SNMP over SIP for network management
2004, 2004 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37507)
https://doi.org/10.1109/NOMS.2004.1317779…
2 pages
1 file
Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
AI
AI
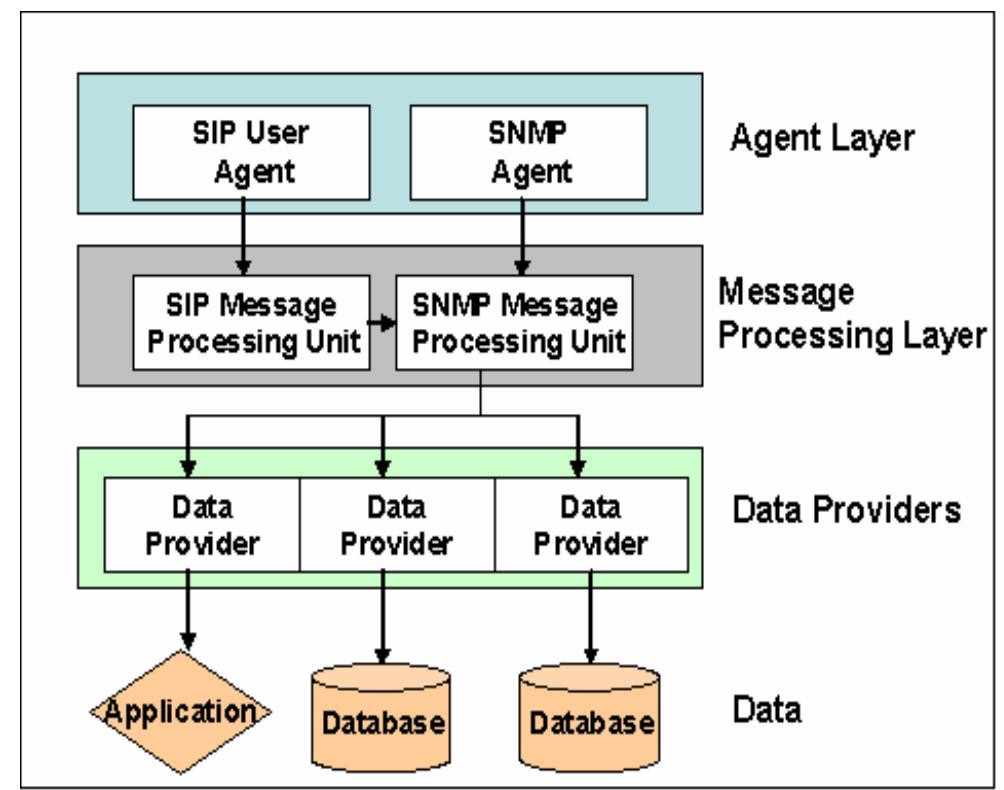
This paper proposes a novel approach to large-scale network management by utilizing SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) over SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). It addresses the limitations of traditional SNMP in terms of scalability and bandwidth utilization, offering a system architecture that integrates a SIP User Agent on devices, an SNMP proxy, and a centralized SIP Proxy server. The resulting architecture allows for efficient management through the collection of inventory data and the indication of system presence, enhancing network reliability and management efficiency while ensuring compatibility with existing SNMP systems.
Related papers
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an applicationlayer protocol for creating, modifying and terminating sessions. SIP [1] is designed in a modular way so that it is independent of the type of session established and of the lower-layer transport protocol used. Its modularity is one of the most important strengths of SIP. It makes SIP flexible and easy to extend with new features.
2001
This document specifies an Internet standards track protocol for the Internet community, and requests discussion and suggestions for improvements. Please refer to the current edition of the "Internet Official Protocol Standards" (STD 1) for the standardization state and status of this protocol. Distribution of this memo is unlimited.
Telecommunication Network Intelligence, 2000
This paper proposes the introduction of a Service Platform for the creation, execution and management of multimedia services in heterogeneous networks. Examining the business-roles, the actors in the Service Platform are identified. Furthermore several common building blocks for developing services for the Internet are described and a brief overview of some modern technologies for an object-oriented, component-based, distributed platform for multimedia services is given. The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) has been identified as very useful to implement all functions according to the multimedia part of the Platform. The usage of the PARLAY API as an open interface between the Platform Services and SIP, the PSTN or the mobile network provides a lot of additional advantages. The interworking between SIP and PARLAY is shown in a call-routing example. Furthermore the call-setup for a multimedia (e.g. video) conference is explained. This should demonstrate the usefulness and the ability of this protocol for introducing a session concept. Finally an outlook of open research topics regarding this concept is given as well as a short overview of related work.
The paper deals with the development of an advanced solution for a SIP communication server. Works were carried out within the scope of Bright Embedded Solution for IP Telephony (BESIP) project. The output of the project should be a modular architecture with additional functionality such as speech quality monitoring and security of IP telephony. We sought to unify the configuration of individual components based on the NETCONF protocol. In order to be able to implement the idea into OpenWrt, we had to integrate a complex support for the NETCONF configuration protocol. Our modifications of OpenWrt in respect of NETCONF were accepted by the OpenWrt community and have been included in OpenWrt/Trunk branch. The paper explains and describes the whole concept of the BESIP project and its individual modules.
2010
This paper describes an approach for combining Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) based voice communication with Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) based presence enhancements. The actual role of SIP and XMPP in the Internet Protocol (IP) based communication was analyzed, especially from the telecommunication carrier (Telco) point of view. The proposed infrastructure extends a typical SIP infrastructure with XMPP for presence status integration. XMPP will be used as instant messaging and presence (IM/P) service infrastructure, the presence information will be extended with SIP phone status information of telecommunication endpoints. A first prototype has been developed and tested successfully.
2007
With more than a decade of development led by the IETF, and a plethora of devices and software systems speaking its dialect, SIP together with its related standards has grown in size and scale, raising concerns over interoperability. In this paper, we explore SIP interoperability (or lack thereof) by proposing systematic methodologies for identifying and analyzing the basic-level protocol interoperability issues that plague SIP usage in the real-world. We also dissect and describe a few of the commonly observed SIP interoperability issues and their implications. Our test results clearly indicate that even the basic- level of SIP interoperability is far from ideal.
1993
Status of this Memo This RFC specifies an IAB standards track protocol for the Internet community, and requests discussion and suggestions for improvements. Please refer to the current edition of the "IAB Official Protocol Standards" for the standardization state and status of this protocol. Distribution of this memo is unlimited.
2003
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application-level control protocol for setting up, changing and terminating multimedia sessions between participants on IP data networks. In 1999 SIP was approved as an official standard and RFC2543 was published. SIP can enable a range of services, such as Internet telephony, multimedia conferencing, registration and redirection services, and simplifies connecting to VPNs. As
1999
Mobile Code is an emerging paradigm that is gaining momentum in several fields of application. Network Management is a potential area for the use of this technology, provided it will be able to interoperate with well established solutions for Network Management. This paper presents the integration a classic NM protocol, like SNMP, into a platform of Mobile Agents. Our platform, called JAMES, has been developed in the context of an Eureka Project (Σ!1921) where the project partners are University of Coimbra, Siemens SA and Siemens AG. Since the main target of the platform is network management, it includes a set of SNMP services allowing mobile agents to easily interface with SNMP agents, as well as with legacy SNMP-based management applications. In the paper we present a brief overview of the general architecture of the platform and we describe in some detail the framework we used to provide for integration between mobile agent applications and SNMP.
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a multimedia signalling protocol that has evolved into a widely adopted communication standard. The integration of SIP into existing IP networks has fostered IP networks becoming a convergence platform for both realtime and non-real-time multimedia communications. This converged platform integrates data, voice, video, presence, messaging, and conference services into a single network that offers new communication experiences for users. The open source community has contributed to SIP adoption through the development of open source software for both SIP clients and servers. In this paper, we provide a survey on open SIP systems that can be built using publically available software. We identify SIP features for service development and programming, services and applications of a SIP-converged platform, and the most important technologies supporting SIP functionalities. We propose an advanced converged IP communication platform that uses SIP for service delivery. The platform supports audio and video calls, along with media services such as audio conferences, voicemail, presence, and instant messaging. Using SIP Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), the platform allows the deployment of advanced integrated services. The platform is implemented with open source software. Architecture components run on standardized hardware with no need for special purpose investments.

Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
 Shiva Shiva
Shiva Shiva