IJESRT Vol 3 5 May 2014
Abstract
A typical WSN is composed of a large number of computing devices known as nodes embodying limited set of resources. These nodes are interfaced with sensors whose job is to sense and monitor the surrounding environment for various purposes and disseminate sensed data to some special computing devices called destination or base-stations in a coordinated manner where the destination nodes further process and analyze the reported data to draw conclusions about the reported activity. Since the sensors in Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) operate independently, their local clocks may not be synchronized with one another. This can cause difficulties when trying to integrate and interpret information sensed at different nodes. Time synchronization of WSNs is crucial to maintain data consistency, coordination, and perform other fundamental operations. Synchronization is considered a critical problem for wireless adhoc networks due to its de-centralized nature and the timing uncertainties introduced by the imperfections in hardware oscillators and message delays in both physical and medium access control (MAC) layers. All these uncertainties cause the local clocks of different nodes to drift away from each other over the course of a time interval. Therefore, Time synchronization is considered as an important research issue in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Many applications based on these WSNs assume local clocks at each sensor node that need to be synchronized to a common notion of time. Features and concept of a lightweight tree structured referencing time synchronization (TSRT) approach to achieve a long-term network-wide synchronization with minimum message exchanges and exhibits a number of attractive features such as highly scalable and lightweight is presented in this paper. We have also shown evaluation, analysis and comparison study of TSRT with existing synchronization protocols.
Key takeaways
AI
AI
- The Tree Structured Referencing Time Synchronization (TSRT) approach minimizes message exchanges for network-wide synchronization.
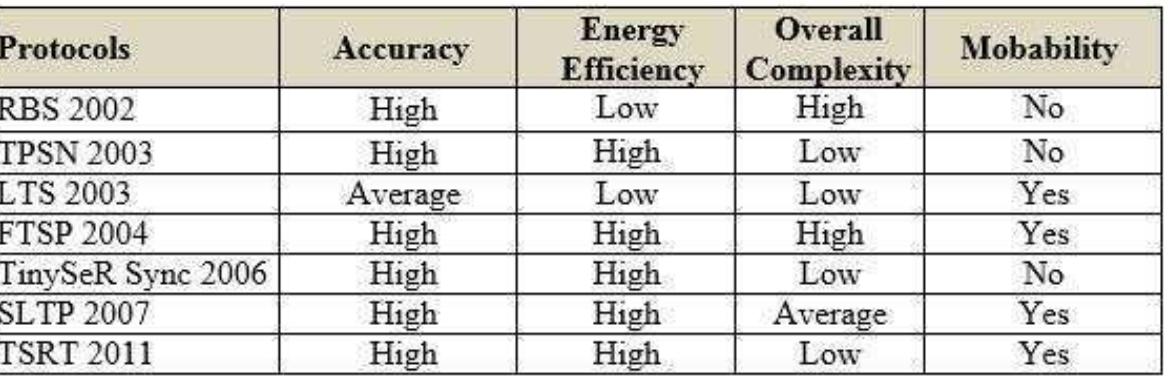
- TSRT is highly scalable, lightweight, and energy-efficient compared to existing synchronization protocols.
- The study evaluates TSRT against protocols like RBS and TPSN, highlighting fewer message requirements for synchronization.
- TSRT effectively compensates for clock drift using linear regression to maintain synchronization accuracy.
- Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) require time synchronization to ensure consistent data across decentralized nodes.
References (7)
- F.L. Lewis, 2004. Wireless Sensor Networks. In Smart Environments: Technologies, Protocols, Applications, ed.D.J. Cook and S.K. Das, Wiley, New York.
- Rahamatkar, Surendra. Agarwal, Dr. Ajay. 2011. A reference Based, Tree Structured Time Synchronization Approach and Its Analysis In WSN. International Journal of Ad hoc, Sensor and Ubiquitous Comput-ing (IJASUC) Vol.2(1).
- Mills, D. L. 1991. Internet Time Synchronization: The Network Time Protocol. IEEE Trans. Comm. 39 (10), pp. 1482-1493.
- Elson, J. E., Girod, L. Estrin, D. 2002. Fine- Grained Network Time Synchronization using Reference Broadcasts. In 5 th Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, pp. 147-163.
- Ganeriwal, S. Kumar, R, Srivastava, M. B. 2001. Timing-Sync Protocol for Sensor Networks. In First ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor System (SenSys), pp. 138-149.
- PalChaudhuri, S. Saha, A. K. Johnson, D. B. 2004. Adaptive clock synchronization in sensor networks. In 3rd int. Symp. on inf. Processing in Sensor Networks, pp. 340- 348.
- Sun, K. Ning, P. Wang, C. 2006. TinySeRSync: Secure and Resilient time synchronization in wireless sensor networks.
 Dr Sunil V K Gaddam
Dr Sunil V K Gaddam