Figure 18 – uploaded by Tuong Manh Vu

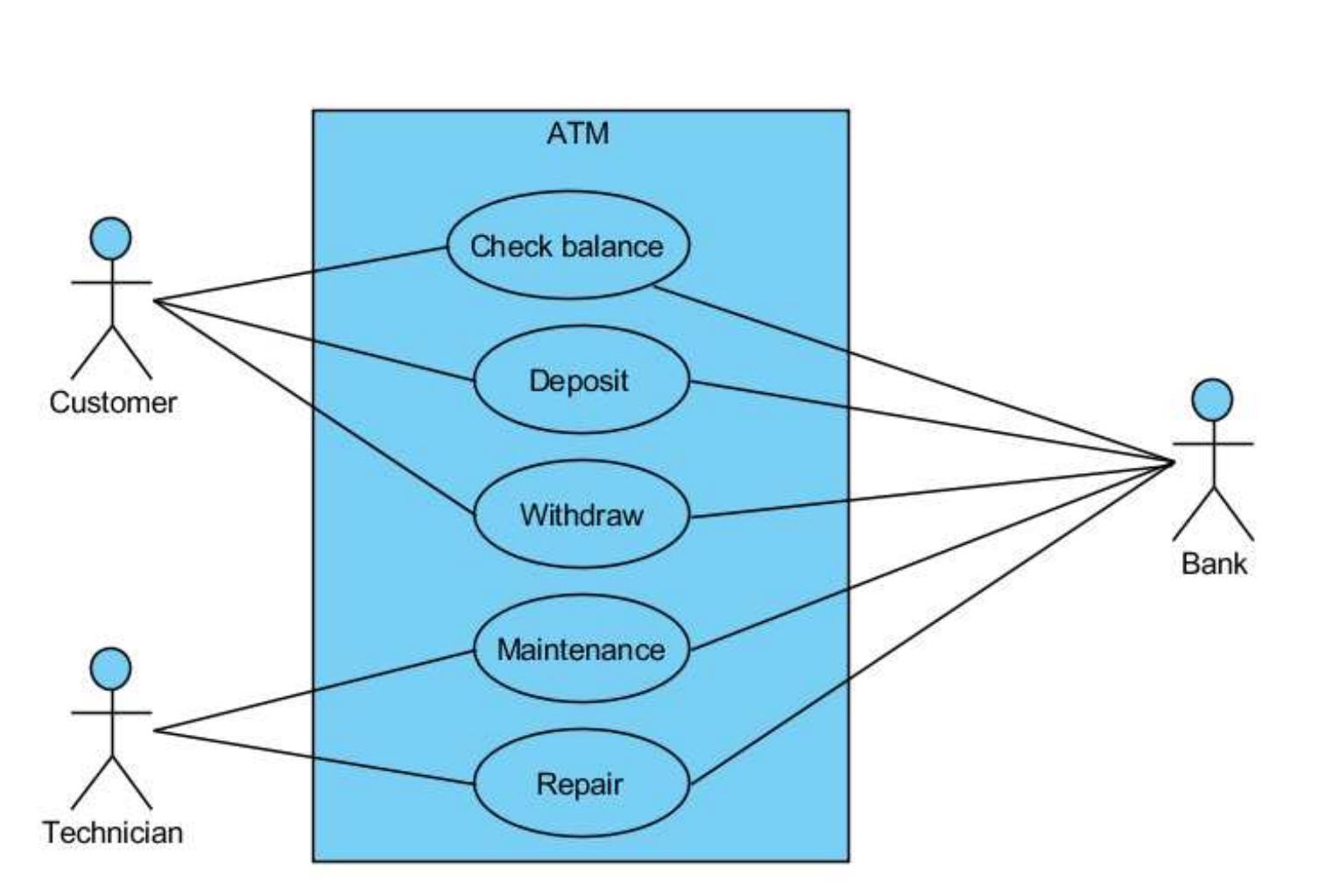
Figure 3 11 A sequence diagram of an ATM system line, called a lifeline. Messages are drawn as a horizontal arrow from a sender to a receivet Figure 3.11 shows a sequence diagram when a customer uses an ATM to check the balance of his bank account. There are three entities: customer, bank system, and database. Afte: inserting the card into the ATM, the customer enters the PIN. The bank system will check the PIN against the database. If the PIN is correct, the customer will be granted access, then car request his balance. The bank system will get the balance from the database, then inform the customer. If the PIN is wrong, the customer cannot gain access, and has to enter the PIN again To represent the loop (keep entering PIN) and if-then-else logic (correct or wrong PIN), twc kinds of combined fragments (loop and alt) are used. Each is represented as a box. A loof combined fragment executes multiple times. An alt (alternatives) combined fragment shows conditional flow by modelling if-then-else logic. In Figure 3.11, the alt combined fragmen is split into two sections by a dashed line: the first section shows the interaction when wrong PIN is enter, while the second section shows the messages when the PIN is correct and the use: requests the balance.
Related Figures (82)






































































Connect with 287M+ leading minds in your field
Discover breakthrough research and expand your academic network
Join for free