Figure 2 – uploaded by Josep Antoni Alcover
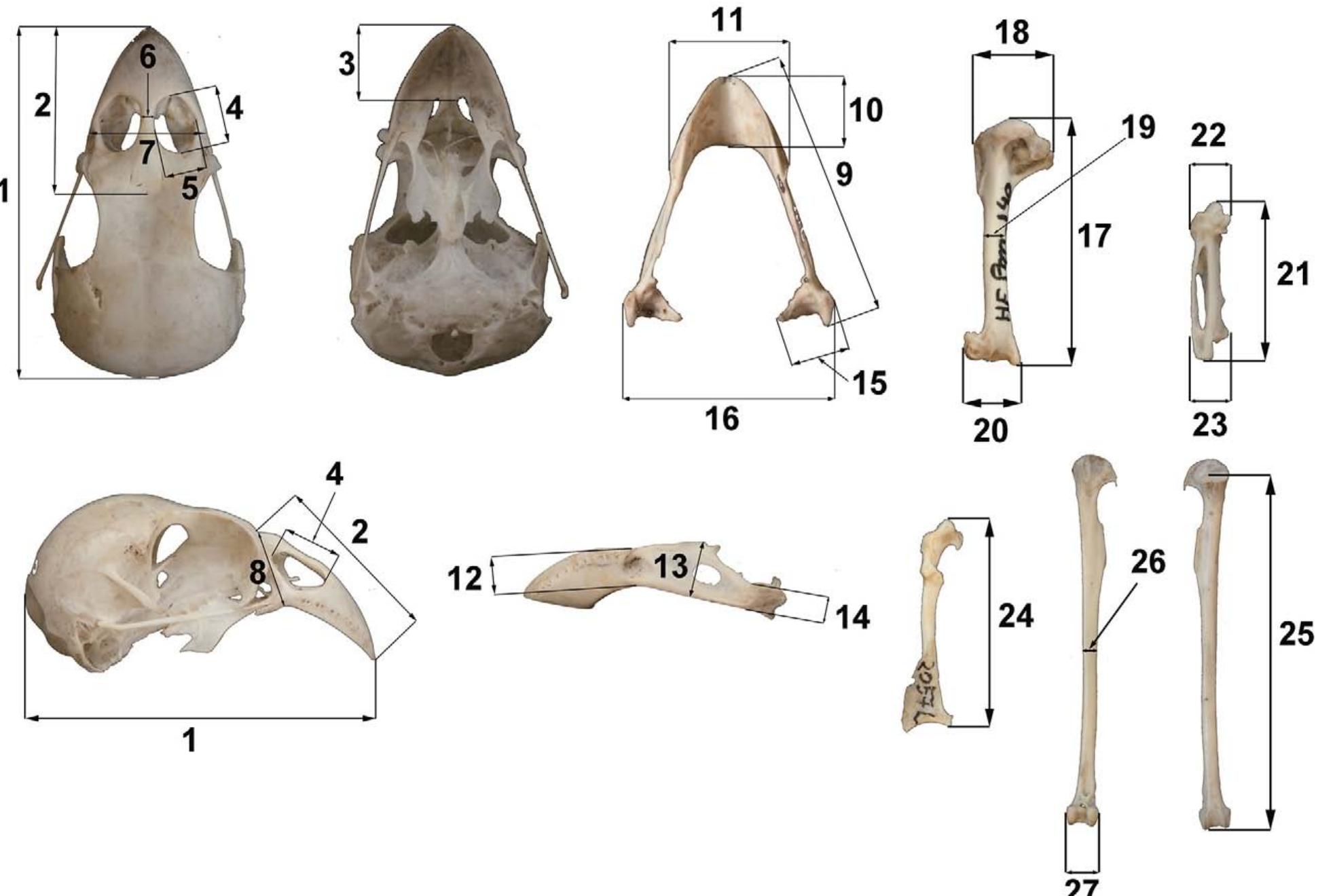
Figure 2 Measurements. 1: cranium length, from the apex of t premaxilla, from the nasofrontal hinge to the premaxillary apex; the premaxillary apex; 4: nostril length, 5: nostril width; 6: proc ht; 9: mandible length; 10: length of the mandibu ht of mandibular ramus; 13: maximum mandibular h ateral cotyla; 16: maximum width of the mandible; 17: humerus length, from the caput humeris to the end of processu. ft at midpoint; 20: humerus distal width; 21: carpometacarpu: heig! heig! the | eng flexorius; 18: proximal humerus width; 19: humerus wid h; 22: carpometacarpus proximal width; 23: carpometacarpus distal width; 24: coracoid acrocoracoideus to the angulus medialis coracoidei. 25 the d end. istal part o f the distal condyles; 26: tibiotarsus widt ar symp 3: ventral length of the premaxi minimal mandibular height at t th of sha he premaxilla to the end of the cranium; 2: dorsal length of th la, from the palatine notch t essus dorsonarialis width; 7: premaxilla width; 8: premaxill: hysis; 11: maximum width of the symphysis; 12: minimun eight; 14: he lateral cotyla; 15: length o length, from the processu. : tibiotarsus length from the apex of the facies articularis medialis t h of shaft at midpoint; and 27: tibiotarsus maximum width of the dista









