National address databases - a data grid approach
Abstract
The original purpose of addresses was to enable the correct and unambiguous delivery of postal mail. The advent of computers and more specifically geographic information systems (GIS) opened up a whole new range of possibilities for the use of addresses, such as routing and vehicle navigation, spatial demographic analysis, geo-marketing, and service placement and delivery. Such functionality requires a database which can store spatial data effectively. In this paper we present address databases and motivate the need for national address databases. We describe models used for national address databases, and present our evaluation framework for an address database at a national level within the context of a spatial data infrastructure (SDI). The models of data harvesting, federated databases and data grids are analyzed and evaluated according to our novel framework, and we show that the data grid model has some unique features that make it attractive for a national address database in an environment where centralized control and/or coordination is difficult or undesirable.
Key takeaways
AI
AI
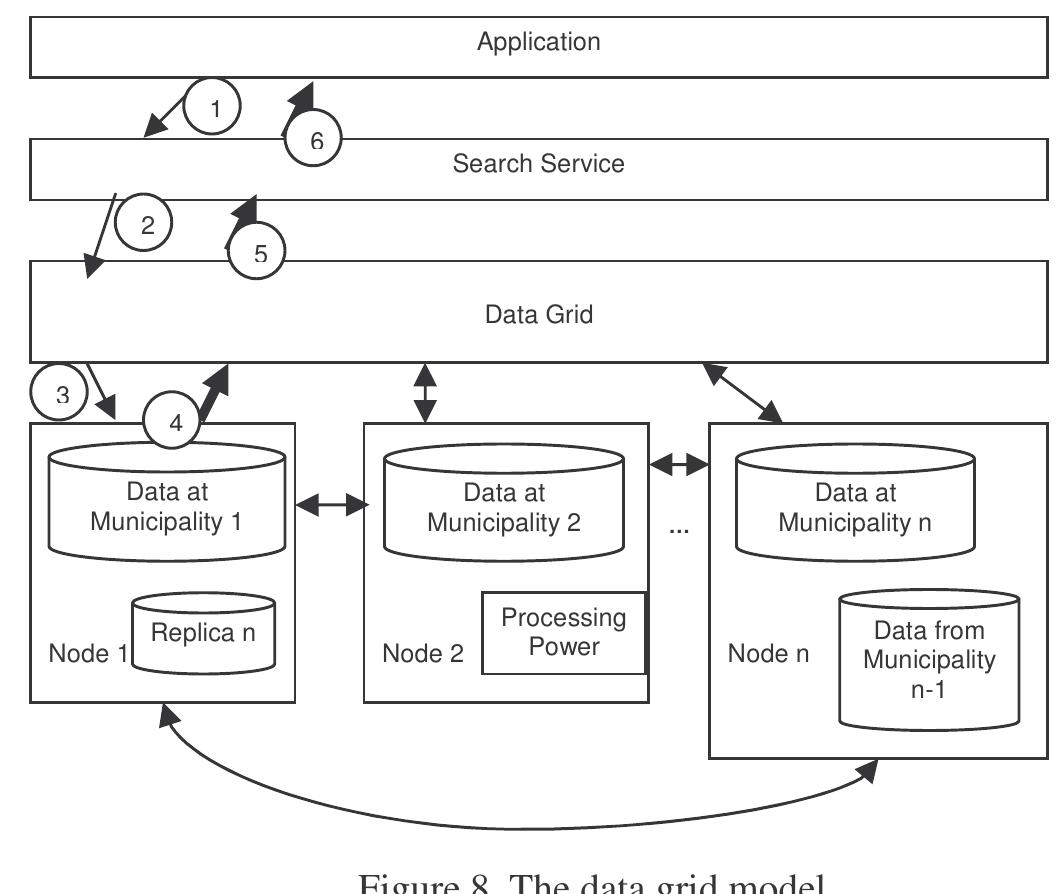
- The data grid model offers a decentralized approach for national address databases, enhancing flexibility and heterogeneity.
- National address databases (NAD) are essential for effective public service delivery, particularly in spatial planning.
- The research evaluates three information federation models: data harvesting, federated databases, and data grids.
- Address data in South Africa is diverse, necessitating standardization to resolve ambiguities and ensure accessibility.
- The paper aims to propose an evaluation framework for assessing national address database models within spatial data infrastructures (SDI).
References (30)
- AREFIN M. A., SADIK M.S., COETZEE S.M., BISHOP J.M., 2006, Alchemi vs Globus: a performance comparison, 4th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, December 19-21 2006, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- BAKER M., APON A., FERNER C., BROWN J., 2005, Emerging grid standards, IEEE Computer April 2005, Vol. 38 No.4 pp.43-50.
- COETZEE S.M. AND BISHOP J.M., 1998, A new way to query GIS on the web, IEEE Software, May/June 1998, 15(3): 31-40.
- Constitution of the Republic of South Africa 1996, available online at http://www.polity.org.za
- CROMPVOETS J., BREGT A., RAJABIFARD A., WILLIAMSON I., 2005, Accessing the worldwide developments of national spatial data clearinghouses, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, October-November 2004, vol. 18, no. 7, pp.665-689.
- FAHEY D. AND FINCH F., 2006, Geodirectory Technical Guide, available at http://www.geodirectory.ie/downloads/GeoDirectoryTechnicalGuide_v8.pdf, (accessed April 2007).
- Financial Intelligence Centre Act of South Africa, 2001, available online at http://www.acts.co.za/fica/index.htm (accessed April 2007)
- FOSTER I., What is the Grid? A three point checklist, GRIDToday, Vol. 1 No. 6, July 22, 2002.
- FOSTER I. AND KESSELMAN C., 1999, Epilogue in The GRID Blueprint for a New Computing Infrastructure, (Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Francisco USA).
- HARVEY F and TULLOCH D, 2006, Local-government data sharing: Evaluating the foundations of spatial data infrastructures, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, August 2006, Vol. 20, No. 7, pp743-768.
- GeoDirectory website. http://www.geodirectory.ie (accessed April 2007)
- GEORGIADOU S.K., PURI S.K. and SAHAY S., 2006, Towards a potential research agenda to guide the implementation of spatial data infrastructures -A case study from India, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, November 2005, Vol. 19, No. 10, pp1113-1130.
- JACOBY S., SMITH J., TING L., AND WILLIAMSON I., 2002, Developing a common spatial data infrastructure between state and local government-an Australian case study, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, June 2002, Vol. 6 No 4, pp 305-322.
- MATHERI M., 2005, Challenges facing the creation of a standard South African address system, FIG Working Week and 8 th Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Conference (GSDI-8), 16-21 April 2005, Cairo, Egypt.
- MCDOUGALL K., RAJABIFARD A. AND WILLIAMSON I., 2005, What will motivate local governments to share spatial information?, SSC 2005 Spatial Intelligence, Innovation and Praxis: The national biennial Conference of the Spatial Sciences Institute, September, 2005, Melbourne, Australia.
- MORAD M., 2002, British standard 7666 as a framework for geocoding land and property information the UK, Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, September 2002, Volume 26, Issue 5, pp 483-492.
- OGF Transaction Management Research Group (GGF), 2005, Proposed Grid Transactions RG -Charter, available online at http://www.ogf.org/tm-rg- charter.html (accessed September 2006)
- Open Grid Forum (OGF), OGSA Glossary of Terms, July 2006, available online at http://forge.gridforum.org/projects/ogsa-wg (accessed April 2007)
- OGSA-DAI Website. http://www.ogsadai.org.uk/ (accessed April 2007)
- Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC), Geospatial Semantic Web Interoperability Experiment Report, August 2006, available online at http://www.opengeospatial.org/standards/dp (accessed April 2007)
- PAULL D., 2003, A Geocoded National Address File for Australia: The G-NAF What, Why, Who and When, Report by the CEO of PSMA Australia Limited, available online at http://www.psma.com.au/resources/the-g-naf-what-why-who- and-when (accessed April 2007)
- Public Sector Mapping Agencies (PSMA) Australia Website. www.psma.com.au (last accessed April 2007)
- RAJABIFARD A., BINNS A., MASSER I. and WILLIAMSON I., 2006, The role of sub- national government and the private sector in future spatial data infrastructures, International Journal of Geographical Information Science, August 2006, Vol.20, No.7, pp727-741.
- SHETH A.P. AND LARSON J.A., 1990, Federated database systems for managing distributed, heterogenous, and autonomous databases, ACM Computing Surveys, September 1990, Vol.22, No.3, pp.183-236.
- SOUTH AFRICAN BUREAU OF STANDARDS (SABS), 2007, Geographic Information -Address Standard, Draft Standard, April 2007, SABS Technical Sub-committee 71E -Geographic Information.
- Spatial Data Infrastructure Act of South Africa, 2003, available online at www.polity.org.za
- TULADHAR A., RADWAN M., KADER F. AND EL-RUBY S., 2005, Federated data model to improve accessibility of distributed cadastral databases in land administration, Proceedings of 8 th Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Conference (GSDI-8), 16-21 April 2005, Cairo, Egypt.
- VENUGOPAL S., BUYYA.R. AND RAMAMOHANARAO K., 2006, A taxonomy of data grids for distributed data sharing, management and processing, ACM Computing Surveys, March 2006, Vol. 38, Article 3, pp.1-53.
- WILLIAMSON I., GRANT D. AND RAJABIFARD A., 2005. Land administration and spatial data infrastructures, Proceedings of 8 th Global Spatial Data Infrastructure Conference (GSDI-8), 16-21 April 2005, Cairo, Egypt.
- YILDIRIM V. AND YOMRALIOGLU T., 2004, An address-based geospatial application, FIG Working Week, 22-27 May 2004, Athens, Greece.
 Serena Coetzee
Serena Coetzee