Elastic textures for additive fabrication
2015, ACM Transactions on Graphics
https://doi.org/10.1145/2766937Abstract
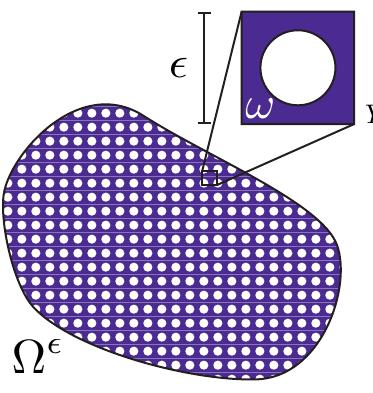
Figure 1: Six basic elastic textures are used to obtain a large range of homogenized isotropic material properties. A 3 × 3 × 1 tiling of each pattern is shown, along with rendered (left) and fabricated (right) cell geometry below. The naming convention is explained in Section 4.
References (44)
- AGARWAL, S., MIERLE, K., AND OTHERS. Ceres solver. http: //ceres-solver.org.
- ALLAIRE, G. 2002. Shape optimization by the homogenization method, vol. 146. Springer.
- ANDREASSEN, E., LAZAROV, B. S., AND SIGMUND, O. 2014. Design of manufacturable 3D extremal elastic microstructure. Mechanics of Materials 69, 1, 1-10.
- AVELLANEDA, M. 1987. Optimal bounds and microgeometries for elastic two-phase composites. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathe- matics 47, 6, 1216-1228.
- BENDSØE, M. P., AND SIGMUND, O. 2003. Topology optimiza- tion: theory, methods and applications. Springer.
- B ÜCKMANN, T., STENGER, N., KADIC, M., KASCHKE, J., FR ÖLICH, A., KENNERKNECHT, T., EBERL, C., THIEL, M., AND WEGENER, M. 2012. Tailored 3d mechanical metamate- rials made by dip-in direct-laser-writing optical lithography. Ad- vanced Materials 24, 20, 2710-2714.
- CADMAN, J. E., ZHOU, S., CHEN, Y., AND LI, Q. 2013. On design of multi-functional microstructural materials. Journal of Materials Science 48, 1, 51-66.
- CHEN, D., LEVIN, D. I., DIDYK, P., SITTHI-AMORN, P., AND MATUSIK, W. 2013. Spec2fab: a reducer-tuner model for trans- lating specifications to 3d prints. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4, 135.
- CHERKAEV, A. 2000. Variational methods for structural optimiza- tion, vol. 140. Springer.
- CHU, J., ENGELBRECHT, S., GRAF, G., AND ROSEN, D. W. 2010. A comparison of synthesis methods for cellular structures with application to additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyping Journal 16, 4, 275-283.
- CIGNONI, P., PIETRONI, N., MALOMO, L., AND SCOPIGNO, R. 2014. Field-aligned mesh joinery. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 1 (Feb.), 11:1-11:12.
- CIORANESCU, D., AND DONATO, P. 1999. An introduction to homogenization. Oxford University Press.
- GRABOVSKY, Y., AND KOHN, R. V. 1995. Microstructures mini- mizing the energy of a two phase elastic composite in two space dimensions. II: the Vigdergauz microstructure. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 43, 6, 949-972.
- GREAVES, G. N., GREER, A. L., LAKES, R. S., AND ROUXEL, T. 2011. Poisson's ratio and modern materials. Nature Materials 10, 11, 823-837.
- GUEST, J. K., AND PR ÉVOST, J. H. 2006. Optimizing multi- functional materials: Design of microstructures for maximized stiffness and fluid permeability. International Journal of Solids and Structures 43, 2223, 7028 -7047.
- HART, G. W. 2008. Sculptural forms from hyperbolic tessella- tions. In Shape Modeling and Applications, 2008. SMI 2008. IEEE International Conference on, IEEE, 155-161.
- HILDEBRAND, K., BICKEL, B., AND ALEXA, M. 2012. Crdbrd: Shape fabrication by sliding planar slices. Comp. Graph. Forum 31, 2pt3 (May), 583-592.
- HILLER, J., AND LIPSON, H. 2009. Design and analysis of dig- ital materials for physical 3d voxel printing. Rapid Prototyping Journal 15, 2, 137-149.
- HOLLISTER, S. J. 2005. Porous scaffold design for tissue engi- neering. Nature Materials 4, 7, 518-524.
- KANG, H. S. 2010. Hierarchical design and simulation of tissue engineering scaffold mechanical, mass transport, and degrada- tion properties. PhD thesis, The University of Michigan.
- KHAREVYCH, L., MULLEN, P., OWHADI, H., AND DESBRUN, M. 2009. Numerical coarsening of inhomogeneous elastic ma- terials. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 3 (July), 51:1-51:8.
- LIN, C. Y., KIKUCHI, N., AND HOLLISTER, S. J. 2004. A novel method for biomaterial scaffold internal architecture design to match bone elastic properties with desired porosity. Journal of Biomechanics 37, 5, 623-636.
- LIN, C.-Y., HSIAO, C.-C., CHEN, P.-Q., AND HOLLISTER, S. J. 2004. Interbody fusion cage design using integrated global lay- out and local microstructure topology optimization. Spine 29, 16, 1747-1754. PMID: 15303018.
- LIU, L., JAMES, R. D., AND LEO, P. H. 2007. Periodic inclusion- atrix microstructures with constant field inclusions. Metallurgi- cal and Materials Transactions A 38, 4, 781-787.
- MELA, K., AND KOSKI, J. 2013. Distributed loads in truss topol- ogy optimization. In Proceedings of the 10th world congress on structural and multidisciplinary optimization, Orlando.
- MILTON, G. W. 2002. The theory of composites. Cambridge University Press.
- MIRONOV, V., VISCONTI, R. P., KASYANOV, V., FORGACS, G., DRAKE, C. J., AND MARKWALD, R. R. 2009. Organ printing: tissue spheroids as building blocks. Biomaterials 30, 12, 2164- 2174.
- MITANI, J., AND SUZUKI, H. 2004. Making papercraft toys from meshes using strip-based approximate unfolding. In ACM SIG- GRAPH 2004 Papers, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH '04, ACM, 259-263.
- MORI, Y., AND IGARASHI, T. 2007. Plushie: An interactive design system for plush toys. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 Papers, ACM, New York, NY, USA, SIGGRAPH '07, ACM.
- NAKASONE, P., AND SILVA, E. 2010. Dynamic design of piezo- electric laminated sensors and actuators using topology opti- mization. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures 21, 16, 1627-1652.
- RADMAN, A., HUANG, X., AND XIE, Y. 2013. Topological op- timization for the design of microstructures of isotropic cellular materials. Engineering Optimization 45, 11, 1331-1348.
- SCHWARTZBURG, Y., AND PAULY, M. 2013. Fabrication-aware design with intersecting planar pieces. Comput. Graph. Forum 32, 2, 317-326.
- SCHWARTZBURG, Y., TESTUZ, R., TAGLIASACCHI, A., AND PAULY, M. 2014. High-contrast computational caustic design. ACM Trans. Graph. 33, 4 (July), 74:1-74:11.
- SCHWERDTFEGER, J., WEIN, F., LEUGERING, G., SINGER, R. F., KRNER, C., STINGL, M., AND SCHURY, F. 2011. Design of auxetic structures via mathematical optimization. Advanced Materials 23, 22, 2650-2654.
- SI, H. 2010. A quality tetrahedral mesh generator and a 3D Delau- nay triangulator. URL http://tetgen.berlios.de.
- SIGMUND, O. 1995. Tailoring materials with prescribed elastic properties. Mechanics of Materials 20, 4, 351-368.
- SKOURAS, M., THOMASZEWSKI, B., COROS, S., BICKEL, B., AND GROSS, M. 2013. Computational design of actuated de- formable characters. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4, 82.
- TORQUATO, S., AND DONEV, A. 2004. Minimal surfaces and multifunctionality. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London.
- Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 460, 2047, 1849-1856.
- TORQUATO, S., HYUN, S., AND DONEV, A. 2002. Multifunc- tional composites: optimizing microstructures for simultaneous transport of heat and electricity. Physical review letters 89, 26, 266601.
- TORQUATO, S., HYUN, S., AND DONEV, A. 2003. Optimal de- sign of manufacturable three-dimensional composites with mul- tifunctional characteristics. Journal of Applied Physics 94, 9, 5748-5755.
- TORQUATO, S. 2002. Random heterogeneous materials: mi- crostructure and macroscopic properties, vol. 16. Springer.
- VIDIM ČE, K., WANG, S.-P., RAGAN-KELLEY, J., AND MA- TUSIK, W. 2013. Openfab: A programmable pipeline for multi- material fabrication. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 32, 4, 136.
- WEYRICH, T., PEERS, P., MATUSIK, W., AND RUSINKIEWICZ, S. 2009. Fabricating microgeometry for custom surface re- flectance. ACM Trans. on Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH) 28, 3, 32:1-32:6.
 Nico Pietroni
Nico Pietroni