Figure 7 – uploaded by Ihsan Sabuncuoglu

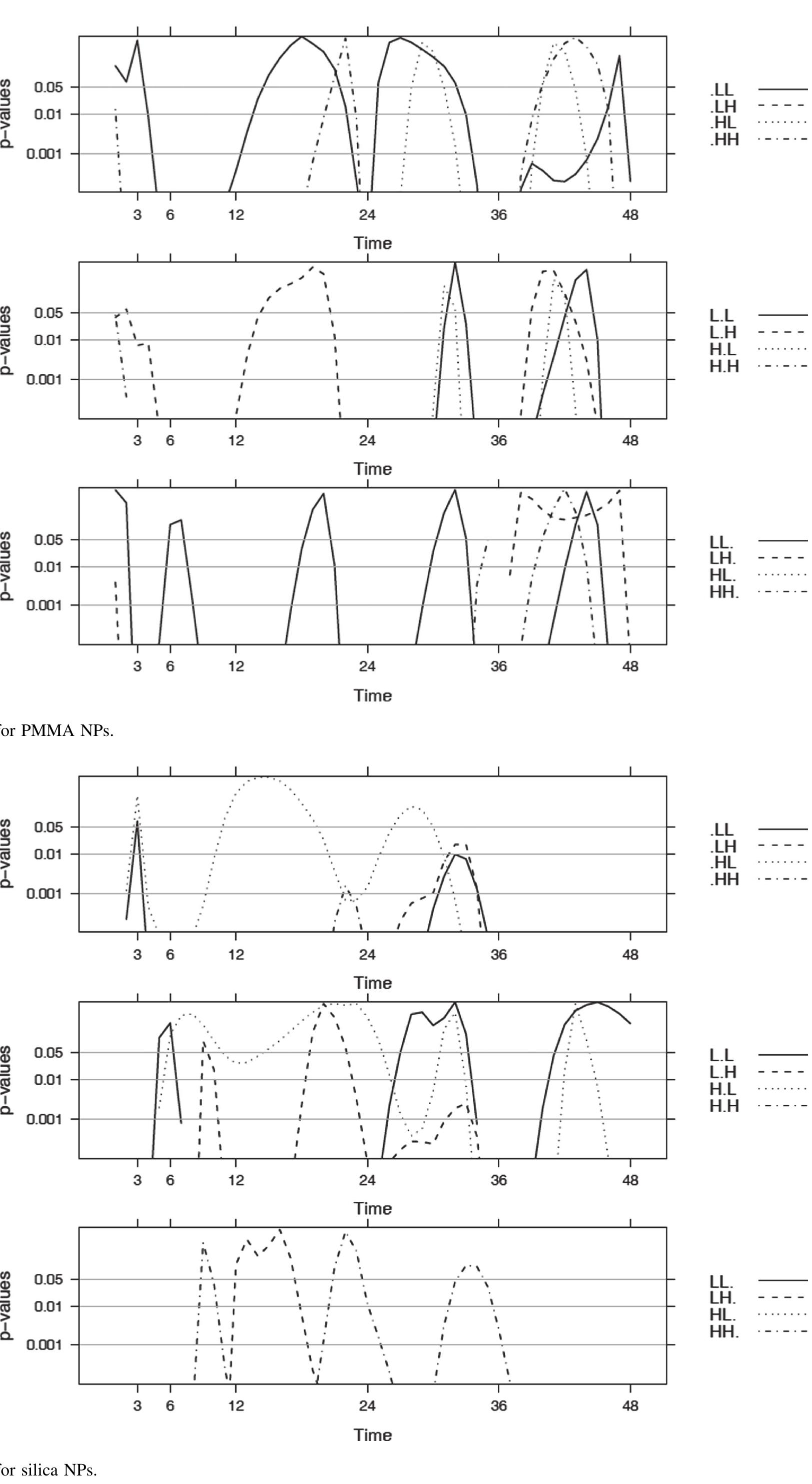
Figure 8 Silica simulation (Concentration: 1/1000 mg/l). The null hypothesis is rejected when the p-value is less than the significance level. Based on the two-sample t-test statistic and the DF, the p-value is determined. Since we have a two-tailed test, the p-value is the probability that a t-ratio having 49 degrees of freedom is greater than 2.01 or less than —2.01. The significance level is 0.05; P(t < —2.01) = 0.025 and P(t > 2.01) = 0.025. In order to have a p-value lower than the significance level (0.05), the t-score should be less than —2.01 or greater than 2.01.