Learning Rules of Simplified Boardgames by Observing
2012
https://doi.org/10.3233/978-1-61499-098-7-175…
6 pages
1 file
Sign up for access to the world's latest research
Abstract
General Game Playing (GGP) agents learn strategies to skillfully play a wide variety of games when given only the rules of the game. The rules are provided in a language called Game Description Language (GDL) and specify the initial game setup, what constitutes legal moves and how they update the game state when played, how the game terminates, and what the outcome is. In here we extend this line of research further, that is, we assume that the game-playing agent must learn the rules of a game by observing others play instead of them being provided. Our focus here will mainly be on modeling piece movements with less attention placed on the remaining game-rule properties. We define a subset of games, we name simplified boardgames, that despite constituting only a small subset of games expressible in GDL nonetheless encapsulate a large variety of interesting piece movement patterns found in popular boardgames. We provide a well-defined formalism and a practicable algorithm for learnin...









Related papers
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1995
In this paper we describe game-independent strategies, capable of learning explanation patterns (XPs) for evaluation of any basic game pattern. A basic game pattern is defined as a minimal configuration of a small number of pieces and squares which describes only one salient game feature. Each basic pattern can be evaluated by a suitable XP. We have developed five gameindependent strategies (replacement, specialization, generalization, deletion, and insertion) capable of learning XPs or parts of them. Learned XPs can direct players' attention to important analysis that might have been overlooked otherwise. These XPs can improve their understanding, evaluating and planning abilities. At present, the application is only in the domain of chess. The proposed strategies have been further developed into 21 specific chess strategies, which are incorporated in an intelligent educational chess system that is under development.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2003
Compared to their ancestors in the early 1970s, present day computer games are of incredible complexity and show magnificent graphical performance. However, in programming intelligent opponents, the game industry still applies techniques developed some 30 years ago. In this paper, we investigate whether opponent programming can be treated as a problem of behavior learning. To this end, we assume the behavior of game characters to be a function that maps the current game state onto a reaction. We will show that neural networks architectures are well suited to learn such functions and by means of a popular commercial game we demonstrate that agent behaviors can be learned from observation.
Fictitious play, an algorithm to predict the opponents next move based on the observed history of play, is one of the oldest simple yet very effective algorithms in game theory. Although using pattern recognition as a more sophisticated way to analyze the history of play seems a logical step, there is little research available on this subject. In this paper we will examine two different types of pattern recognition, and formulate several algorithms that incorporate these approaches. These algorithms and the basic fictitious play variants they extend are empirically tested in eight tournaments on some well known formal-form games. The results obtained will show that adding pattern recognition to fictitious play improves performance, and demonstrate the general possibilities of applying pattern recognition to agents in game theory.
International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1997
Game Theory is mainly seen as a mathematical theory which tries to replace pure chance and intuitive behavior in a competitive situation by calculations. This theory has been widely used to define computer programs. The aim of the research described here is to design an artificial system which is able to play efficiently certain games to which Game Theory cannot be applied satisfactorily (such as games with incomplete or imperfect information). When it cannot find a winning solution, the system is able to play through a process of anticipation. This is done by building and refining a model of the adversary's behavior in real time during the game. The architecture proposed here relies on two genetic classifiers, one of which models the adversaries' behaviors while the other uses the models thus built in order to play. The system's strategy learning ability has been tested on a simple strategic game. The results show the advantages of this approach over human and traditional artificial adversaries (simple probabilistic and adaptive probabilistic) and illustrate how the system learns the strategies used by its adversaries.
Advances in Artificial Intelligence- …, 2006
Abstract. Systems able to learn from visual observations have a great deal of potential for autonomous robotics, scientific discovery, and many other fields as the necessity to generalise from visual observation (from a quotidian scene or from the results of a scientific enquiry) is inherent ...
Aaai, 1999
Computer programs now play many board games as well or better than the most expert humans. Human players, however, learn, plan, allocate resources, and integrate multiple streams of knowledge. This paper highlights recent achievements in game playing, describes some cognitively-oriented work, and poses three related challenge problems for the AI community. Game Playing as a Domain Work on games has had several traditional justifications. Given unambiguous rules, playing a game to win is a well-defined problem. A game's rules create artificial world states whose granularity is explicit. There is an initial state, a state space with clear transitions, and a set of readily describable goal states. Without intervening instrumentation, games are also noise-free. For these reasons, as well as for their ability to amuse, games have often been referred to as "toy domains." To play the most difficult games well, however, a program must contend with fundamental issues in AI: knowledge representation, search, learning, and planning. There are two principal reasons to continue to do research on games, despite Deep Blue's triumph (Hamilton and Hedberg 1997). First, human fascination with game playing is long-standing and pervasive. Anthropologists have catalogued popular games in almost every culture. Indeed, the same game, under various names, often appears on many continents (Bell 1969; Zaslavsky 1982). Games intrigue us because they address important cognitive functions. In particular, the games humans like to play are probably the ones we are good at, the ones that capitalize on our intellectual strengths and forgive our weaknesses. A program that plays many games well must simulate important cognitive skills. The second reason to continue game-playing research is that some difficult games remain to be won, games that people play very well but computers do not. These games clarify what our current approach lacks. They set challenges for us to meet, and they promise ample rewards. This paper summarizes the role of search and knowledge in game playing, the state of the art, and recent relevant data on expert human game players. It then shows how cognitive skills can enhance a game-playing program, and poses three new challenge problems for the AI community. Although rooted in game playing, these challenges could enhance performance in many domains.
1994
A rst order system, PAL, that can learn Chess patterns in the form of Horn clauses from simple example descriptions and general purpose knowledge about Chess is described. This is the rst time that Chess patterns which can be used for over-the-board play have been learned. To test if the patterns learned by PAL can be used to play, a simple playing strategy for the King and Rook against King (KRK) endgame was constructed with patterns learned by PAL. Limitations of PAL in particular, and rstorder systems in general, are exposed in domains like Chess where a large number of background de nitions may be required for induction. Conclusions and future research directions are given.
Künstliche Intelligenz, 2011
Although we humans cannot compete with computers at simple brute-force search, this is often more than compensated for by our ability to discover structures in new games and to quickly learn how to perform highly selective, informed search. To attain the same level of intelligence, general game playing systems must be able to figure out, without human assistance, what a new game is really about. This makes General Game Playing in ideal testbed for human-level AI, because ultimate success can only be achieved if computers match our ability to master new games by acquiring and exploiting new knowledge. This article introduces five knowledge-based methods for General Game Playing. Each of these techniques contributes to the ongoing success of our FLUXPLAYER (Schiffel and Thielscher in Proceedings of the National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 1191–1196, 2007), which was among the top four players at each of the past AAAI competitions and in particular was crowned World Champion in 2006.
Applied Sciences
In general, games pose interesting and complex problems for the implementation of intelligent agents and are a popular domain in the study of artificial intelligence. In fact, games have been at the center of some of the most well-known achievements in artificial intelligence. From classical board games such as chess, checkers, backgammon and Go, to video games such as Dota 2 and StarCraft II, artificial intelligence research has devised computer programs that can play at the level of a human master and even at a human world champion level. Planning and learning, two well-known and successful paradigms of artificial intelligence, have greatly contributed to these achievements. Although representing distinct approaches, planning and learning try to solve similar problems and share some similarities. They can even complement each other. This has led to research on methodologies to combine the strengths of both approaches to derive better solutions. This paper presents a survey of the ...
2008
General Game Playing (GGP) aims at developing game playing agents that are able to play a variety of games and in the absence of game specific knowledge, become proficient players. Most GGP players have used standard tree-search techniques enhanced by automatic heuristic learning. In this paper we explore knowledge representation and learning in GGP using Reinforcement Learning and Ant Colony Algorithms. Knowledge is created by simulating random games. We test the quality of the knowledge by comparing the performance of players using the knowledge in a variety of games. The ideas presented in this paper provide the potential for a framework for learning and knowledge representation, given the total absence of any prior knowledge.
Learning Rules of Simplified Boardgames by Observing
Yngvi Björnsson 1
Abstract
General Game Playing (GGP) agents learn strategies to skillfully play a wide variety of games when given only the rules of the game. The rules are provided in a language called Game Description Language (GDL) and specify the initial game setup, what constitutes legal moves and how they update the game state when played, how the game terminates, and what the outcome is. In here we extend this line of research further, that is, we assume that the game-playing agent must learn the rules of a game by observing others play instead of them being provided. Our focus here will mainly be on modeling piece movements with less attention placed on the remaining game-rule properties. We define a subset of games, we name simplified boardgames, that despite constituting only a small subset of games expressible in GDL nonetheless encapsulate a large variety of interesting piece movement patterns found in popular boardgames. We provide a well-defined formalism and a practicable algorithm for learning game rules of simplified boardgames. We empirically evaluate the learning algorithm on different boardgames and under different assumptions of availability of observations. Furthermore, we show that our formalism offers at least an order of magnitude speedup over state-of-the-art logic-based GDL reasoners for fitting boardgames. The method is thus directly relevant for GGP systems.
1 Introduction
From the inception of the field of artificial intelligence, over half a century ago, games have played a significant role as a test-bed for advancements in the field. The focus was initially on developing general problem-solving approaches but gradually shifted towards - and stayed for decades on - building high-performance gameplaying systems capable of playing a specific game at a world-class level. As a case in point are game-playing programs for chess (DeepBLUE), checkers (CHINOOK), and Othello (LOGISTELLO) [10].
Interest in general approaches to intelligent game playing was recently revitalized with at the advent of the General Game Playing (GGP) competition [5]. The focus of GGP research is to build intelligent agents that automatically learn to play a wide variety of games skillfully, given only a description of the game rules. This requires that the agents learn diverse game-playing strategies without any game-specific knowledge being provided by their developers. A successful realization of this task poses many research challenges for artificial intelligence, bringing in various subfields of study like knowledge representation, agent-based reasoning, planning, heuristic search, and machine learning.
Games in GGP are described in a language named Game Description Language (GDL) [7], which has axioms for describing the initial game state, the generation of legal moves and how they alter the game state, and how to detect and score terminal positions. GDL is a
[1]first-order-logic-based language capable of expressing a wide range of deterministic, perfect-information, single- or multi-player games. This expressibility, however, comes at a cost: in the general case a theorem-proving-based reasoning approach (e.g., Prolog) is required to execute GDL-described state manipulation tasks, such as for generating legal moves. This results in GGP systems typically being orders of magnitude slower than their game-specific counterparts.
The GDL game description is sent to participating GGP agents at the beginning of a match and the agents are given a modest time period (typically a few minutes or less) to analyze the description before the match game commences. One of the main challenges of GGP systems is thus to learn in real-time from the game description and through self-play the game-specific knowledge necessary to play the game at hand skillfully. Based on the exact reasoning approach used by the GGP agent, such learned knowledge may take the form of either an evaluation function for assessing the merits of nonterminal game positions [11] or search-control heuristics for controlling simulation-based playouts [4].
In this paper we extend the line of GGP research a step further. The focus is still on learning, however, instead of being provided with the rules of the game as in GGP, the game-playing agent is now required to learn the rules simply by observing others play. Once the game rules have been learned, all methods developed for GGP agents are applicable - we thus concern us here with only the task of learning the game rules. We provide a well-defined formalism for doing this and give a practicable algorithm for inducing the games rules directly from observations. Although, under the new formalism, we restrict ourselves to a substantially narrower set of games than expressible in GDL, nonetheless, a variety of interesting boardgames can be learned. For fitting boardgames we show that the learned representation offers a speedup of at least an order of magnitude over GDL-based reasoners.
The paper is organized as following. Section 2 introduces the necessary terminology and provides preliminaries. Section 3 introduces the learning approach, which is then evaluated empirically in Section 4. We summarize related work in Section 5 and, finally, conclude and discuss future work in Section 6.
2 Preliminaries
A boardgame “is a game which involves counters or pieces being moved on a pre-marked surface or ‘board’, according to a set of rules” [2]. The rules, beside describing how the pieces move on the board, include axioms for stating other necessary game logistics such as the initial board setup, how players alternate turns, how the game terminates, and what the possible game outcomes are.
The above definition of boardgames encompasses a vast set of diverse arbitrarily complex games. In here we focus on a restricted form of boardgames, that is, two-player zero-sum turn-taking
1 School of Computer Science / CADIA, Reykjavik University, Iceland, email: yngvi@ru.is ↩︎
boardgames of the following characteristics, henceforth referred to as simplified boardgames:
- The game is played on a rectangular board consisting of n×m squares. Each player controls an army of pieces, possibly of multiple types (e.g., pawn, knight, rook), initially placed on distinct squares on the board in a predetermined arrangement. At most one piece can be on a square at any time.
- Players take turns acting. On its turn a player moves one of his or her pieces from its current square to a different one in a pattern adhering to the rules of the game. More specifically, the movement must be describable as a piece-movement pattern (to be defined shortly). If a piece, own or opponent’s, happens to be on the destination square it will be captured (and removed from the board). The movement of a piece may, and typically is, affected by the location of other pieces on the board, however, it should be impartial to the absolute location of the piece itself (e.g., a knight on c3 should in principle move no differently than if it were on d5 ).
- A terminal position arises when a piece of a certain type reaches a goal square (e.g., a pawn or a knight reaching a square on the opponent’s back rank). The set of eligible piece types and the set of goal squares are preset for each player (and may differ from one player to the next).
- The game ends in a win for the player moving into a terminal position, in a loss for the player to move if no legal moves are possible, or in a tie when a preset maximum game length is reached. If one player wins, the other loses, but a tie applies to both players. The goal is to win the game (or tie if a win is not possible).
This framework of a simplified boardgame is general enough to allow a wide range of disparate piece movements, which is the primary focus of this work. Other game aspects are thus deliberately kept uncomplicated, in particular the conditions for terminating a game.
A relative coordinate (Δx,Δy) references a square relative to another one. The Δx indicates the relative file (column) distance and Δy the relative rank (row) distance. For example, the left, up, right and down adjacent squares would be referenced as (−1,0),(0,+1),(+1,0) and (0,−1), respectively; diagonally adjacent squares would similarly be referenced as (−1,+1),(+1,+1), (+1,−1) and (−1,−1). A relative square can be non-adjacent to the reference square, for example (+1,+2).
A relative square content is defined in the context of a board position P and a square s as a pair (rc,on), where rc is a relative coordinate (to s ) and on∈{e,w,p} tells the content of that relative square in board position P. The letter e indicates an empty square, w an own piece, and p an opponent’s piece. For a shorthand notation we write relative square content ((Δx,Δy),on) as a triplet (Δx,Δy,on); for example, we write (0,+1,e) instead of ((0,+1),e).
A piece-movement pattern is a sequence of relative square contents. For example, the two-step sequence (0,+1,e)(+1,0,p) describes a pattern consisting of first moving a piece one square up to an empty square and from there one square to the right to land on a square occupied by an opponent’s piece. Given a piecemovement pattern pmp of length n we define I(pmp) as the set of subsequences of pmp of length n−1 ( n in total). One semantic constraint is imposed on legitimate piece-movement patterns, that is, within a sequence the same square cannot be implicitly reference more than once. This constraint forbids sequences that move pieces in circles, such as sliding back and forth (e.g, (0,+1,e)(0,+1,e)(0,−1,e)…). Piece-movement patterns can be used to describe complex piece movements found in many popular boardgames, for example, as shown in Figures 1 and 2.

Figure 1. A chess example. Two potential moves are shown for the pawn on d4, advancing to d5 or capturing on c5. The former move yields the one-step piece-movement pattern (0,1,e) and the latter (−1,1,p). The knight move b1−d2 and the bishop move c1−g5 yield the piece-movement patterns (2,1,e) and (1,1,e)(1,1,e)(1,1,e)(1,1,e), respectively
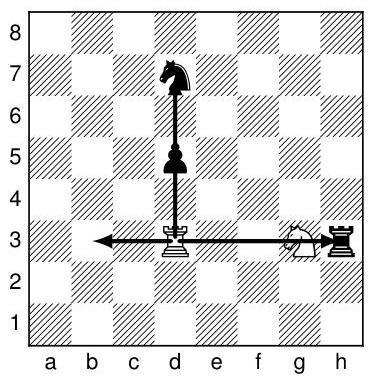
Figure 2. A Chinese-chess inspired example. The cannon in chinese chess slides orthogonally, but to capture it must leap over exactly one piece (either own or opponent’s) before landing on the opponent’s piece being captured. Assuming the piece on d3 moves like a cannon, the move d3−h3 yields the piece-movement pattern (−1,0,e)(−1,0,e), the move d3−h3 the pattern (+1,0,e)(+1,0,e)(+1,0,w)(+1,0,p), and the move d3−d7 the pattern
(0,+1,e)(0,+1,p)(0,+1,e)(0,+1,p)
3 Learning by Observing
Assume we observe an unfamiliar simplified boardgame in progress. On a player’s turn we will observe him or her moving a piece in a specific way, for example, a knight jumping in an L-shape, a rook sliding along the file or rank it stands on, or some other foreignlooking piece moving in an even more obscure pattern. Over time we start noticing regularities in the movements from which we can induce a general model or set of rules that describe the movements of each individual piece. Similarly, we will notice under which conditions the game terminates and what the outcome is.
Our learning agent faces the same task. The following subsections describe how the agent models piece movements (and terminal conditions), how the training observations are presented to the agent, and the learning algorithm for inducing the model from the observations. The model, once correct, can subsequently be used to generate legal moves for any board position that can arise in that particular game.

Figure 3. A DFA, Drank , describing the movements of a rook in chess
3.1 Model
We model each piece type in the game individually. The piecemovement patterns we observe for pieces of the given type can be thought of as words in a language. Because both the number of possible piece-movements patterns and their length is limited, the language is finite and thereby also regular. We can use a deterministic finite automata (DFA), or equivalently a regular expression, to model a regular language. More specifically, we define a DFA for modeling the movements of a piece of type pt as a quintuple Dpt=(Q,δ,Σ,q0,F) where Q is a finite set of states, Σ is a finite alphabet consisting of all possible relative square contents, q0∈Q is the start state, F⊆Q is the set of accepting states, and δ is the transition function Q×Σ→Q. Figure 3 shows an example DFA describing the movements of a rook in chess.
The DFA formalism is not only expressive enough to represent the language, but also gives a permission to handy mechanisms for inducing a generalized language from knowing only a subset of the strings it contains, as shown in the following subsection. The learning task of the agent, when it comes to piece movements, is thus to induce for each piece type a DFA that describes the movement patterns of that piece type. The DFA, when run in a generation mode in the context of a specific board position, should produce the exact set of legal moves for a piece of the given type. When generating the moves the DFA is traversed in a depth-first manner. On each transition the relative square content label of an edge is used to find which square to reference and its expected content. If there are no matching edges the search backtracks. A transition into a final state s∈F generates a move in the form of a piece-movement pattern consisting of the edge labels that were traversed from the start state to reach s. A special provision is taken to detect and avoid cyclic square reference in piece-movement patterns.
3.2 Training Data
The observations of how a particular game is being played are presented to the agent in a log file consisting of a set of records, each listing a game position and a subset of the moves permitted in that position. The details can differ from one record to the next, depending on available information when observing. For example, in an ideal

Figure 4. Two example training records from a chess-like game. First is a sequential record number, following by the current board position (one line per row, listed top to bottom), and then the game outcome ( (∗) stands for a non-terminal position and {−1,0,1} for a terminal position that is lost, tied, or won for the player just moving, respectively). The line that follows has three fields: the first tells which player has the move, the next whether all legal moves in the position are listed or only a subset ([all, some]), and the third the number of moves subsequently listed. The listing of the moves then concludes the record, one per line where the piece-movement pattern follows the square the piece is on (a1=0,b1=1,c1=2…)
case we might know for each position the exact set of legal moves, whereas in the other extreme we might know only the single move played. As usual when learning from data, we assume the training data to be representative of the real world. Figure 4 shows an example training-data record from a chess-like game.
A DFA is consistent with the training data if for each position it generates all moves known to be legal 2 and no moves known to be illegal. This consistency check is straightforward in positions where all legal moves are known, because the DFA should generate the exact same set of moves. This check is not as straightforward in positions where only a subset of the legal moves is listed. The DFA should as before generate all the moves known to be legal (i.e., the listed subset), however, we cannot tell whether additional moves the DFA generates are illegal or not. To handle such scenarios we make the following assumption: Let U be the union of all piece-movement patterns in the training data; then for those positions in the training set that list only subset of legal moves, a generated piece-movement pattern pmp is legal if either pmp∈U or F(pmp)⊆U. Algorithm 1 shows a detailed pseudo-code for checking a DFA’s consistency.
2 The set of known legal moves in a position may possibly be only a subset of all the legal moves in that position. ↩︎
Algorithm 1 consistent(Piecetype pt, DFA dfa, TrainingDatatd)
1: for all \(\{\operatorname{pos} \in t d\}\) do
for all \(\{\operatorname{sq} \in \operatorname{pos} . b o a r d \mid \operatorname{perType}(s q)=p t\}\) do
movesDFA \(\leftarrow\) generateMoves(dfa, pos, sq)
if pos.moves \((\operatorname{sq}) \nsubseteq\) movesDFA then
return false
end if
if pos.movelisting \(=\) all then
return ( movesDFA \(\nsubseteq\) pos.moves \((\operatorname{sq}))\)
else \(\{\) pos.movelisting \(=\) some \(\}\)
for all \(\{\operatorname{pmp} \in\) moves \(D F A \backslash U\}\) do
if \(I(p m p) \nsubseteq U\) then
return false
end if
end for
end if
end for
end for
return true
3.3 Learning Algorithm
Algorithm 2 shows the procedure for learning a DFA for a given piece type. It proceeds in several steps. First we construct a Prefix Tree Automata (PTA) from the training data (line 1), a specialized DFA assembled by aggregating all the piece-movement patterns for the given piece type into a prefix tree (an example is depicted as the top-most DFA in Figure 5). The resulting DFA is checked for consistency. The only reason for a DFA built as a PTA to be inconsistent with the training data is if our assumption that piece movements are independent of the square a piece is standing on is violated, in which case the learning procedure returns null. Otherwise, we minimize the DFA (line 5) and insert it into a priority queue, named Q (line 7). The priority queue stores the generalized DFAs created so far that still remain unexplored, and is ordered in an increasing order by the DFAs
Algorithm 2 LearnDFA(Piecetype pt, TrainingData td)
\(d f a \leftarrow\) construct \(P T A(p t, t d)\)
if not consistent \((p t, d f a, t d)\) then
return null
end if
\(d f a_{\min } \leftarrow \operatorname{minimizeDFA}(d f a)\)
\(n \leftarrow 0\)
Q.insert(dfa \(\left._{\min }\right)\)
while not \(Q . e m p t y()\) and \(n<\operatorname{MaxExpansions}\) do
\(d f a \leftarrow Q \cdot p o p()\)
if \(\mid d f a|<\mid d f a_{\min } \mid\) then
\(d f a_{\min } \leftarrow d f a\)
end if
statepairs \(\leftarrow\) generalizingCandidates \((d f a, K)\)
for all \(\left(s, s^{\prime}\right) \in\) statepairs do
\(d f a^{\prime} \leftarrow N F A t o D F A\left(c o l l a p s e\left(d f a, s, s^{\prime}\right)\right)\)
if consistent \(\left(p t, d f a^{\prime}, t d\right)\) then
\(d f a^{\prime} \leftarrow \operatorname{minimizeDFA}\left(d f a^{\prime}\right)\)
Q.insert \(\left(d f a^{\prime}\right)\)
end if
end for
\(n \leftarrow n+1\)
end while
return \(d f a_{\min }
size (the size of a dfa, noted ∣dfa∣, is defined as the number of states it contains). The while loop (lines 8-22) expands from the queue in a best-first order, that is, removes the smallest DFA from the queue (line 9), keeps track of the smallest one found so far (lines 10-12), generalizes it by collapsing states in the DFA (lines 13 and 15), and adds back to the queue the resulting generalized DFAs that remain consistent with the training data (lines 16-19). More specifically, the function generalizingCandidates returns a set of pairs, each proposing two states in the DFA to collapse. It would be infeasible to consider all O(∣dfa∣2) state pairs and thus a smaller candidate set of size O(∣dfa∣) is generated, containing only pair of states of a (geodesic) distance K or less from each other and of the same acceptance status (that is, either both states are final or both non-final). The collapse function merges the two states into one. This may result in a nondeterministic automata (NFA), which is retransformed into a DFA (the NFAtoDFA function) and then minimized (minimizeDFA function). Figure 5 gives an example thereof.
The transformation of a NFA to a DFA may in the worst case produce an exponentially larger DFA (O(2∣nfa∣)). In practice this worst-case behavior is extremely rare, although we often experience that an unfavorable generalization results in an NFA that transforms into a DFA that grows by an order of magnitude. The best-first-search expansion policy, however, bypasses for the most part the negative effect of this, that is, a large DFA may get created but it is unlikely that it will be generalized further.
3.4 Remaining Game Properties
We have seen how to learn the generation of legal moves in a simple boardgame. The remaining game properties must be learned as well, that is, what the initial board setup is, what constitutes a terminal position and how is it scored, and what the maximum game length is. There is, however, no need to learn how playing a move updates the current board position nor the game outcomes as this is already decided in the definition of a simple boardgame. Because the remaining game properties were deliberately kept simple it is somewhat trivial to learn them in comparison to learning the piece movements. The start position is fixed for each particular game, and can simply be recorded. To learn the terminal conditions we record in each nontie terminal position in the training data which piece was moved last and to which square it went. This way we collect for each player the eligible pieces and goal squares, both of which is necessary (and sufficient) for deciding whether a position is terminal. The following generalization is done: if there are more than two goal squares on the same file or rank, the entire file/rank is assumed to be goal squares unless counter-evidence show otherwise. As for the maximum game length we simply record the ply number of any record labeled with a tie outcome. To be able to derive the above information given the current training record format the training data must come from complete games listed sequentially. Furthermore, for consistency the first move listed in each position should be the one that was played.
4 Empirical Evaluation
In here we empirically evaluate the effectiveness of the learning algorithms and the resulting models. We first describe the three simple boardgame variants used in our experiments, then the experimental setup, and finally the results of the experiments.

Figure 5. A simple example assuming a rook-like piece that slides only forwards. The four finite state machines emerge during different steps in the learning process (Algorithm 2). The first one is the PTA as constructed from the training data (line 1) and the second one is the DFA resulting from minimizing that PTA (line 5). The third one is the NFA resulting from collapsing the second and third state of the previous DFA (line 15, as returned from the collapse call), and the fourth one shows the final DFA after converting the NFA back to a DFA and minimizing it (line 17)
4.1 Games
Breakthrough is a two-player game played on an 8×8 chess or checkers board. Each player starts with sixteen pieces, named pawns, initially placed on the player’s own two back ranks, White at the bottom and Black at the top. White moves first and the player then alternate turns. On a turn the player to move advances one of his or her pawns one step forward. This can be done either straight or diagonally when moving onto an empty square, but only diagonally if capturing an opponent’s piece. The goal of the game is to break through the opponent’s defenses to reach his or her backrank with your own piece. The first player to do so wins. This game has frequently been played in the international GGP competitions in several variants.
Checkers-Breakthrough is played on a 8×8 checkers board with checkers pieces. The initial board setup and basic piece movements are the same as in checkers. A checker piece can move either onto a diagonally forward adjacent empty square or jump over a diagonally adjacent opponent piece (possibly repeatedly). Unlike checkers, however, jumps are not mandatory and jumped-over pieces are not captured. The first player to reach the opponent’s backrank wins (thus no king promotions).
Chess-Breakthrough is played using a regular chess board and pieces and from the standard chess start position. The first player to place a pawn or a knight on the opponent’s backrank wins (thus no promotions). The normal chess rules for piece movements have also been slightly modified to fit our simplified boardgame framework: castling, en-passant, and two-step pawn moves are not allowed; a
king can be moved into and left in check (and thus captured); and the draw-by-threefold-repetition and 50-move rules do not apply.
4.2 Results
We ran two sets of experiments using different kind of training data: in the former all legal moves are known in each position whereas in the latter only a single move is known. The training data was generated by having two random agents play against each other, with the maximum game length set to 80 moves (per player). Each experiment was repeated 20 times with new training data generated each time. We report the average, min, and max values over the 20 trials. In the learning algorithm we set K to 2 (in candidate generation) and MaxExpensions to 20. The start position, max game length, and terminal conditions were trivially learned (and thus not reported). All experiments were run on an 2 GHz Intel Core i7 processor.
4.2.1 All Moves Known
Table 1 shows the learning results when all moves are known, using a training data with 50 complete games. The learning produced the optimal DFAs in all cases, often almost instantly but in the worst case in slightly under 50 seconds. The sliding pieces (rook, bishop and queen) take noticeable longer to learn than the other pieces. Also of interest is that only 50 games (and this is an upper bound) seem sufficient to robustly learn the piece movements in the tested games.
Table 1. Learning time (sec.) when all moves are known (G=50)
| First player | Second player | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Pawn | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| CheckBT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Checker | 0.45 | 0.09 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 0.87 |
| ChessBT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Pawn | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| King | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Knight | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Bishop | 10.25 | 7.38 | 12.42 | 10.32 | 8.66 | 13.08 |
| Rook | 11.65 | 10.18 | 13.56 | 11.58 | 10.00 | 13.21 |
| Queen | 40.22 | 32.40 | 47.05 | 40.73 | 30.61 | 49.01 |
This type of learning could for example be useful in GGP agents where move generation is typically very slow. If suitable games are encountered, such as Breakthrough, one could handily use random simulations to generate training data from which appropriate DFAs could be learned, allowing faster move generation. Faster state manipulation results in more simulations being run in a given time frame, which yields significant improvement in playing strength [3]. We compared the speed of move generation in our model to that of a world-class GGP player [1] in the game Breakthrough. In our DFA-based model a move generation in a position took on average 7 microseconds, whereas in the GGP player it took on average 159 microseconds. This is almost a 23 -fold speedup. 3
3 To ensure a fair comparison we timed only the move generation routine, which is functionally equivalent in both systems. In simulation-based search, which is the dominating search approach in GGP, the move generation is typically by far the most time consuming component. Furthermore, from our experience with GGP systems, we expect the speedup to be even higher in the other two game variants (we did not have GDL description for them to try), however, this must be tested before drawing conclusions. ↩︎
Table 2. Learning time (sec.) when a single move is known (G=1000)
| First player | Second player | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Pawn | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| CheckBT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Checker | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ChessBT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Pawn | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| King | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Knight | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Bishop | 104.82 | 115.64 | 114.74 | 104.78 | 87.81 | 116.94 |
| Rook | 121.01 | 115.64 | 127.88 | 121.28 | 113.60 | 128.77 |
| Queen | 421.69 | 369.35 | 457.82 | 412.64 | 368.28 | 454.32 |
Table 3. Number of games needed to produce consistent training data
| BT | First player | Second player | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| avg | min | max | avg | min | max | |
| Pawn | 1.40 | 1 | 3 | 1.3 | 1 | 2 |
| CheckBT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Checker | >1000 | >1000 | ||||
| ChessBT | avg | min | max | avg | min | max |
| Pawn | 1.95 | 1 | 5 | 1.50 | 1 | 3 |
| King | 6.5 | 1 | 17 | 5.95 | 1 | 17 |
| Knight | 12.55 | 4 | 28 | 12.50 | 3 | 28 |
| Bishop | 149.40 | 10 | 448 | 135.25 | 14 | 353 |
| Rook | 85.65 | 22 | 249 | 85.85 | 19 | 249 |
| Queen | 148.55 | 29 | 448 | 160.75 | 15 | 416 |
4.2.2 A Single Move Known
Table 2 shows the result when only a single legal move is known in each position (the move played), using a training data from 1000 complete games. Many more games are required than in the previous setup to compensate for both fewer and less variety in known piece-movement patterns. The learning is more difficult in this setting, as witness by longer learning times and the inability to learn the checkers piece moves. The problem is that under our definition of consistency many games are required to even get a consistent dataset, which is a necessary condition for successful learning (although not sufficient). This is further evaluated in Table 3. We see, for example, that even with 1000 games we do not have a varied enough data to be consistent with the optimal DFAs for the checkers pieces. The diagonally sliding pieces in chess also require up to 500 games. An example of a poorly represented move is a queen or a bishop sliding from one corner of the board to an opposite one with a capture. It is rare for a position to occur where such a move is possible and even rarer that this exact move will be played in that position. This move was for example not present is some of the 1000 -game training sets, but because a 6 -square diagonal-sliding capture was seen the I() subsequences ensured that the data was nonetheless consistent.
5 Related Work
Learning is at the core of GGP systems, but focusses on learning either evaluation functions for assessing the merits of nonterminal game positions [11] or search-control heuristics for controlling simulation-based playouts [4]. This is the first work (in GGP) on learning an efficient representation for a game by observing play. As finding a more efficient representation for state manipulation in GGP offers great benefits - for example, this was the prime novelty in the reigning GGP world-champion TURBOTURTLE - and several other work also exists in that direction [13, 6, 12]. That work, however, uses different formalisms and focuses on analyzing the GDL game
rules as opposed to observing play. In ILP work exists on inducing chess variant rules (written as first-order-logic programs) from a set of positive and negative examples, background knowledge, and theory revision [8]. We are in our work, however, avoiding the computationally expensive first-order-logic representation. Aside from games DFAs are commonly used to learn regular languages (e.g., [9]).
6 Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper we introduced a novel method for learning the rules of simple boardgames by observing play. The method learns effectively, in particular, when all legal moves are known in the given game positions. Whereas this would be unrealistic scenario when observing humans play, this has direct practical relevance in e.g. GGP systems. Even though the game rules are known in GGP one could, for applicable games, relearn the rules in the simplified boardgame framework to get an order of magnitude faster mechanism for game state manipulation. Our learning method is already efficient enough for this to be practicable in real-time, but could be even further sped up with an optimized implementation and learning different piece type movements in parallel (many GGP systems use multiple processors). When only a single move is known in a given position the learning is not as effective, the main reason being the large number of games required for the training data to become representative. This could be alleviated with more powerful generalization mechanisms; for example, our definition of a consistent training data seems too restrictive.
In future work the focus will be on deriving more sophisticated generalization schemes, as well as implementing the method in a state-of-the-art GGP system. Also, an important future work is to extend the approach to be applicable in a broader range of boardgames, for example, such that the complete ruleset of games like chess and checkers could be learned. This would require adding pre- and postconditions for piece movements, side-effects of moves (e.g., to handle en-passant and castling), and more general terminal conditions.
REFERENCES
[1] CadiaPlayer. Web site: http://cadia.ru.is/wiki/public:cadiallayer:main.
[2] Wikipedia. Web site: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boardgame.
[3] Hilmar Finnsson and Yngvi Björnsson, ‘Simulation-based approach to general game playing’, in AAAI’08, pp. 259-264, (2008).
[4] Hilmar Finnsson and Yngvi Björnsson, ‘Learning simulation control in general game-playing agents’, in AAAI’10, pp. 954-959, (2010).
[5] Michael R. Genesereth, Nathaniel Love, and Barney Pell, ‘General Game Playing: Overview of the AAAI competition.’, AI Magazine, 26(2), 62-72, (2005).
[6] Peter Kissmann and Stefan Edelkamp, ‘Gamer, a general game playing agent’, KI, 25(1), 49-52, (2011).
[7] Nathaniel Love, Timothy Hinrichs, and Michael Genesereth, ‘General Game Playing: Game description language specification’, Technical Report April 4 2006, Stanford University, (2006).
[8] Stephen Muggleton, Aline Paes, Vítor Santos Costa, and Gerson Zaverscha, ‘Chess revision: Acquiring the rules of chess variants through FOL theory revision from examples’, in ILP, ed., Luc De Raedt, volume 5989 of LNCS, pp. 123-130. Springer, (2009).
[9] Rajesh Parekh and Vasant Honavar, ‘Learning DFA from simple examples’, Machine Learning, 44(1/2), 9, (2001).
[10] J. Schaeffer and H. J. van den Herik, Chips challenging champions: Games, computers and artificial intelligence, Elsevier, 2002.
[11] Stephan Schiffel and Michael Thielscher, ‘Fluxplayer: A successful general game player’, in AAAI’07, pp. 1191-1196, (2007).
[12] Eric Schkufza, Nathaniel Love, and Michael R. Genesereth, ‘Propositional automata and cell automata: Representational frameworks for discrete dynamic systems’, in AUS-AI, pp. 56-66, (2008).
[13] Kevin Waugh, ‘Faster state manipulation in general games using generated code’, in Proceedings of the 1st General Intelligence in GamePlaying Agents (GIGA), (2009).
References (13)
- CadiaPlayer. Web site: http://cadia.ru.is/wiki/public:cadiaplayer:main.
- Wikipedia. Web site: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Boardgame.
- Hilmar Finnsson and Yngvi Björnsson, 'Simulation-based approach to general game playing', in AAAI'08, pp. 259-264, (2008).
- Hilmar Finnsson and Yngvi Björnsson, 'Learning simulation control in general game-playing agents', in AAAI'10, pp. 954-959, (2010).
- Michael R. Genesereth, Nathaniel Love, and Barney Pell, 'General Game Playing: Overview of the AAAI competition.', AI Magazine, 26(2), 62-72, (2005).
- Peter Kissmann and Stefan Edelkamp, 'Gamer, a general game playing agent', KI, 25(1), 49-52, (2011).
- Nathaniel Love, Timothy Hinrichs, and Michael Genesereth, 'General Game Playing: Game description language specification', Technical Report April 4 2006, Stanford University, (2006).
- Stephen Muggleton, Aline Paes, Vítor Santos Costa, and Gerson Za- verucha, 'Chess revision: Acquiring the rules of chess variants through FOL theory revision from examples', in ILP, ed., Luc De Raedt, volume 5989 of LNCS, pp. 123-130. Springer, (2009).
- Rajesh Parekh and Vasant Honavar, 'Learning DFA from simple exam- ples', Machine Learning, 44(1/2), 9, (2001).
- J. Schaeffer and H. J. van den Herik, Chips challenging champions: Games, computers and artificial intelligence, Elsevier, 2002.
- Stephan Schiffel and Michael Thielscher, 'Fluxplayer: A successful general game player', in AAAI'07, pp. 1191-1196, (2007).
- Eric Schkufza, Nathaniel Love, and Michael R. Genesereth, 'Propo- sitional automata and cell automata: Representational frameworks for discrete dynamic systems', in AUS-AI, pp. 56-66, (2008).
- Kevin Waugh, 'Faster state manipulation in general games using gen- erated code', in Proceedings of the 1st General Intelligence in Game- Playing Agents (GIGA), (2009).
 Yngvi Björnsson
Yngvi Björnsson