipping. Econ. Bull. 4, 1-10.
MacInnis, M.L.M., 2007. Do rats time filled and empty intervals of equal duration differently? Behav. Processes 75, 182-187.
Malott, R.W., Whaley, D.L., Malott, M.E., 1993. Elementary Principles of Behavior. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Mattaini, M.A., 1995. Contingency diagrams as teaching tools. Behav. Anal. 18, 93-98.
Mazur, J.E., 1987. An adjusting procedure for studying delayed reinforcement. In: Commons, M.L., Mazur, J.E., Nevin, J.A., Rachlin, H. (Eds.), The Effect of Delay and of Intervening Events on Reinforcement Value Quantitative Analyses of Behavior, vol. 5. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale, NJ, pp. 55-73.
Mazur, J.E., 2001. Hyperbolic value addition and general models of animal choice. Psych. Review 108, 96-112.
Mechner, F., 1959. A notation system for the description of behavioral procedures. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2, 133-150.
Mechner, F., Guvverkian, L., Mechner, V., 1963. A fixed interval schedule in which the interval is initiated by a response. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 6, 323-330.
Mechner, F., Latranyi, M., 1963. Behavioral effects of caffeine, methamphetamine, and methylphenidate in the rat. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 6, 331−342.
Mechner, F., 2008. Applications of the language for codifying behavioral contingencies. At http://www.mechnerfoundation.org/.
Michael, J., 1963. Laboratory Studies in Operant Behavior. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Michael, J., Shafer, E., 1995. State notation for teaching about behavioral procedures. Behav. Anal. 18, 123-140.
Millenson, J.R., Leslie, J.C., 1979. Principles of Behavior Analysis, second ed. Macmillan, New York.
Nevin, J.A., Davison, M., Shahan, T.A., 2005. A theory of attending and reinforcement in conditional discriminations. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 84, 281-303.
Pierce, W.D., Epling, W.F., 1995. Behavior Analysis and Learning. PrenticeHall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Rachlin, H., 1995. The value of temporal patterns in behavior. Curr. Direct. Psych. Sci. 4, 188-192.
Rachlin, H., 2006. Notes on discounting. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 85, 425-435.
Rachlin, H., Brown, J., Baker, F., 2001. Reinforcement and punishment in the prisoner’s dilemma game. In: Medin, D.L. (Ed.), The Psychology of Learning and Motivation: Advances in Research and Theory. Academic Press, Dan Diego, CA, pp. 327-364.
Rapoport, A., Chammah, A.M., 1965. Prisoner’s Dilemma. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor, MI.
Sidman, M., 2004. Meeting the world halfway. In: Talk given at the Annual conference of the Association for Behavior Analysis International.
Skinner, B.F., 1938. The Behavior of Organisms: An Experimental Analysis. Appleton-Century-Crofts, Oxford, England. 457 pp.
Skinner, B.F., 1958. Diagramming schedules of reinforcement. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1, 67-68.
Skinner, B.F., 1969. Contingencies of Reinforcement: A Theoretical Analysis. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York.
Snapper, A.G., Kadden, R.M., Inglis, G.B., 1982. Computer technology: state notation of behavioral procedures. Behav. Res. Meth. Instrum. 14, 329−342.
Stephens, K.R., van Haaren, F.P., 1977. The origins and development of state notation and SKED. Behav. Res. Meth. Instrum. 9, 72-74.
Tanaka, H.K., Nomura, M., 1993. SN-FORTH/MSX: a state notation system for controlling behavioral experiments with a low-priced computer. Nippon Seorigaku Zasshi 55, 47-53.
Thomas, E.A.C., Feldman, M.W., 1988. Behavior-dependent contexts for repeated plays of the prisoner’s dilemma. J. Conflict Resolut. 32, 699-726.
Wachtel, P., 1997. Psychoanalysis, Behavior Therapy, and the Relational World. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC.
Weingarten, K., Mechner, F., 1966. A notation system for the analysis of social interaction. In: Verhave, T. (Ed.), Readings in the Experimental Analysis of Behavior. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp. 447-459.
Yi, R., Rachlin, H., 2004. Contingencies of reinforcement in a five-person prisoner’s dilemma. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 82, 161-176.
References (63)
- Baum, W., 1979. Matching, undermatching and overmatching in studies of choice. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 32, 269-281.
- Baum, W.M., Heath, J.L., 1992. Behavioral explanations and intentional expla- nations in psychology. Amer. Psychologist 47, 1312-1317.
- Becker, G.S., 1976. The Economic Approach to Human Behavior. The Univer- sity of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL, 320 pp.
- Becker, G.S., 1995. Crime and punishment: An economic approach. In: Febrero, R., Schwartz, P.S. (Eds.), The Essence of Becker. Hoover Institution Press, Stanford, CA, pp. 463-517.
- Becker, G.S., 1997. The economic way of looking at life: Nobel lecture. In: Persson, T. (Ed.), Nobel Lectures, Economics 1991-1995. World Scientific Publishing Co, Singapore, pp. 38-58.
- Camerer, C.F., Lowenstein, G., 2003. Behavioral economics: past, present, future. In: Camerer, C.F., Lowenstein, G., Rabin, M. (Eds.), Advances in Behavioral Economics. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp. 3-51.
- Case, D.A., Fantino, E., 1989. Instructions and reinforcement in the observing behavior of adults and children. Learning and Motivation 20, 373-412.
- Chisholm, R.M., 1957. Perceiving: A Philosophical Study. Cornell University Press, Oxford, England, 203 pp.
- Chisholm, D.C., Cook, D.A., 1995. A model of cause-effect relations in the study of behavior. Behav. Anal. 18, 99-111.
- Clemons, E.K., Schimmelbusch, H., 2007. The environmental prisoners' dilemma. At http://opim.wharton.upenn.edu/clemons/blogs/prisonersblog. pdf. Commons, M.L., 1987. Preface. In: Commons, M.L., Mazur, J.E., Nevin, J.A., Rachlin, H. (Eds.), The Effect of Delay and of Intervening Events on Reinforcement Value Quantitative Analyses of Behavior, vol. 5. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale, NJ.
- Critchfield, T.S., Kollins, S.H., 2001. Temporal discounting: basic research and the analysis of socially important behavior. J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 34, 101-122.
- Dinsmoor, J.A., 1983. Separating the effects of salience and disparity on the rate of observing. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 40, 253-264.
- Dinsmoor, J.A., Browne, M.P., Lawrence, C.E., 1972. A test of the negative discriminative stimulus as a reinforcer of observing. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 18, 79-85.
- Erickson, S.J., Achilles, G., 2004. Cognitive behavioral therapy with children and adolescents. In: Steiner, H. (Ed.), Handbook of Mental Health Interven- tions in Children and Adolescents: An Integrated Developmental Approach. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco, pp. 525-556.
- Fantino, E., Gaitan, S., Kennelly, A., Stolarz-Fantino, S., 2007. How rein- forcer type affects choice in economic games. Behav. Processes 75, 107-114.
- Ferster, C.F., Skinner, B.F., 1957. Schedules of Reinforcement. Appleton- Century-Crofts, New York.
- Findley, J.D., 1962. An experimental outline for building and exploring multi- operant behavior repertoires. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 5, 113-166.
- Foxall, G.R., 2007. Explaining consumer choice: coming to terms with inten- tionality. Behav. Processes 75, 129-145.
- Gelman, A., 2003. Forming voting blocks and coalitions as a prisoner's dilemma: a possible theoretical explanation for political instability. Contrib. to Econ. Anal. Policy, 2, Article 13.
- Glenn, S.S., 2003. Operant contingencies and the origin of cultures. In: Lat- tal, K.A., Chase, P.N. (Eds.), Behavior Theory and Philosophy. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp. 223-242.
- Glenn, S.S., 2004. Individual behavior, culture and social change. Behavior Analyst 27, 133-151.
- Glenn, S.S., Madden, G.J., 1995. Units of interaction, evolution and replication: Organic and behavioral parallels. Behavior Analyst 18, 237-251.
- Goldwater, B.C., Acker, L.E., 1995. A descriptive notation system for contin- gency diagramming in behavior analysis. Behav. Anal. 18, 113-121.
- Green, L., Myerson, J., Schneider, R., 2003. Is there a magnitude effect in tipping? Psychon. Bull. Rev. 10, 381-386.
- Green, L., Myerson, J., Holt, D.D., Slevin, J.R., Estle, S.J., 2004. Discounting of delayed food rewards in pigeons and rats: Is there a magnitude effect? J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 81, 39-50.
- Green, L., Myerson, J., Shah, A.K., Estle, S.J., Holt, D.D., 2007. Do adjusting- amount and adjusting-delay procedures produce equivalent estimates of subjective value in pigeons? J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 87, 337-347.
- Herrnstein, R.J., 1970. On the law of effect. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 13, 243-266.
- Herrnstein, R.J., Rachlin, H., Laibson, D.I., 1997. The Matching Law: Papers in Psychology and Economics. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
- Hertwig, R., Ortmann, A., 2001. Experimental practices in economics: A methodological challenge for psychologists? Behav. & Brain Sci. 24, 383-451.
- Hineline, P.N., 2003. When we speak of intentions. In: Lattal, K.A., Chase, P.N. (Eds.), Behavior Theory and Philosophy. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, 422 pp.
- Johnson, M.W., Bickel, W.K., 2002. Within-subject comparison of real and hypothetical money rewards in delay discounting. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 77, 129-146.
- Keller, F.S., Schoenfeld, W.N., 1950. Principles of Psychology: A Systematic Text in the Science of Behavior. Appleton-Century-Crofts, East Norwalk, CT. Kowal, B.P., Yi, R., Erisman, A.C., Bickel, W.K., 2007. A comparison of two algorithms in computerized temporal discounting procedures. Behav. Pro- cesses 75, 231-236.
- Lattal, K.A., 1987. Considerations in the experimental analysis of reinforcement delay. In: Commons, M.L., Mazur, J.E., Nevin, J.A., Rachlin, H. (Eds.), The Effect of Delay and of Intervening Events on Reinforcement Value Quantitative Analyses of Behavior, vol. 5. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale, NJ, pp. 107-123.
- Lin, T., 2007. Economic behavior of restaurant tipping. Econ. Bull. 4, 1-10.
- MacInnis, M.L.M., 2007. Do rats time filled and empty intervals of equal dura- tion differently? Behav. Processes 75, 182-187.
- Malott, R.W., Whaley, D.L., Malott, M.E., 1993. Elementary Principles of Behavior. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- Mattaini, M.A., 1995. Contingency diagrams as teaching tools. Behav. Anal. 18, 93-98.
- Mazur, J.E., 1987. An adjusting procedure for studying delayed reinforcement. In: Commons, M.L., Mazur, J.E., Nevin, J.A., Rachlin, H. (Eds.), The Effect of Delay and of Intervening Events on Reinforcement Value Quantitative Analyses of Behavior, vol. 5. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Hillsdale, NJ, pp. 55-73.
- Mazur, J.E., 2001. Hyperbolic value addition and general models of animal choice. Psych. Review 108, 96-112.
- Mechner, F., 1959. A notation system for the description of behavioral proce- dures. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2, 133-150.
- Mechner, F., Guevrekian, L., Mechner, V., 1963. A fixed interval schedule in which the interval is initiated by a response. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 6, 323-330.
- Mechner, F., Latranyi, M., 1963. Behavioral effects of caffeine, metham- phetamine, and methylphenidate in the rat. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 6, 331-342.
- Mechner, F., 2008. Applications of the language for codifying behavioral con- tingencies. At http://www.mechnerfoundation.org/.
- Michael, J., 1963. Laboratory Studies in Operant Behavior. McGraw-Hill, New York.
- Michael, J., Shafer, E., 1995. State notation for teaching about behavioral pro- cedures. Behav. Anal. 18, 123-140.
- Millenson, J.R., Leslie, J.C., 1979. Principles of Behavior Analysis, second ed. Macmillan, New York.
- Nevin, J.A., Davison, M., Shahan, T.A., 2005. A theory of attending and reinforcement in conditional discriminations. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 84, 281-303.
- Pierce, W.D., Epling, W.F., 1995. Behavior Analysis and Learning. Prentice- Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- Rachlin, H., 1995. The value of temporal patterns in behavior. Curr. Direct. Psych. Sci. 4, 188-192.
- Rachlin, H., 2006. Notes on discounting. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 85, 425-435.
- Rachlin, H., Brown, J., Baker, F., 2001. Reinforcement and punishment in the prisoner's dilemma game. In: Medin, D.L. (Ed.), The Psychology of Learn- ing and Motivation: Advances in Research and Theory. Academic Press, Dan Diego, CA, pp. 327-364.
- Rapoport, A., Chammah, A.M., 1965. Prisoner's Dilemma. University of Michi- gan Press, Ann Arbor, MI.
- Sidman, M., 2004. Meeting the world halfway. In: Talk given at the Annual conference of the Association for Behavior Analysis International.
- Skinner, B.F., 1938. The Behavior of Organisms: An Experimental Analysis. Appleton-Century-Crofts, Oxford, England, 457 pp.
- Skinner, B.F., 1958. Diagramming schedules of reinforcement. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 1, 67-68.
- Skinner, B.F., 1969. Contingencies of Reinforcement: A Theoretical Analysis. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York.
- Snapper, A.G., Kadden, R.M., Inglis, G.B., 1982. Computer technology: state notation of behavioral procedures. Behav. Res. Meth. Instrum. 14, 329-342.
- Stephens, K.R., van Haaren, F.P., 1977. The origins and development of state notation and SKED. Behav. Res. Meth. Instrum. 9, 72-74.
- Tanaka, H.K., Nomura, M., 1993. SN-FORTH/MSX: a state notation system for controlling behavioral experiments with a low-priced computer. Nippon Seirigaku Zasshi 55, 47-53.
- Thomas, E.A.C., Feldman, M.W., 1988. Behavior-dependent contexts for repeated plays of the prisoner's dilemma. J. Conflict Resolut. 32, 699-726.
- Wachtel, P., 1997. Psychoanalysis, Behavior Therapy, and the Relational World. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC.
- Weingarten, K., Mechner, F., 1966. A notation system for the analysis of social interaction. In: Verhave, T. (Ed.), Readings in the Experimental Analysis of Behavior. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp. 447-459.
- Yi, R., Rachlin, H., 2004. Contingencies of reinforcement in a five-person pris- oner's dilemma. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 82, 161-176.
 Francis Mechner
Francis Mechner